This topic describes how to configure and use WebAuthn authentication in Alibaba Cloud IDaaS EIAM (Enterprise Identity Access Management). WebAuthn provides a more secure and convenient passwordless logon experience. It introduces feature advantages and configuration steps to help administrators quickly integrate WebAuthn into their enterprise identity systems.
Introduction
WebAuthn is a component of Fast Identity Online (FIDO) 2.0.
WebAuthn implements password-free logon to web pages by providing the optimal experience and hardware-level security. WebAuthn allows users to log on to a website by using the native device encryption and biometric authentication capabilities of a PC.
The following types of authenticators are supported:
Cross-platform authenticator (also known as roaming authenticator): an external authenticator that is used across different devices, such as YubiKey.
Platform authenticator: the native authenticator of a browser, such as macOS Touch ID or Windows Hello.
For more information, see WebAuthn.
WebAuthn is supported by almost all modern browsers. For more information about how to check the version compatibility of a browser, see Duo Passwordless.
Logon example
Users can log on by entering only a username. Users do not need to enter the password. The following video shows how to register the device information for WebAuthn.
Register an authenticator
Before users log on by using an authenticator, users must bind the authenticator to their accounts.
Go to the My Account page. Find WebAuthn Authenticator in the Security Information section and click Manage. In the Manage WebAuthn Authenticator panel, register an authenticator.
The registration process requires 1 minute to complete. After you click Register New Authenticator, complete the configurations as prompted.
After the registration is complete, the enabled authenticator can be used for logon. Users can also manage the registered authenticators.
Administrators cannot manage the authenticators of users. Each user can individually register and manage an authenticator.
Logon scenarios
Scenario 1: Password-free logon
WebAuthn can be used for password-free logon. This is one of the most common and convenient scenarios in which WebAuthn is used.
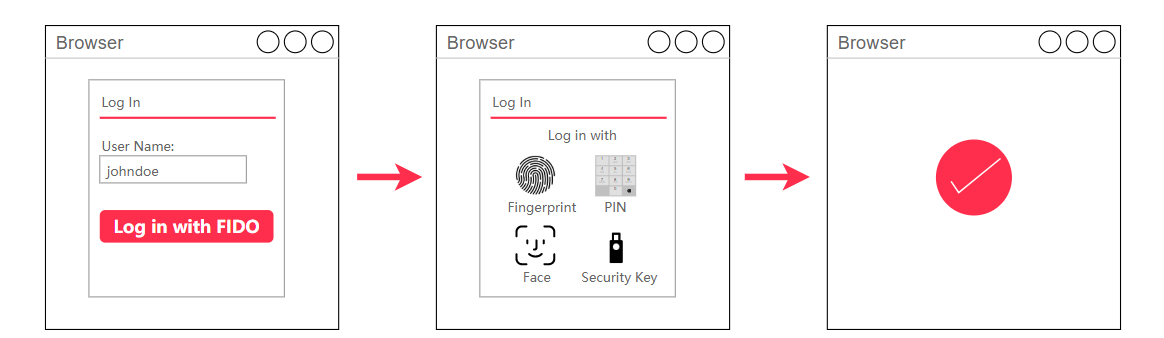
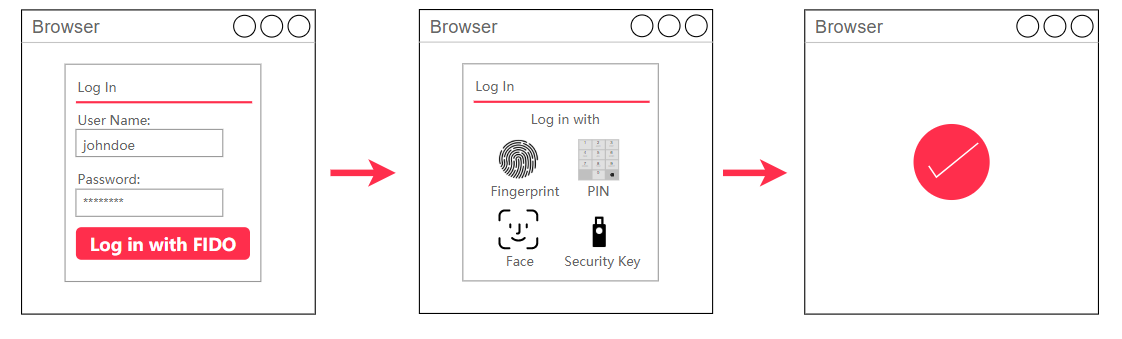
On the IDaaS logon page, a user enters a username and selects a WebAuthn authentication method for verification. Log on to the application after the user passes the authentication. This method can be used to log on to all web applications. The following flowchart shows the process.
