An entire availability zone failure, such as a power outage or network disruption, can halt your critical data analytics workloads and potentially violate strict compliance mandates. To address this, MaxCompute provides a comprehensive Zone-disaster Recovery solution that leverages the multi-zone architecture within a single region. By synchronously replicating your data across three zones (Multi-zone Storage) and reserving compute capacity in healthy zones (Multi-zone Compute High Availability (HA)), MaxCompute ensures that your data remains fully accessible and your compute jobs can automatically fail over. This approach guarantees business continuity with zero data loss (RPO=0) even during a data center-level disaster.
Overview
MaxCompute Zone-disaster Recovery extends the availability of data storage and compute services from a single zone to three zones within the same region. By leveraging the physical isolation and low-latency network connections among the three zones, this architecture provides cross-data center, real-time data synchronization and fault isolation. This design prevents service interruptions caused by a single data center failure and enhances the resilience of your business.
MaxCompute Zone-Disaster Recovery comprises two key components: Multi-zone Storage and Multi-zone Compute HA.
Multi-zone Storage: Enabled at the project level, this feature migrates your data from a single zone to redundant storage across three zones. It synchronously writes new data to all three zones. During an zone-level failure, Multi-zone Storage ensures uninterrupted data read and write services with no data loss, achieving a Recovery Point Objective (RPO) of 0. It protects all user data within a project, including metadata, user permissions, all table types, materialized views, UDFs, and resources.
Multi-zone Compute HA: By associating Multi-zone HA Computing Resource with a project that has Multi-zone Storage enabled, you can achieve comprehensive disaster recovery for both storage and compute. You can reserve sufficient Multi-zone HA Computing Resource across multiple zones. During an zone-level failure, compute resources automatically fail over from the affected zone to an unaffected zone. Multi-zone HA Computing Resource support all job types, including SQL Task, MaxFrame, Cupid Task, and MapReduce Task.
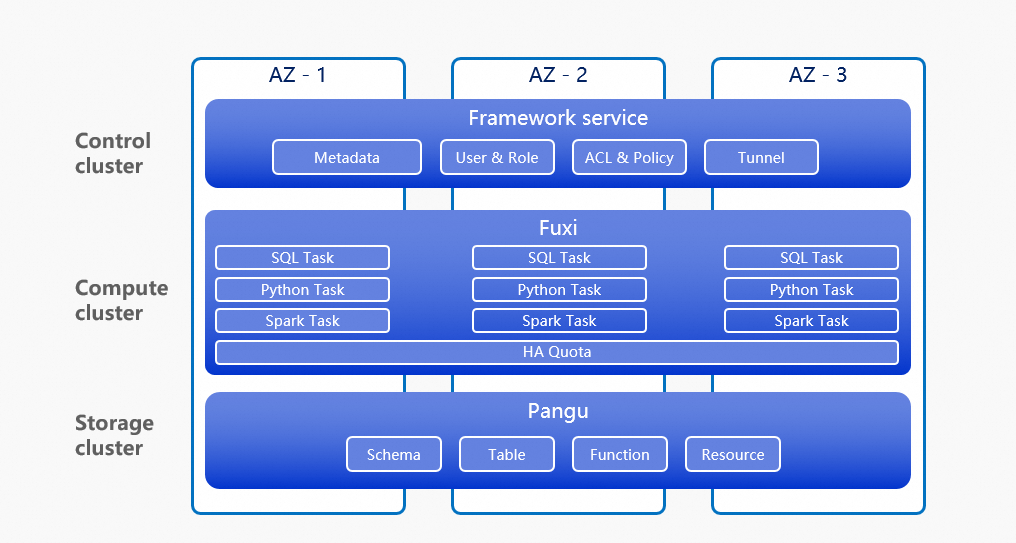
Disaster recovery process
If an zone fails after you enable Zone-disaster Recovery, the system performs the following recovery operations:
You receive a notification from Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute about the failure.
The server-side immediately allocates compute resources in a healthy zone. The system checks the integrity and availability of data such as tables, partitions, and permissions in the project.
Jobs submitted from the client may fail. You must resubmit the failed jobs. You do not need to change your MaxCompute configurations, such as the Endpoint, authentication information, project_name, or quota_name.
After the jobs resume, continue to monitor the status of your upstream business applications to ensure that the entire business has fully recovered.
Use cases
Financial Services
It ensures that financial services can continuously analyze and process business transaction data without service interruptions caused by data center failures.
Critical Infrastructure
It safeguards data analysis systems for public utilities such as electricity, water, and transportation, ensuring that critical information services essential to public welfare are not disrupted by data center failures.
Benefits
Data redundancy and backup.
Reduced service downtime.
Compliance with industry regulations.
Improved customer experience for upstream business applications.
Supported regions
China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China East 2 Finance, China (Hong Kong), Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), and Germany (Frankfurt) regions.
Billing
After you enable Multi-zone Storage, MaxCompute bills you based on the Billing for multi-zone storage.
To use Muliti-zone Compute HA, you must purchase multi-zone high availability compute resources.
