To start a live stream, the host needs an ingest URL for pushing their stream, and the viewers need a streaming URL for playback. This topic explains how to generate signed ingest and streaming URLs for ApsaraVideo Live. You'll learn both the console method for quick testing and the code-based approach for production environments.
Before you begin
Before generating URLs, ensure that you have:
An ingest domain and streaming domain added and associated in the console. For instructions, see Add domains.
URL signing enabled for your domains.
Concurrent stream limits
Each ingest domain has a default limit on the number of concurrent streams it can support, depending on the live center regions:
China (Beijing), China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen): Up to 300 streams
Other regions: Up to 50 streams.
For more information, see Limits.
URL structures
A standard live stream URL consists of five components: protocol, domain name, AppName, StreamName, and access token.
Format: {Protocol}://{Domain}/{AppName}/{StreamName}?auth_key={access_token}

Component | Description | Example |
Protocol | The streaming protocol. |
|
Domain name | The ingest domain for pushing streams, or the streaming domain for playback. |
|
AppName | A custom name for your application to distinguish between different applications or business scenarios. |
|
StreamName | A unique, custom name for a live stream. |
|
Access token | An encrypted string generated using the MD5 algorithm based on the authentication key configured for your domain. For details, see URL signing. |
|
Generate URLs
Choose one of the following methods:
Generate in the console: Suitable for trials and testing. Generate URLs with one click that automatically include an encrypted access token.
Generate by code: Suitable for production environments. Automate URL generation on the server-side for flexible management and distribution.
Generate in the console
Go to the URL Generators page.
Configure the following parameters and click Generate URLs.
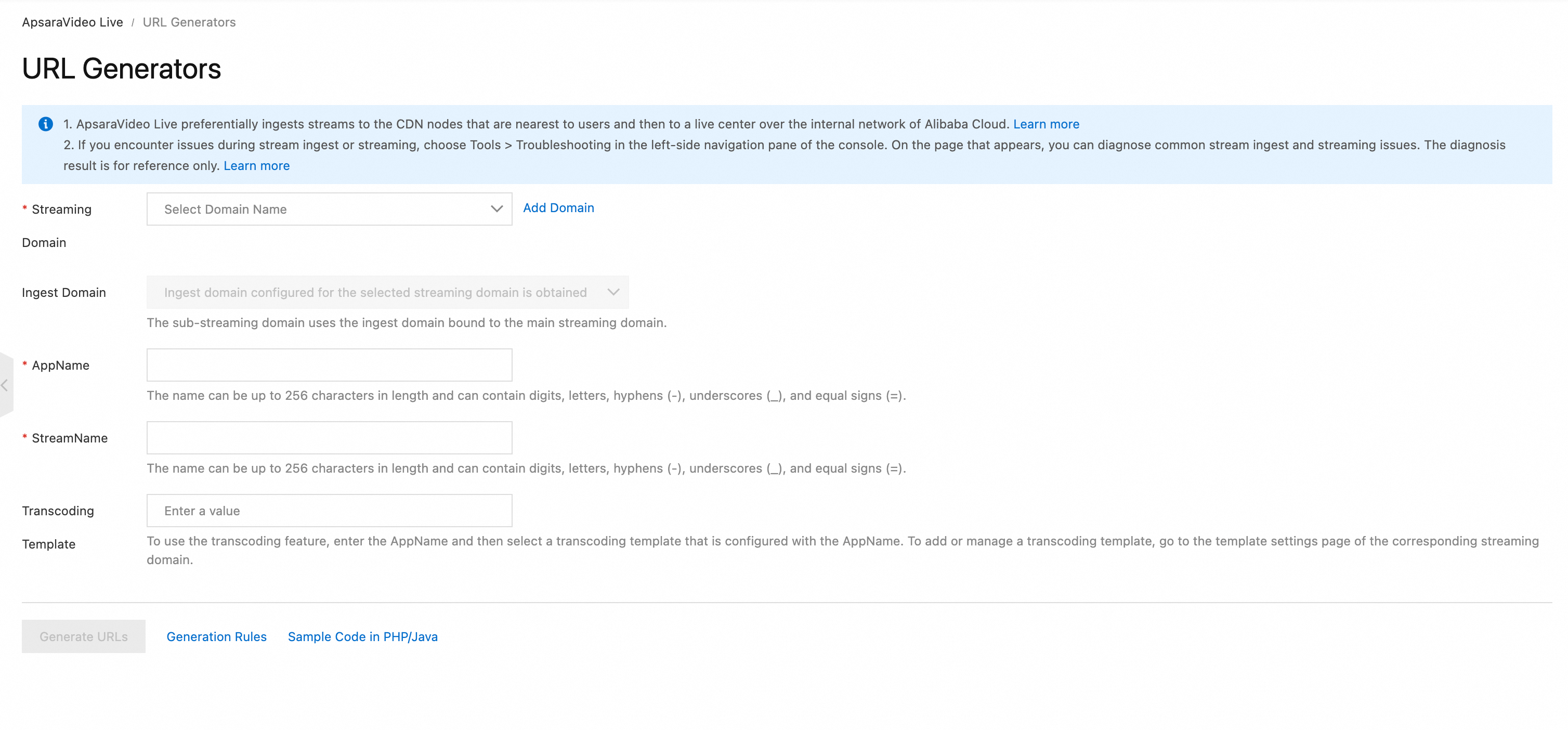 Note
NoteThe URL generator does not support generating live subtitles stream URLs.
Generate by code
Step 1: Construct the URI
The base URI format is {Protocol}://{Domain}/{AppName}/{StreamName}. For URL examples of different protocols, see Ingest URL examples and Streaming URL examples.
// Pseudocode
protocol = "rtmp"
domain = "example.aliyundoc.com"
appName = "liveApp"
streamName = "liveStream"
uri = protocol + "://" + domain + "/" + appName + "/" + streamName
