This topic describes how to use the ANALYZE command and the simpler AUTO ANALYZE mechanism.
ANALYZE
Statistics are crucial for the optimizer to generate an accurate execution plan. Hologres collects sampled statistics about your data, such as data distribution and characteristics, table statistics, column statistics, row count, column count, field width, cardinality, frequency, maximum value, minimum value, most frequent values, and bucket distribution characteristics. The optimizer uses this information to update operator cost estimates, prune search spaces, estimate optimal JOIN ORDER, estimate memory overhead, and estimate degree of parallelism—ultimately generating better execution plans.
The ANALYZE command collects statistics about table contents in your database. The optimizer uses these statistics to generate the best query plan and improve query efficiency.
Syntax
-- Update statistics for a specific table. By default, statistics for all columns in the table are collected. ANALYZE <tablename>; -- Update statistics for specific columns. This samples more data than updating the entire table and provides higher accuracy. Use this primarily for columns used in filter conditions. ANALYZE <tablename>(<colname>, <colname>);Parameter description
tablename is the name of the table for which you want to update statistics. colname is the name of the column for which you want to update statistics.
Syntax details
The following describes the two Analyze commands.
Similarities
Column statistics provide information about the number of rows, column width, most common values (MCV), a histogram, and the number of distinct values (NDV).
Both commands overwrite statistics only for the specified columns and leave other columns unchanged. For example, the command
ANALYZE <tablename>(<colname1>);overwrites (updates) previously collected statistics forcolname1but does not affect statistics forcolname2.
Differences
ANALYZE <tablename>;computes statistics based on sampled data.ANALYZE <tablename>(<colname>, <colname>);calculates NDV using APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT. In many cases, this yields more accurate results than sampling but incurs higher overhead. Therefore, use this form only for critical columns. Statistics such as histogram and width are still derived from sampling.
For a table with two columns,
table (colname1, colname2),ANALYZE table;is not fully equivalent toANALYZE table(colname1, colname2);.For commonly used JOIN columns or GROUP BY columns, use
ANALYZE <tablename>(<colname>, <colname>);to collect additional statistics.
When to run ANALYZE
Run
ANALYZE <tablename>;in the following situations.After performing large numbers of INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations on a table, such as data imports.
Before running multi-table JOIN queries when performance degrades. Run ANALYZE on JOIN columns and GROUP BY columns.
After running
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE, collect statistics for the foreign table using ANALYZE.After running
IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA, run ANALYZE on tables you plan to query.After running
CREATE EXTERNAL DATABASE, collect statistics for the foreign table using ANALYZE.
Notes
In Hologres V0.10 and V1.1, if you query a parent partitioned table, run ANALYZE on the parent table. If you query child tables directly, run ANALYZE on those child tables. If you do both, run ANALYZE on both to avoid missing statistics.
If you encounter the following issues, run ANALYZE before starting your import task to systematically improve efficiency.
Multi-table JOIN exceeds memory (OOM): This typically produces an error such as
Query executor exceeded total memory limitation xxxxx: yyyy bytes used.Low import efficiency: Queries or data imports in Hologres run slowly, and tasks take a long time to complete.
If your table contains very wide columns (such as Bitmap or other Bytea data, or Text data exceeding 1 KB), statistics for these columns provide no benefit and increase memory consumption during sampling. For such tables, avoid running
ANALYZE <tablename>;. Instead, useANALYZE <tablename>(<colname>, <colname>);to skip wide columns and analyze only necessary columns (such as JOIN columns, GROUP BY columns, and filter columns).Note1 KB is an empirical threshold. You can adjust this based on your business needs.
AUTO ANALYZE
To reduce repetitive manual ANALYZE operations, Hologres V0.10 and later support AUTO ANALYZE. When enabled, the system automatically determines whether to run ANALYZE on relevant tables in the background based on table creation, data writes, and modifications. This eliminates the need for manual ANALYZE, reduces operational complexity, and prevents missing statistics because of oversight.
Syntax
Check if AUTO ANALYZE is enabled
SHOW hg_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker; -- Syntax for V1.1 and later versions to check current status SHOW hg_experimental_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker; -- Syntax for V0.10 to check current statusThe syntax for enabling or disabling is as follows. This command requires Superuser privileges.
