Starting from V1.3, Hologres lets you configure multiple read-only secondary instances in Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) to implement simple load balancing. This topic describes how to implement JDBC-based load balancing.
Background information
In Hologres, a primary instance can be attached to multiple read-only secondary instances. The instances share storage, but their compute resources are isolated from each other. This provides a high availability (HA) deployment with read/write splitting. For more information, see Primary and secondary instances with read/write splitting (shared storage).
Hologres lets you use JDBC to configure multiple read-only secondary instances to implement simple load balancing, as shown in the following figure: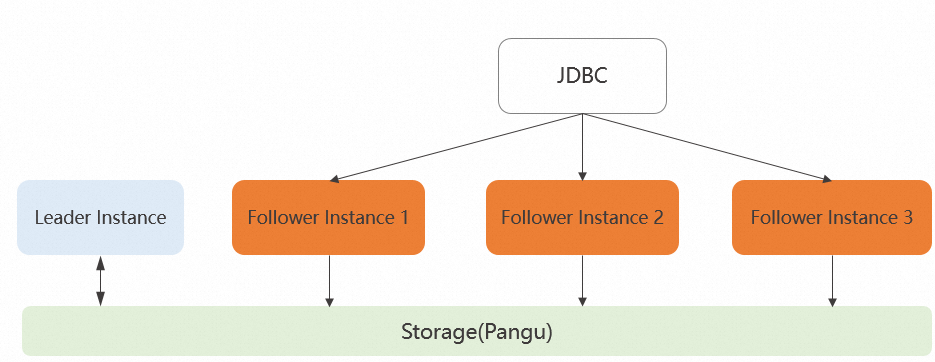
You can configure multiple read-only secondary instances in JDBC to achieve the following:
-
Randomly distribute query requests to your read-only secondary instances to prevent high payloads on a single instance.
-
Connect to read-only secondary instances in sequence to improve service availability in the event of an instance failure. The process is as follows:
-
If the connection to read-only secondary instance 1 fails, JDBC automatically tries to connect to read-only secondary instance 2.
-
If connections to both read-only secondary instance 1 and read-only secondary instance 2 fail, JDBC automatically tries to connect to read-only secondary instance 3.
-
The system reports a connection failure only if the connections to all three instances fail.
-
Starting from Hologres V2.0.10, the targetServerType parameter supports more values to accommodate more load balancing scenarios.
Usage notes
Prerequisites
-
You have purchased multiple Hologres read-only secondary instances and attached them to a Hologres primary instance. For more information, see Configure primary and secondary instances that use shared storage.
-
You have downloaded a PostgreSQL JDBC driver, version 42.3.2 or later. For more information, see JDBC.
Command format
To configure multiple read-only secondary instances in JDBC, separate the Endpoint:Port information of each instance with a comma (,) in the connection URL. The command format is as follows:
jdbc:postgresql://<Endpoint1>:<Port1>,<Endpoint2>:<Port2>,<Endpoint3>:<Port3>.../<DBNAME>?user=<AccessKey ID>&password=<AccessKey Secret>&targetServerType=any&loadBalanceHosts=<value>[&hostRecheckSeconds=<value>]Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Endpoint |
The network address of the Hologres instance. Go to the Instance Details page in the Hologres console to obtain the network address. |
|
Port |
The port of the Hologres instance. Go to the Instance Details page in the Hologres console to obtain the port. |
|
DBNAME |
The name of the database created in Hologres. |
|
AccessKey ID |
The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account. Click AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey ID. |
|
AccessKey Secret |
The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account. Click AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey secret. |
|
targetServerType |
Specifies the status of the instances to which connections are allowed. A value of The following values are supported only in Hologres V2.0.10 and later:
JDBC determines whether an instance is a primary or read-only secondary instance based on the value of the
|
|
loadBalanceHosts |
Specifies the order in which to try to connect to the read-only secondary instances. Valid values:
|
|
hostRecheckSeconds |
The cache duration for the list of connectable Endpoints. The default value is If you want to change the cache duration, modify the value of the |
For more information about JDBC configurations, see the JDBC documentation.
Examples
-
The following example shows how to randomly distribute queries to three read-only secondary instances. If a connection to one instance fails, JDBC automatically tries to connect to another instance.
import java.sql.*; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; public class hatest { public static void main(String[] args) { // Set the connection endpoint of the Hologres instance. This is read-only secondary instance 1. String endpoint1 = "hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx01-cn-shanghai.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80"; // Set the connection endpoint of the Hologres instance. This is read-only secondary instance 2. String endpoint2 = "hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx02-cn-shanghai.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80"; // Set the connection endpoint of the Hologres instance. This is read-only secondary instance 3. String endpoint3 = "hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx03-cn-shanghai.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80"; // Set the name of the database to connect to. String dbname = "postgres"; String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://" + endpoint1 + "," + endpoint2 + "," + endpoint3 + "/" + dbname; Properties properties = new Properties(); // Set the username for the database connection. properties.setProperty("user", "xxxx"); // Set the password for the database connection. properties.setProperty("password", "xxxx"); // Configure targetServerType. In this example, it is set to any, which indicates that requests can be sent to any endpoint. properties.setProperty("targetServerType", "any"); // Configure the LoadBalance policy. In this example, it is set to true, which indicates that load balancing is enabled. properties.setProperty("loadBalanceHosts", "true"); // Configure the hostRecheckSeconds duration. In this example, it is set to 10 seconds. properties.setProperty("hostRecheckSeconds", "10"); try { Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver"); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, properties); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("show hg_frontend_endpoints;" ); ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); Map map = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { map.put(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1).toLowerCase(), resultSet.getObject(i + 1)); } System.out.println(map); } } catch (Exception exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } } } -
The following example shows how to distribute 100 queries to two instances using polling.