// Result: rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStreamStep 2: Get the authentication key
Obtain the authentication key from one of these sources:
Console: Go to the URL signing configuration page.
API: Call the DescribeLiveDomainConfigs API.
Use the ingest domain key for ingest URLs and the streaming domain key for streaming URLs.
Step 3: Concatenate a signed URL
The following examples show how to generate an access token and assemble a complete URL using the RTMP protocol.
Java
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class AuthDemo {
private static String md5Sum(String src) {
MessageDigest md5 = null;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
md5.update(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode(src));
return String.format("%032x", new BigInteger(1, md5.digest()));
}
private static String aAuth(String uri, String key, long exp) {
String pattern = "^(rtmp://)?([^/?]+)(/[^?]*)?(\\\\?.*)?$";
Pattern r = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher m = r.matcher(uri);
String scheme = "", host = "", path = "", args = "";
if (m.find()) {
scheme = m.group(1) == null ? "rtmp://" : m.group(1);
host = m.group(2) == null ? "" : m.group(2);
path = m.group(3) == null ? "/" : m.group(3);
args = m.group(4) == null ? "" : m.group(4);
} else {
System.out.println("NO MATCH");
}
String rand = "0"; // "0" by default, other value is ok
String uid = "0"; // "0" by default, other value is ok
String sString = String.format("%s-%s-%s-%s-%s", path, exp, rand, uid, key);
String hashValue = md5Sum(sString);
String authKey = String.format("%s-%s-%s-%s", exp, rand, uid, hashValue);
if (args.isEmpty()) {
return String.format("%s%s%s%s?auth_key=%s", scheme, host, path, args, authKey);
} else {
return String.format("%s%s%s%s&auth_key=%s", scheme, host, path, args, authKey);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The ingest or streaming URL to be signed. example.aliyundoc.com is the ingest or streaming domain, liveApp is the AppName, and liveStream is the StreamName.
// Ingest and streaming URLs use the same signing method.
// The AppName or StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=).
String uri = "rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStream";
// The authentication key. To generate ingest URLs, use the key of the ingest domain. To generate streaming URLs, use the key of the streaming domain.
String key = "<input private key>";
// exp is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. The URL's final expiration time is this timestamp plus the validity period configured for URL signing on the domain.
