This topic describes how to use Eclipse to develop MaxCompute Graph programs because Graph development plug-ins are unavailable in MaxCompute.
- Compile Graph code and perform local debugging to test basic functions.
- Perform cluster debugging to verify the result.
Development example
This topic uses the SSSP algorithm as an example to describe how to use Eclipse to develop and debug a MaxCompute Graph program.
- Create a Java project named graph_examples.
- Add the JAR package in the lib directory on the MaxCompute client to Java Build Path of the Eclipse project.

- Develop a MaxCompute Graph program.
In the actual development process, an example program, such as SSSP, is first copied and then modified. In this example, only the package path is changed to package com.aliyun.odps.graph.example.
- Compile and package the code.
In an Eclipse environment, right-click the source code directory, namely, the src directory, and choose to generate a JAR package. Select the path to store the JAR package, such as D:\\odps\\clt\\odps-graph-example-sssp.jar.
- Run SSSP on the MaxCompute client. For more information, see (Optional) Submit Graph jobs.
Local debugging
MaxCompute Graph supports the local debugging mode. You can use Eclipse for breakpoint debugging.
- Download a Maven package named odps-graph-local.
- Select the Eclipse project, right-click the main program file that contains the
mainfunction of a Graph job, and choose to configure parameters. - On the Arguments tab, set Program arguments to 1 sssp_in sssp_out as the input parameter of the main program.
- On the Arguments tab, set VM arguments to the following content:
-Dodps.runner.mode=local -Dodps.project.name=<project.name> -Dodps.end.point=<end.point> -Dodps.access.id=<access.id> -Dodps.access.key=<access.key>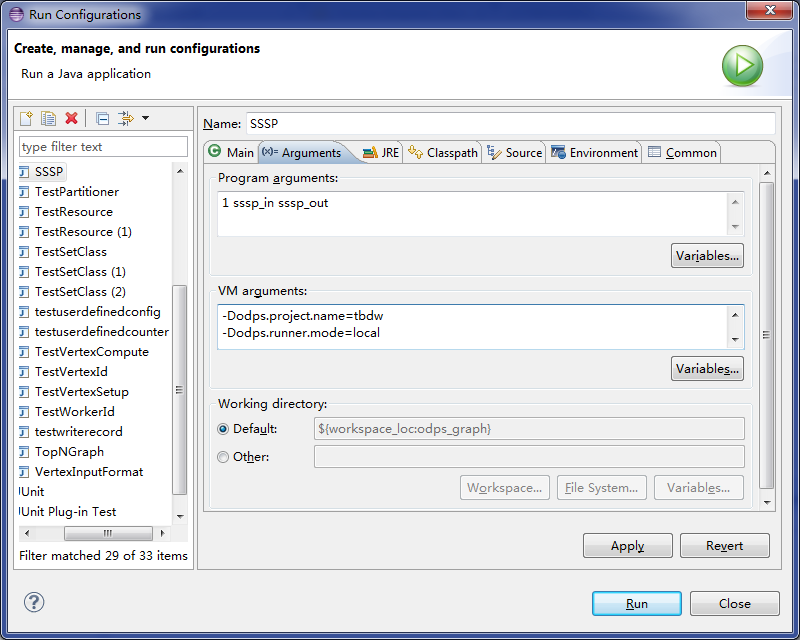
- In local mode in which odps.end.point is not specified, create the sssp_in and sssp_out tables in the warehouse directory and add the following data to the sssp_in table:
1,"2:2,3:1,4:4" 2,"1:2,3:2,4:1" 3,"1:1,2:2,5:1" 4,"1:4,2:1,5:1" 5,"3:1,4:1"For more information about the warehouse directory, see Local run.
- Click Run to run SSSP on the local client.
Note Configure the parameters based on the settings in conf/odps_config.ini on the MaxCompute client. The preceding parameters are commonly used. Descriptions of other parameters:
- odps.runner.mode: The value is local. This parameter is required for the local debugging feature.
- odps.project.name: specifies the current project. This parameter is required.
- odps.end.point: specifies the endpoint of MaxCompute. This parameter is optional. If this parameter is not specified, metadata and data of tables or resources are only read from the warehouse directory. An exception is reported if such data does not exist in the directory. If this parameter is specified, metadata and data are read from the warehouse directory first and then from the remote MaxCompute server if such data does not exist in the directory.
- odps.access.id: specifies the AccessKey ID used to access MaxCompute. This parameter is valid only if odps.end.point is specified.
- odps.access.key: specifies the AccessKey secret used to access MaxCompute. This parameter is valid only if odps.end.point is specified.
- odps.cache.resources: specifies the resources you want to use. This parameter functions the same as
-resourcesof the jar command. - odps.local.warehouse: specifies the local path to warehouse. The default value is ./warehouse.