Usage notes
To achieve comprehensive disaster recovery for both storage and compute, you must enable both Multi-zone Storage and Muliti-zone Compute HA.
The storage data migration process does not affect your running jobs and is transparent to your applications.
During the data migration process, if a long-running streaming write is in progress for a table partition, the migration for that partition waits until the write operation commits. Periodically switch to new partitions for data writes (for example, daily or weekly) to ensure a timely migration for all tables and partitions.
Local backup data and TimeTravel data generated before you enable Multi-zone Storage remain in the local storage of the original zone.
MaxCompute redundantly stores local backup data and TimeTravel data generated after you enable Multi-zone Storage across three zones.
Enable Multi-zone Storage
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Disaster Recovery page, click the Zone-disaster Recovery tab.
Click Enable Zone-disaster Recovery. In the Enable Zone-disaster Recovery dialog box, select the project for which you want to enable disaster recovery from the Select Project dropdown list. Select the confirmation checkbox, and then click OK.
After the task is created, the system prepares for storage disaster recovery by migrating project data from a single zone to be stored across three zones. This process takes approximately two days to complete. When the process is complete, the project has storage disaster recovery capabilities.
Enable Muliti-zone Compute HA (available in specific regions)
To enable Muliti-zone Compute HA, you must purchase Multi-zone HA Computing Resource and configure the target project's default compute quota to use these resources. This feature is currently only available in specific regions.
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Quotas page, click New Quota.
On the resource purchase page, configure the purchase parameters.
Specifications Type: Select Multi-zone HA Computing Resource.
Multi-zone HA CU: Select the number of CUs to purchase. The minimum purchase is 50 CUs, and must be purchased in increments of 1 CU.
Click Buy Now and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the payment.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
You can view the Multi-zone HA Computing Resources that you created.
Configure the Default Quota of the target project to the Multi-zone HA Computing Resource.
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Projects page, find the target project and click Manage in its Actions column.
On the Project Settings page, click the Parameter Configuration tab.
In the Basic Information section, click Edit.
Set Default Quota to the Multi-zone HA Computing Resource, and then click Submit.
Monitor disaster recovery status
On the disaster recovery monitoring page, you can view the project's overall disaster recovery status, zone monitoring information, and table data details.
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Disaster Recovery page, click the Zone-disaster Recovery tab.
On the Zone-disaster Recovery page, click the name of the project to open the project-level monitoring page.
In the Basic Information section, view the project's overall disaster recovery status, including the zone, control disaster recovery information, current status, disaster recovery creation time, and last failover time.
If the Current Status is Preparing, it indicates that MaxCompute is migrating the data to Multi-zone storage.
If the Current Status is Normal, the data is stored across multiple zones and is protected by zone-level storage disaster recovery.
Zone Monitoring
This section displays monitoring information for Multi-zone HA Compute. You can view the zones where your purchased and project-bound Multi-zone HA Computing Resource are located.
A zone with an In Use status is the active zone where your jobs are currently running.
A zone with a (Reserved) status is a standby zone. If the active zone fails, compute resources will automatically fail over to this reserved zone.
Table Data Details
Search for a specific table by schema name and table name. If you do not apply any filters, the system displays information for all tables in the project.
Column
Description
Schema Name
The schema within the project.
Table Name
The name of the table.
Partitioned Table
Indicates whether the table is a partitioned table.
Last Data Update Time
The last time the data in the table was updated.
Data Volume
The size of the data in the table.
Data Distribution
The zones where the table data is distributed.
A zone status of (Preparing) indicates that MaxCompute is migrating the data to Multi-zone storage.
A zone status of (In Use) indicates that MaxCompute redundantly stores the data across multiple zones.
Actions
If the table is partitioned, click View Partition Details to view the Last Data Update Time, Data Volume, and Data Distribution for each partition.
Perform a disaster recovery drill
If you need to conduct a disaster recovery drill, MaxCompute provides a project-level disaster simulation and failover solution. The process is as follows.
Submit a support ticket to Alibaba Cloud to request a disaster recovery drill. In the ticket, provide the Region, Project Name, Quota Name, and the desired drill time window. Schedule drills during off-peak hours to minimize business impact.
Once Alibaba Cloud approves your ticket, a Failover button appears on the project-level Monitor disaster recovery status page. You can then follow the on-screen prompts to manually trigger a failover, which switches the active zone for your compute resources. After the failover, newly submitted jobs will execute immediately. You must manually resubmit any jobs that failed during the failover process.
The preceding operations are for drill scenarios only. In a real zone-level disaster, the system automatically fails over the compute resources.
Disable disaster recovery
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Disaster Recovery page, click the Zone-disaster Recovery tab.
On the Zone-disaster Recovery tab, click Disable Disaster Recovery in the Actions column for the target project.
In the Disable Zone-disaster Recovery dialog box, select the confirmation checkbox and click OK.
Disabling disaster recovery is a high-risk operation. The project immediately loses its disaster recovery capabilities. Proceed with caution and carefully evaluate the potential impact.
After you disable disaster recovery, the system redistributes the project data back to single-zone local storage.