// For example, if you set exp to the current time + 3600 seconds, the final expiration time is the current time + 3600 seconds + the validity period. If you set exp to the current time, the final expiration time is the current time + the validity period.
long exp = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 + 1 * 3600;
String authUri = aAuth(uri, key, exp);
System.out.printf("URL : %s\nAuth: %s", uri, authUri);
}
}Python
import re
import time
import hashlib
import datetime
def md5sum(src):
m = hashlib.md5()
if isinstance(src, str):
src = src.encode('utf-8')
m.update(src)
return m.hexdigest()
def a_auth(uri, key, exp):
p = re.compile("^(rtmp://)?([^/?]+)(/[^?]*)?(\\?.*)?$")
if not p:
return None
m = p.match(uri)
scheme, host, path, args = m.groups()
if not scheme: scheme = "rtmp://"
if not path: path = "/"
if not args: args = ""
rand = "0" # "0" by default, other value is ok
uid = "0" # "0" by default, other value is ok
sstring = "%s-%s-%s-%s-%s" %(path, exp, rand, uid, key)
hashvalue = md5sum(sstring.encode('utf-8'))
auth_key = "%s-%s-%s-%s" %(exp, rand, uid, hashvalue)
if args:
return "%s%s%s%s&auth_key=%s" %(scheme, host, path, args, auth_key)
else:
return "%s%s%s%s?auth_key=%s" %(scheme, host, path, args, auth_key)
def main():
# The ingest or streaming URL to be signed. example.aliyundoc.com is the ingest or streaming domain, liveApp is the AppName, and liveStream is the StreamName.
# Ingest and streaming URLs use the same signing method.
# The AppName or StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=).
uri = "rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStream"
# The authentication key. To generate ingest URLs, use the key of the ingest domain. To generate streaming URLs, use the key of the streaming domain.
key = "<input private key>"
# exp is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. The URL's final expiration time is this timestamp plus the validity period configured for URL signing on the domain.
# For example, if you set exp to the current time + 3600 seconds, the final expiration time is the current time + 3600 seconds + the validity period. If you set exp to the current time, the final expiration time is the current time + the validity period.
exp = int(time.time()) + 1 * 3600
authuri = a_auth(uri, key, exp)
print("URL : %s\nAUTH: %s" %(uri, authuri))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Go
package main
import (
"crypto/md5"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"regexp"
"time"
)
func md5sum(src string) string {
h := md5.New()
h.Write([]byte(src))
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
}
func a_auth(uri, key string, exp int64) string {
p, err := regexp.Compile("^(rtmp://)?([^/?]+)(/[^?]*)?(\\?.*)?$")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return ""
}
m := p.FindStringSubmatch(uri)
var scheme, host, path, args string
if len(m) == 5 {
scheme, host, path, args = m[1], m[2], m[3], m[4]
} else {
scheme, host, path, args = "rtmp://", "", "/", ""
}
rand := "0" // "0" by default, other value is ok
uid := "0" // "0" by default, other value is ok
sstring := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d-%s-%s-%s", path, exp, rand, uid, key)
hashvalue := md5sum(sstring)
auth_key := fmt.Sprintf("%d-%s-%s-%s", exp, rand, uid, hashvalue)
if len(args) != 0 {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s%s%s%s&auth_key=%s", scheme, host, path, args, auth_key)
} else {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s%s%s%s?auth_key=%s", scheme, host, path, args, auth_key)
}
}
func main() {
// The ingest or streaming URL to be signed. example.aliyundoc.com is the ingest or streaming domain, liveApp is the AppName, and liveStream is the StreamName.
// Ingest and streaming URLs use the same signing method.
// The AppName or StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=).
uri := "rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStream"
// The authentication key. To generate ingest URLs, use the key of the ingest domain. To generate streaming URLs, use the key of the streaming domain.
key := "<input private key>"
// exp is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. The URL's final expiration time is this timestamp plus the validity period configured for URL signing on the domain.