-- Database-level setting. Takes effect for the entire database. Syntax for V1.1 and later. ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker = ON; -- Enable (default) ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker = OFF; -- Disable -- Database-level setting. Takes effect for the entire database. Syntax for V0.10. ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_experimental_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker = ON; -- Enable (default) ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_experimental_enable_start_auto_analyze_worker = OFF; -- Disable -- Enable AUTO ANALYZE for an External Database ALTER EXTERNAL DATABASE dbname WITH enable_auto_analyze 'true';
Limits
AUTO ANALYZE in Hologres has the following limits:
AUTO ANALYZE is supported only in Hologres V0.10 and later. You can check your instance version on the instance details page in the Hologres Management Console. If your instance runs a version earlier than V0.10, for more information, see Common upgrade preparation failure errors or join the Hologres DingTalk group for support. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
Only Superusers can enable or disable AUTO ANALYZE.
Limits for partitioned tables:
When a partition child table changes and requires AUTO ANALYZE, the system analyzes the parent table.
Partitioned tables have a row scan limit. By default, sampling scans up to 224 rows (16,777,216 rows). If the total number of rows across all partitions exceeds this limit, the system performs partition pruning and samples only a subset of partitions (totaling no more than 16,777,216 rows).
NotePartition key column statistics are always complete and unaffected by pruning. However, this may affect statistics for columns co-located with the partition key (such as columns with identical data). In such cases, some values might be missed, leading to inaccurate row count estimates. If needed, you can search for DingTalk group 32314975 to join the Hologres real-time data warehouse discussion group and contact technical support. Engineers can evaluate your instance and adjust the maximum scan row limit.
AUTO ANALYZE collects statistics for up to 256 columns by default. For tables with more than 256 columns, it processes the first 256. You can change this limit by adjusting
hg_experimental_auto_analyze_max_columns_count.AUTO ANALYZE limits memory usage per worker to 4 GB by default. Tables with very wide columns may exceed this limit and cause ANALYZE to fail. You can adjust the
auto_analyze_work_memory_mbparameter to increase this limit, but consider the impact on system memory. Larger instance types support more workers and higher total memory limits for AUTO ANALYZE.Starting with Hologres V3.1.0, ANALYZE and AUTO ANALYZE support collecting statistics for foreign tables in External Databases.
ANALYZE and AUTO ANALYZE do not support HMS foreign tables.
How AUTO ANALYZE works
After enabling AUTO ANALYZE, the system periodically checks in the background for tables that need ANALYZE.
Standard tables (internal tables, including non-partitioned and partitioned tables)
Every minute, the system checks for recent table activity (primarily DML operations such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE that may change data volume). If any of the following conditions are met, the system triggers ANALYZE to collect statistics:
A DML operation completes and changes more than 10% of the table's current row count. For partition child tables, this means changes exceeding 10% of that partition's row count.
TRUNCATE TABLE empties the table.
A DDL change occurs, such as CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE modifying the table schema. This does not include CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY for changing table properties.
Every 10 minutes, the system checks all internal tables for data changes. If a table's row count changes by more than 10% since the last check, the system triggers ANALYZE.
NoteThis step detects data updated by non-explicit DML operations (such as real-time writes via Flink, data integration, or HoloClient).
External Table
Every 4 hours, the system performs a scheduled inspection of foreign table metadata or data changes. If the following conditions are met, the system triggers ANALYZE on the table in the background to collect statistics information.
The external table corresponding to the foreign table (such as the MaxCompute foreign table and the DLF foreign table) has changed between two inspections (such as within 4 hours). The change is determined by whether the
last_modify_timeof the corresponding MaxCompute table falls within the inspection interval.
NoteInspection and execution occur within the same scheduling task. The next inspection starts only after the current ANALYZE finishes. As long as the time since the last inspection start meets the scheduling cycle, the next inspection begins.
Configuration parameters
After enabling AUTO ANALYZE, the system automatically inspects tables periodically, decides which tables need ANALYZE, and performs sampling to collect statistics. This consumes system resources.
In some business scenarios, the default behavior may not fit your needs. Such as in scenarios with infrequent data updates, you can reduce AUTO ANALYZE frequency by adjusting default parameters. You can modify these parameters as needed for performance tuning.
NoteOnly Superusers can adjust AUTO ANALYZE behavior. All settings apply at the database level and take effect within one minute.
Syntax
-- Superuser syntax to modify AUTO ANALYZE parameter defaults ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET <GUC>=<values>;dbname is the database name. GUC is the parameter name. values is the parameter value.