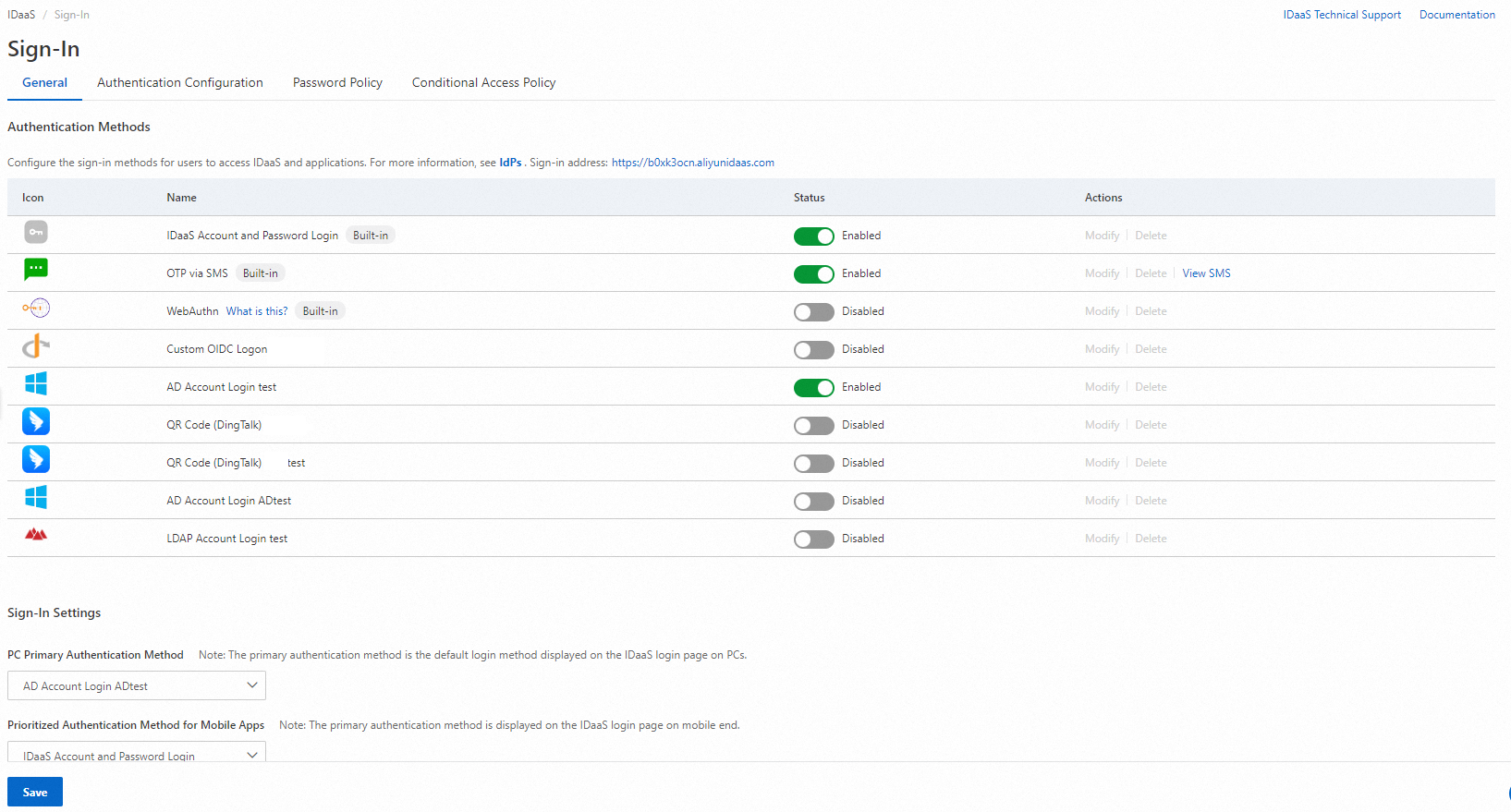
On the General tab of the Sign-In page, the WebAuthn authenticator method is displayed in the Authentication Methods section. By default, this method is disabled. You must enable the method before you can use the method.
After you enable the method, the WebAuthn logon option is available on the logon page. Then, the user can log on by using WebAuthn. The following figure shows an example on how to use macOS Touch ID for logon.