// For example, if you set exp to the current time + 3600 seconds, the final expiration time is the current time + 3600 seconds + the validity period. If you set exp to the current time, the final expiration time is the current time + the validity period.
exp := time.Now().Unix() + 3600
authuri := a_auth(uri, key, exp)
fmt.Printf("URL : %s\nAUTH: %s", uri, authuri)
}PHP
<?php
function a_auth($uri, $key, $exp) {
preg_match("/^(rtmp:\/\/)?([^\/?]+)?(\/[^?]*)?(\?.*)?$/", $uri, $matches);
$scheme = $matches[1];
$host = $matches[2];
$path = $matches[3];
$args = $matches[4];
if (empty($args)) {
$args ="";
}
if (empty($scheme)) {
$scheme ="rtmp://";
}
if (empty($path)) {
$path ="/";
}
$rand = "0";
// "0" by default, other value is ok
$uid = "0";
// "0" by default, other value is ok
$sstring = sprintf("%s-%u-%s-%s-%s", $path, $exp, $rand, $uid, $key);
$hashvalue = md5($sstring);
$auth_key = sprintf("%u-%s-%s-%s", $exp, $rand, $uid, $hashvalue);
if ($args) {
return sprintf("%s%s%s%s&auth_key=%s", $scheme, $host, $path, $args, $auth_key);
} else {
return sprintf("%s%s%s%s?auth_key=%s", $scheme, $host, $path, $args, $auth_key);
}
}
// The ingest or streaming URL to be signed. example.aliyundoc.com is the ingest or streaming domain, liveApp is the AppName, and liveStream is the StreamName.
// Ingest and streaming URLs use the same signing method.
// The AppName or StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=).
$uri = "rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStream";
// The authentication key. To generate ingest URLs, use the key of the ingest domain. To generate streaming URLs, use the key of the streaming domain.
$key = "<input private key>";
// exp is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. The URL's final expiration time is this timestamp plus the validity period configured for URL signing on the domain.
// For example, if you set exp to the current time + 3600 seconds, the final expiration time is the current time + 3600 seconds + the validity period. If you set exp to the current time, the final expiration time is the current time + the validity period.
$exp = time() + 3600;
$authuri = a_auth($uri, $key, $exp);
echo "URL :" . $uri;
echo PHP_EOL;
echo "AUTH:" . $authuri;
?>C#
using System;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
public class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
// The ingest or streaming URL to be signed. example.aliyundoc.com is the ingest or streaming domain, liveApp is the AppName, and liveStream is the StreamName.
// Ingest and streaming URLs use the same signing method.
// The AppName or StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=).
string uri= "rtmp://example.aliyundoc.com/liveApp/liveStream";
// The authentication key. To generate ingest URLs, use the key of the ingest domain. To generate streaming URLs, use the key of the streaming domain.
string key= "<input private key>";
DateTime dateStart = new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 8, 0, 0);
// exp is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. The URL's final expiration time is this timestamp plus the validity period configured for URL signing on the domain.
// For example, if you set exp to the current time + 3600 seconds, the final expiration time is the current time + 3600 seconds + the validity period. If you set exp to the current time, the final expiration time is the current time + the validity period.
string exp = Convert.ToInt64((DateTime.Now - dateStart).TotalSeconds+3600).ToString();
string authUri = aAuth(uri, key, exp);
Console.WriteLine (String.Format("URL :{0}",uri));
Console.WriteLine (String.Format("AUTH :{0}",authUri));
}
public static string aAuth(string uri, string key, string exp)
{