Parameter list
Parameter
Parameter description
Supported version
Default value
Example
autovacuum_naptime
Interval (in seconds) between checks for recent table activity.
V1.1.0 and later
NoteRequires backend adjustment. To request a change, search for DingTalk group 32314975 to join the Hologres real-time data warehouse discussion group.
60s
ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET autovacuum_naptime = 60;ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET autovacuum_naptime = '60s';ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET autovacuum_naptime = '10min';
hg_auto_check_table_changes_interval
Interval (in seconds) for checking data changes in all internal tables.
V1.1.0 and later
600s (10min)
-- Syntax for V1.1 and later ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_auto_check_table_changes_interval = '600s'; -- Syntax for V0.10 ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_experimental_auto_check_table_changes_interval = '600s';hg_auto_check_foreign_table_changes_interval
Interval (in seconds) for checking data changes in all foreign tables.
V1.1.0 and later
14400s (4 hours)
-- Syntax for V1.1 and later ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_auto_check_foreign_table_changes_interval = '14400s'; -- Syntax for V0.10 ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_experimental_auto_check_foreign_table_changes_interval = '14400s';hg_experimental_auto_analyze_max_columns_count
Maximum number of columns for which statistics are automatically collected.
V1.1.0 and later
256
ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_experimental_auto_analyze_max_columns_count = 300;auto_analyze_work_memory_mb
Memory limit (in MB) per table for AUTO ANALYZE.
V1.1.54 and later
Default: 4096 MB (4 GB) per worker. Larger instance types support more workers and higher total memory limits.
Set the memory limit per table to 9 GB.
ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET auto_analyze_work_memory_mb = 9216;hg_experimental_auto_analyze_start_time
Daily start time for AUTO ANALYZE.
NoteMust use the same time zone as end_time, and start time must be less than or equal to end_time.
V1.1.54 and later
00:00 +0800
Configure AUTO ANALYZE to run only between 00:00 and 06:00 if internal and external table data remains unchanged during the day.
ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_experimental_auto_analyze_start_time = '00:00 +0800';ALTER DATABASE <dbname> SET hg_experimental_auto_analyze_end_time = '06:00 +0800';
hg_experimental_auto_analyze_end_time
Daily end time for AUTO ANALYZE.
V1.1.54 and later
23:59 +0800
autovacuum_enabled
Enabling status for AUTO ANALYZE on a table.
V1.1.54 and later
true (enabled by default for all tables).
Disable AUTO ANALYZE for a specific table. Future ANALYZE operations will skip this table.
NoteYou can disable Auto Analyze for Hologres internal tables only using the following command.
ALTER TABLE <tablename> SET (autovacuum_enabled = false);
Additional optimization
Starting with Hologres V3.1, the Fast Rows feature is available. When Hologres detects that a table in a query lacks statistics, it directly retrieves the table's row count from the storage engine. This operation costs approximately 10 ms. Use the following command.
-- Database-level setting. Takes effect for the entire database.
ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_experimental_get_fast_num_of_rows = ON; -- Enable (disabled by default)
-- Database-level setting. Takes effect for the entire database.
ALTER DATABASE dbname SET hg_experimental_get_fast_num_of_rows = OFF; -- Disable (disabled by default)When Fast Rows is disabled, the following scenario helps reduce the chance of incorrect plans:
If a table has no statistics, its row count appears as 1000 in the query plan (indicating missing statistics, with the plan estimated based on 1000 rows).
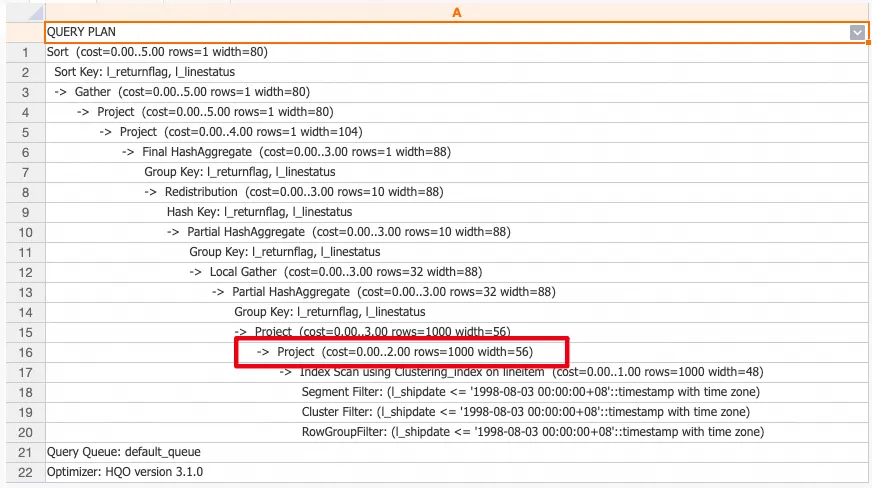
When Fast Rows is enabled and a table has no statistics, the row count in the query plan is not 1000 (the system calls the storage engine to retrieve the actual row count).