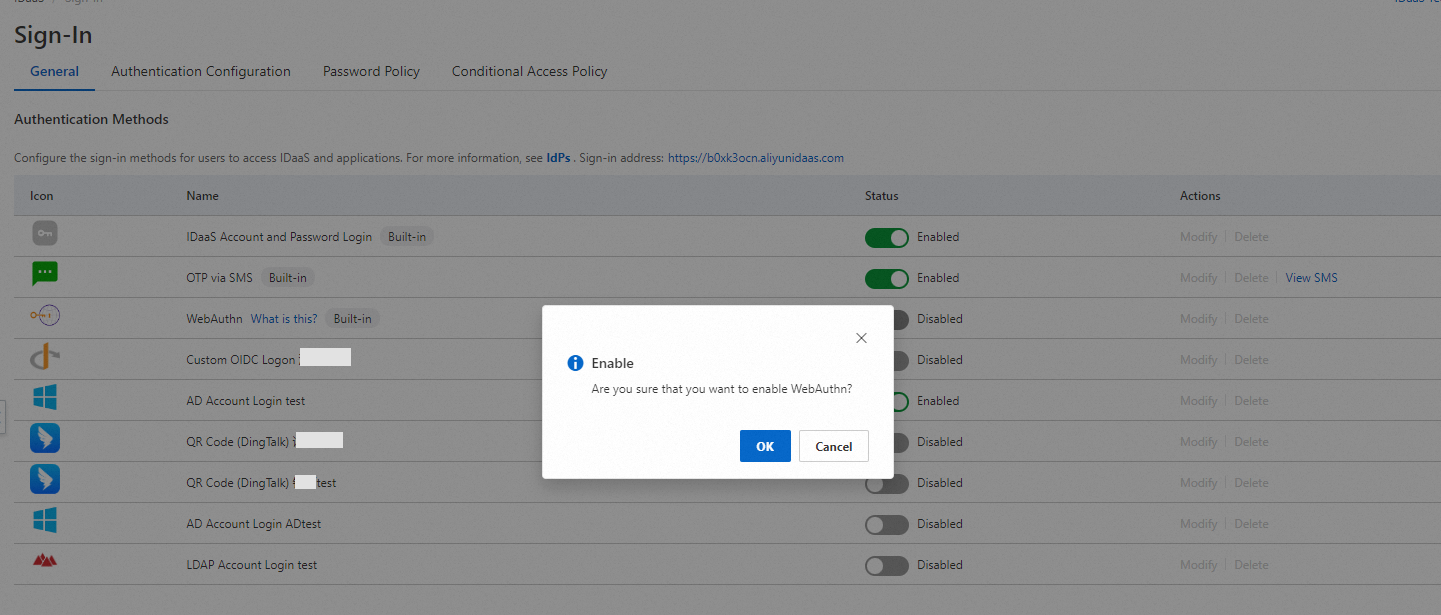
IDaaS obtains information about the registered authenticator of a specific account. If the authenticator is not registered, an error occurs and the authenticator cannot be used.
Scenario 2: Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
WebAuthn can be used for MFA. This is also one of the most common and most secure scenarios in which WebAuthn is used.
If MFA is enabled, users must be re-authenticated after they enter a username and password. Users can use a WebAuthn authenticator for secure logon. The following flowchart shows the process.