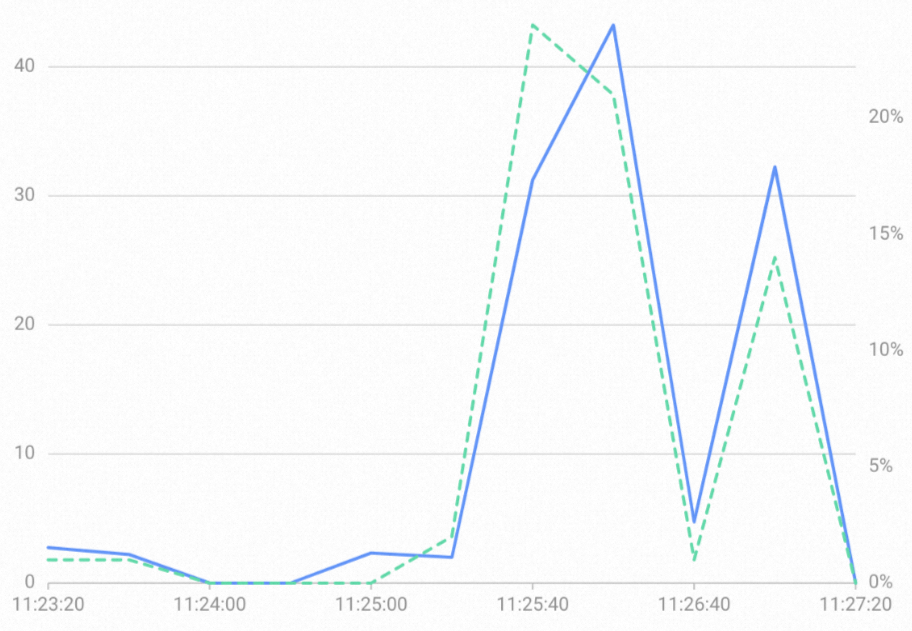
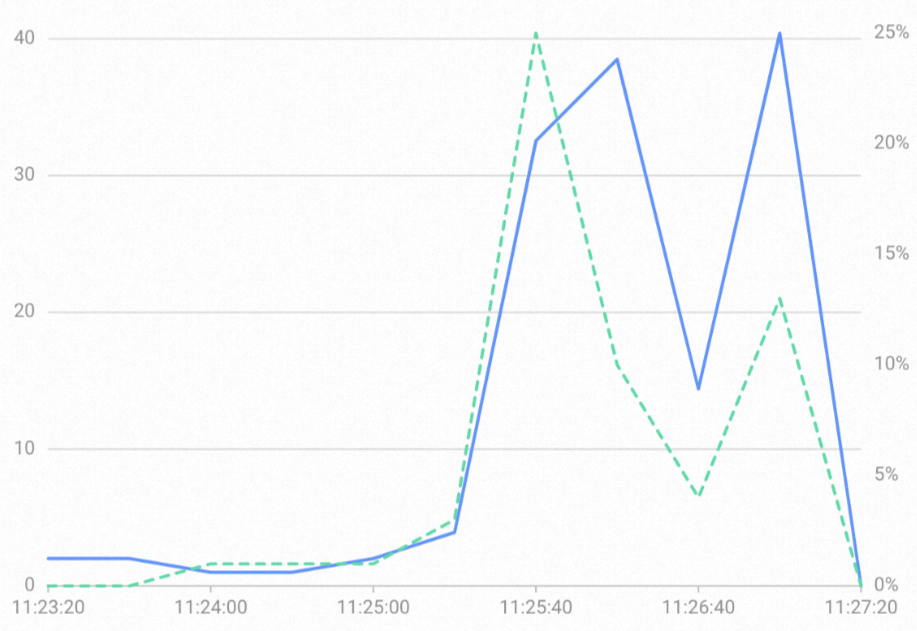
import java.sql.*; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; public class hatest { public static void main(String[] args) { int x = 1; while( x <= 100 ){ // Set the connection endpoint of the Hologres instance. This is the primary instance. String endpoint1 = "hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx04-cn-hangzhou.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80"; // Set the connection endpoint of the Hologres instance. This is the read-only secondary instance. String endpoint2 = "hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx05-cn-hangzhou.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80"; // Set the name of the database to connect to. String dbname = "postgres"; String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://" + endpoint1 + "," + endpoint2 + "/" + dbname ; Properties properties = new Properties(); // Set the username for the database connection. properties.setProperty("user", "xxx"); // Set the password for the database connection. properties.setProperty("password", "xxx"); // Configure targetServerType. In this example, it is set to any, which indicates that requests can be sent to any endpoint. properties.setProperty("targetServerType", "any"); // Configure the LoadBalance policy. In this example, it is set to true, which indicates that load balancing is enabled. properties.setProperty("loadBalanceHosts", "true"); // Configure the hostRecheckSeconds duration. In this example, it is set to 10 seconds. properties.setProperty("hostRecheckSeconds", "10"); try { Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver"); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, properties); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("show hg_frontend_endpoints;" ); ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData(); int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); Map map = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { map.put(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1).toLowerCase(), resultSet.getObject(i + 1)); } System.out.println(map); } } catch (Exception exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } x++; } } }At this point, you can monitor the two instances and see that the number of connections is almost the same for both. For more information about how to view instance monitoring information, see View monitoring metrics.
-
Monitoring metrics for instance hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx04.
-
Monitoring metrics for instance hgpostcn-cn-wxxxxxxxx05.
-