Output of the local SSSP debugging in Eclipse:Counters: 3 com.aliyun.odps.graph.local.COUNTER TASK_INPUT_BYTE=211 TASK_INPUT_RECORD=5 TASK_OUTPUT_BYTE=161 TASK_OUTPUT_RECORD=5 graph task finishNote In this example, the sssp_in and sssp_out tables must exist in the local warehouse directory. For more information about the sssp_in and sssp_out tables, see (Optional) Submit Graph jobs.
Temporary directory of a local job
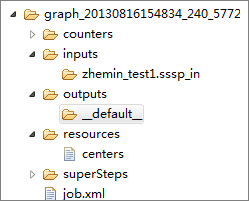
- counters: stores the counter information that is generated during the job running.
- inputs: stores input data of the job. Data is read from the local warehouse directory first. If no data is available, the MaxCompute SDK reads data from the
server if odps.end.point is specified. An input directory reads only 10 data records by default. This threshold can be changed by
using the
-Dodps.mapred.local.record.limitparameter, of which the maximum value is 10000. - outputs: stores output data of the job. If an output table exists in the local warehouse directory, the results in outputs will overwrite data in that table after the job is completed.
- resources: stores resources used by the job. Similar to input data, resource data is read from the local warehouse directory first. If no data is available, the MaxCompute SDK reads data from the server if odps.end.point is specified.
- job.xml: stores job configurations.
- superstep: stores persistent messages from each iteration.
Cluster debugging
After local debugging, you can submit the job to a cluster for testing.
- Configure the MaxCompute client.
- Run the
add jar /path/work.jar -f;command to update the JAR package. - Run a jar command to execute the job and check the operational log and command output.
Performance optimization
setSplitSize(long): specifies the split size of an input table. The unit is MB. The value must be greater than 0. The default value is 64.setNumWorkers(int): specifies the number of workers for a job. The value ranges from 1 to 1000. The default value is 1. The number of workers is determined by the input bytes of the job andsplitSize.setWorkerCPU(int): specifies the CPU resources of the Map. The value ranges from 50 to 800. The default value is 200. A one-core CPU contains 100 resources.setWorkerMemory(int): specifies the memory resources of the Map. The unit is MB. The memory ranges from 256 to 12288. The default value is 4096.setMaxIteration(int): specifies the maximum number of iterations. The default value is -1. If the value is less than or equal to 0, the job does not stop when the maximum number of iterations is reached.setJobPriority(int): specifies the job priority. The value ranges from 0 to 9. The default value is 9. A greater value indicates a lower priority.
- Use
setNumWorkersto increase the number of workers. - Use
setSplitSizeto reduce the split size and increase the data loading speed. - Increase the CPU or memory resources for workers.
- Set the maximum number of iterations. For applications that do not require precise results, you can reduce the number of iterations to accelerate the execution process.
setNumWorkers and setSplitSize can be used together to accelerate data loading. Assume that the value of setNumWorkers equals that of workerNum, the value of setSplitSize equals that of splitSize, and the total number of input bytes is the value of inputSize. The number of split data records is calculated by using the following formula: splitNum = inputSize/splitSize. Relationship between workerNum and splitNum:
- If the value of
splitNumis equal to that ofworkerNum, each worker loads one split data record. - If the value of
splitNumis greater than that ofworkerNum, each worker loads one or more split data records. - If the value of
splitNumis less than that ofworkerNum, each worker uploads one or no split data record.
Therefore, you can adjust workerNum and splitSize to obtain a suitable data loading speed. In the first two cases, data is loaded faster.
In the iteration phase, you only need to adjust workerNum. If you set runtime partitioning to False, we recommend that you either use setSplitSize to adjust the number of workers or make sure that the conditions in the first two
cases are met. In the third case, some workers do not load split data records. Therefore,
you can insert set odps.graph.split.size=<m>; set odps.graph.worker.num=<n>; before the jar command to achieve the same effect as setNumWorkers and setSplitSize.
- Use a combiner to aggregate the messages of the split data records that correspond
to the keys to reduce the number of messages generated.
Developers can define a combiner to reduce the memory and network traffic consumed by message storage, which reduces the job execution duration.
- Improve the business logic.
If the data volume is large, reading data in a disk may take up the processing time. Therefore, you can reduce the data bytes to be read to increase the overall throughput. This improves job performance. To reduce data bytes, use one of the following methods:
- Reduce data input: For some decision-making applications, processing sampled data only affects the precision of the results, not the overall accuracy. In this case, you can perform special data sampling and import the data to the input table for processing.
- Avoid reading fields that are not used: The TableInfo class of the MaxCompute Graph framework supports reading specific columns that are transferred by using column name arrays, rather than reading the entire table or partition. This reduces the input data volume and improves job performance.
Built-in JAR packages
-libjars to specify them in a command:
- commons-codec-1.3.jar
- commons-io-2.0.1.jar
- commons-lang-2.5.jar
- commons-logging-1.0.4.jar
- commons-logging-api-1.0.4.jar
- guava-14.0.jar
- json.jar
- log4j-1.2.15.jar
- slf4j-api-1.4.3.jar
- slf4j-log4j12-1.4.3.jar
- xmlenc-0.52.jar