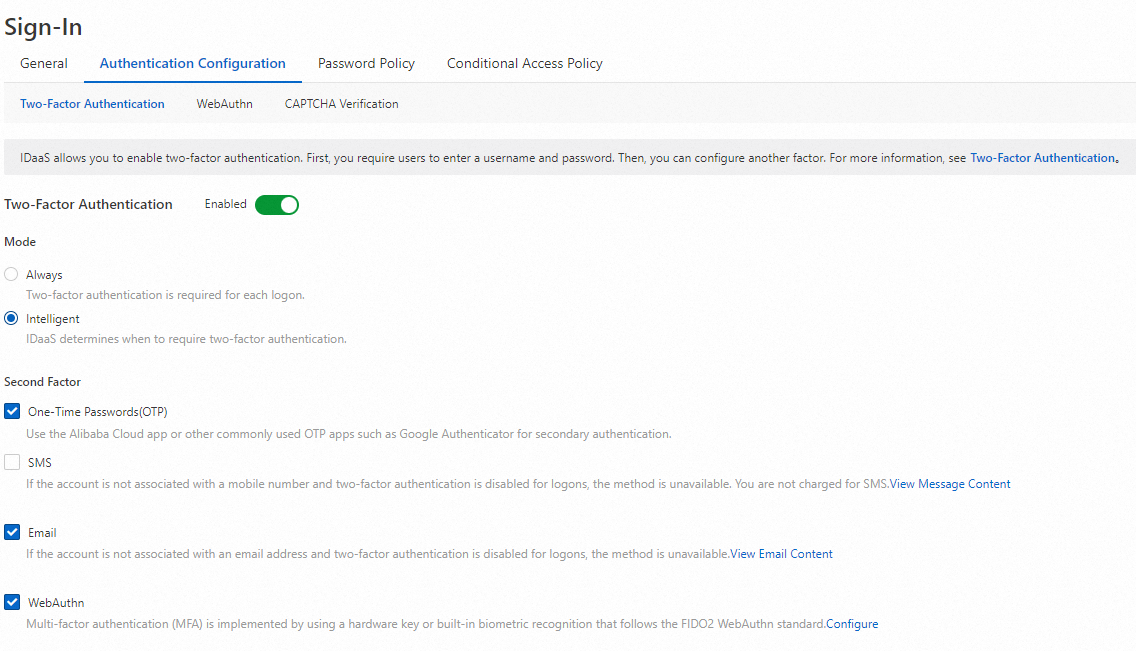
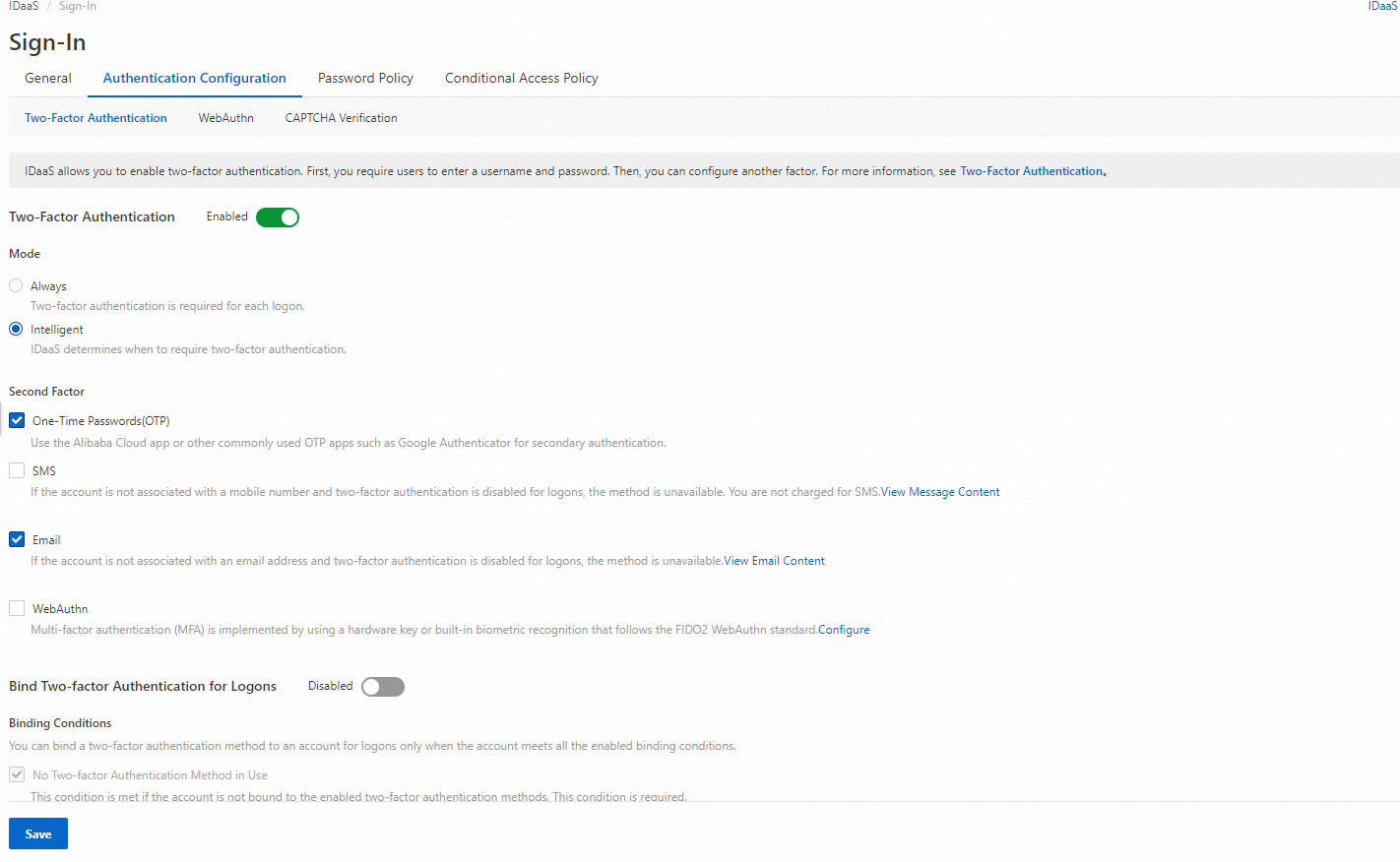
On the Authentication Configuration tab of the Sign-In page, click the Two-Factor Authentication tab. Turn on Two-factor Authentication, select WebAuthn, and then click Save.
Then, users must be re-authenticated after they enter a username and password on the logon page. If users registered a WebAuthn authenticator, users can use WebAuthn to complete identity authentication in a quick and secure manner. The following figure shows an example on how to use macOS Touch ID for MFA.