Regex regex = new Regex("^(rtmp://)?([^/?]+)(/[^?]*)?(\\\\?.*)?$");
Match m = regex.Match(uri);
string scheme = "rtmp://", host = "", path = "/", args = "";
if (m.Success)
{
scheme=m.Groups[1].Value;
host=m.Groups[2].Value;
path=m.Groups[3].Value;
args=m.Groups[4].Value;
}else{
Console.WriteLine ("NO MATCH");
}
string rand = "0"; // "0" by default, other value is ok
string uid = "0"; // "0" by default, other value is ok
string u = String.Format("{0}-{1}-{2}-{3}-{4}", path, exp, rand, uid, key);
string hashValue = Md5(u);
string authKey = String.Format("{0}-{1}-{2}-{3}", exp, rand, uid, hashValue);
if (args=="")
{
return String.Format("{0}{1}{2}{3}?auth_key={4}", scheme, host, path, args, authKey);
} else
{
return String.Format("{0}{1}{2}{3}&auth_key={4}", scheme, host, path, args, authKey);
}
}
public static string Md5(string value)
{
MD5CryptoServiceProvider md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(value);
byte[] encoded = md5.ComputeHash(bytes);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0; i<encoded.Length; ++i)
{
sb.Append(encoded[i].ToString("x2"));
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}Ingest URL examples
Protocol | Example | Description |
RTMP |
| Standard protocol for live stream ingest. |
ARTC |
| Ingest URL for Real-Time Streaming (RTS). |
SRT |
| SRT protocol is disabled by default. To enable it, see SRT stream ingest. |
Streaming URL examples
URL type | Description | Protocol | Example address |
Standard streaming URL | If you use SRT for stream ingest, playback is supported over RTMP, FLV, HLS, and ARTC. | RTMP |
|
FLV |
| ||
HLS |
| ||
ARTC |
| ||
Transcoded stream URL (Default transcoding or custom transcoding) | Append To get the transcoding template ID, configure live stream transcoding. | RTMP |
|
FLV |
| ||
HLS |
| ||
ARTC |
| ||
Transcoded stream URL (Multi-bitrate transcoding) | For adaptive bitrate streams, append To get the transcoding template group ID, configure live stream transcoding. | HLS |
|
Delayed stream URL | For a delayed stream, append Before you use a delayed stream for playback, configure stream delay. | RTMP |
|
FLV |
| ||
HLS |
| ||
ARTC |
| ||
Live subtitles stream URL | Append To create a subtitle template, configure live subtitles. | RTMP |
|
FLV |
| ||
HLS |
|
Verify the generated URLs
To verify the generated URLs, we recommend using the demo app on a mobile device to ingest the stream and VLC media player on a PC to play it. For more ingest and streaming methods, see Live stream ingest and Live stream playback.
Verify the ingest URL:
Download the ApsaraVideo Live demo app by scanning the QR code on a mobile device (Android or iOS).
 Note
NoteOn an iOS device, you may receive a message indicating that the demo is from an untrusted enterprise developer. Go to Settings > General > VPN & Device Management, find the permissions required by Taobao, and tap Trust.
Open the demo application. Choose either Camera Pushing or Screen Sharing. Enter the ingest URL. If you generated the URL in the console, scan the QR code to auto-fill the URL.
Click Start.
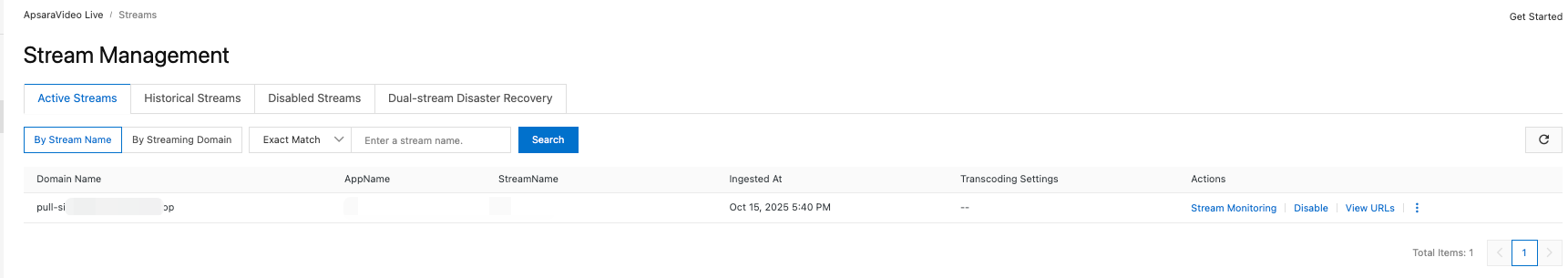
Verify that the stream appears on the Stream Management page. If not, check whether you have followed the previous steps correctly.
Verify the streaming URL:
Keep the ingest client running. Otherwise, playback will fail.
Download and install VLC media player.
Run VLC media player.
In the menu bar, choose Media > Open Network Stream.
On the Network tab, enter the generated streaming URL. Example:
rtmp://pull-singapore.cloud-example.net/ziji/test?auth_key=1750150177-0-0-9b7d7e8b3431acc543a99c69********
Troubleshooting
If you encounter problems during stream ingest or playback, use the troubleshooting tool to validate the URL and authentication information.