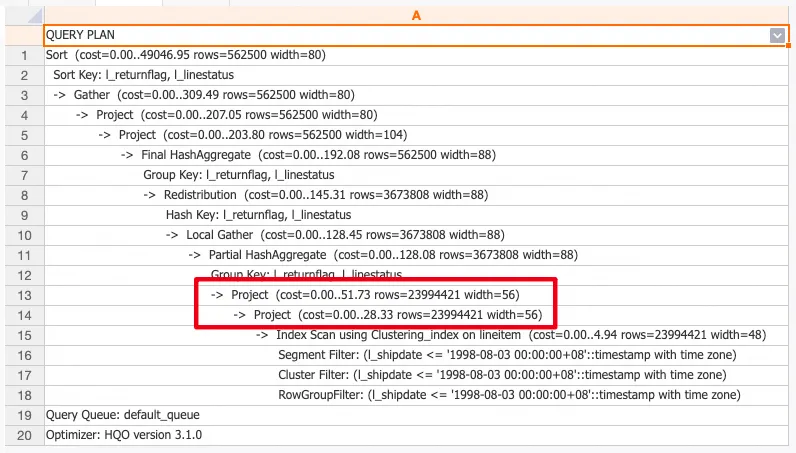
Query statistics
Table statistics are stored in the hologres_statistic.hg_table_statistic table. You can check this table to monitor ANALYZE status. Use the following command.
To find the most recent ANALYZE information, sort by analyze_timestamp.
SELECT schema_name, -- Schema of the table
table_name, -- Table name
schema_version, -- Table schema version
statistic_version, -- Version of the most recent ANALYZE statistics
total_rows, -- Row count from the most recent ANALYZE
analyze_timestamp -- End time of the most recent ANALYZE
FROM hologres_statistic.hg_table_statistic
WHERE table_name = '<tablename>'
ORDER BY analyze_timestamp DESC;Each table has
0–nrecords in hologres_statistic.hg_table_statistic. Zero records mean ANALYZE has never run. One or more records mean ANALYZE has run.If multiple records exist, their schema_version values differ because the table schema changed (such as when running
ADD COLUMNcreates a new version). Older records with outdated schema_version are no longer used.Example query result showing two records for the same table. The second record has a lower schema_version and is obsolete. You can ignore it.
schema_name | table_name | schema_version | statistic_version | total_rows | analyze_timestamp -------------+------------------+----------------+-------------------+------------+--------------------- public | tbl_name_example | 13 | 8580 | 10002 | 2022-04-29 16:03:18 public | tbl_name_example | 10 | 8576 | 10002 | 2022-04-29 15:41:20 (2 rows)Hologres V0.10 and V1.1 do not clean up expired historical records in hg_table_statistic. You can safely ignore old data.
View tables missing statistics
You can use the HG_STATS_MISSING view to identify tables in your database that lack statistics. For more information, see HG_STATS_MISSING View.
FAQ
If any of the following situations occur, AUTO ANALYZE is not working properly. You can follow the solutions provided.
Table statistics show zero records
Issue: Querying hologres_statistic.hg_table_statistic returns no data for the table.
Possible causes:
AUTO ANALYZE is not running, or the table does not meet AUTO ANALYZE trigger conditions.
The issue may be with the AUTO ANALYZE feature itself. For detailed troubleshooting, you can or submit a ticket.
Solution: You can manually trigger ANALYZE once.
analyze_timestampis too small.Issue: The
analyze_timestampin query results is much older than the current time, indicating ANALYZE has not run for a long time.Possible causes:
AUTO ANALYZE failed to run for some reason.
AUTO ANALYZE was manually disabled.
Solution: First, manually trigger ANALYZE. Then, , or submit a ticket to investigate the cause.