To enhance the security of the data link between your client application and Hologres, you can enable Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption in transit. SSL establishes an encrypted connection between a Hologres instance and a client using digital certificates and encryption algorithms, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS). This protects the confidentiality and integrity of your data during transmission.
Scenarios
SSL encryption in transit is suitable for the following scenarios:
-
Remote database access: When a client needs to access a database from a remote location, SSL encryption in transit can improve the security of data during transmission.
-
Meeting security and compliance requirements: Many industry standards and regulations require the use of encryption for data in transit. Using SSL encryption helps your organization meet these security and compliance requirements.
SSL provides transport-layer encryption for network connections. This enhances the security and integrity of communication data but also increases network connection response time.
Prerequisites
-
A Hologres instance is created. For more information, see Purchase a Hologres instance.
-
The PSQL client or Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is downloaded and installed. For more information, see PSQL client or JDBC.
Precautions
-
Hologres V1.1 and later support encryption in transit. V1.2 and later support TLS. V2.1 and later support encryption in transit, encryption in transit that uses CA certificates, and self-service enablement in the management console.
NoteIf your instance is earlier than V1.1, submit your feedback using Common upgrade preparation failure errors or by joining the Hologres DingTalk group. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
-
Enabling or disabling SSL encryption in transit requires an instance restart. Proceed with caution. SSL encryption in transit is disabled by default.
-
After you enable SSL encryption in transit for Hologres, clients are allowed to connect to Hologres using SSL. When a client connects to Hologres, you can choose whether to use an encrypted connection, but you must specify your choice explicitly.
-
After you disable SSL encryption in transit for Hologres, only non-SSL connections are supported.
-
-
Hologres supports the following modes for SSL encryption in transit:
SSL mode
Minimum supported version
Require: Encrypts only the data link.
V1.1
Verify-CA: Encrypts the data link and uses a CA certificate to authenticate the Hologres server.
V2.1
Verify-Full: Encrypts the data link, uses a CA certificate to authenticate the Hologres server, and compares the CN or DNS in the certificate with the Hologres endpoint configured for the connection.
V2.1
-
The SSL certificate is valid for one year. You must manually renew the certificate before it expires. Otherwise, you cannot use SSL encryption to connect to the instance after the certificate expires.
-
Enabling SSL encryption in transit increases CPU utilization and read/write latency.
-
After you enable SSL encryption in transit, existing connections must be disconnected and reconnected for the encryption to take effect.
-
Enabling or disabling SSL encryption in transit and renewing the SSL certificate will restart your Hologres instance. The process takes about 3 minutes. Perform these operations during off-peak hours.
Step 1: Enable encryption in transit for the Hologres instance
-
Log on to the Hologres management console and select a region in the upper-left corner.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, click Instances, and then click the ID of the target instance.
-
On the instance product page, click Data Security.
-
On the SSL tab, turn on the SSL Encryption switch.
-
In the Enable SSL Encryption dialog box, click Enable SSL encryption.
Step 2: Download the CA certificate
Hologres provides an instance CA certificate for you to download. When you remotely connect to a Hologres instance from a client, you can use the instance CA certificate to verify the authenticity of the instance.
-
Log on to the Hologres management console and select a region in the upper-left corner.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, click Instances, and then click the ID of the target instance.
-
On the instance product page, click Data Security.
-
On the SSL tab, click Download Certificate.
Step 3: Connect to Hologres
You can connect to Hologres using the PSQL client or JDBC. During the connection procedure, you can configure parameters to select whether to enable SSL encryption in transit.
Use the PSQL command line to connect to Hologres
-
Connection statement.
PG_USER=<AccessKey ID> PG_PASSWORD=<AccessKey Secret> PG_SSLMODE=<SSL Mode> PG_SSLROOTCERT=<certificate folder> PGSSLMODE=$PG_SSLMODE PGSSLROOTCERT=$PG_SSLROOTCERT PGUSER=$PG_USER PGPASSWORD=$PG_PASSWORD psql -p <Port> -h <Endpoint> -d <Database> -
Parameter description.
Parameter
Description
AccessKey ID
The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account.
Go to AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey ID.
Use environment variables for the username and password to reduce the risk of credential leaks.
AccessKey Secret
The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account.
Go to AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey secret.
Use environment variables for the username and password to reduce the risk of credential leaks.
SSL Mode
The encryption in transit mode for connecting to Hologres using PSQL. Valid values:
-
require: Uses encryption in transit. Only the data link is encrypted.
-
verify-ca: Encrypts the data link and authenticates the Hologres instance.
-
verify-full: Encrypts the data link, authenticates the Hologres instance, and compares the CN or DNS in the certificate with the database endpoint configured for the connection.
-
disable: Does not use encryption in transit.
certificate folder
The storage path of the CA certificate.
This parameter is required if the
SSL Modeparameter is set to verify-ca or verify-full.Port
The public port of the Hologres instance.
Example:
80.Endpoint
The public endpoint of the Hologres instance.
Example:
xxx-cn-hangzhou.hologres.aliyuncs.com.Database
The name of the Hologres database.
After you create a Hologres instance, the system automatically creates the postgres database.
You can use the postgres database to connect to Hologres. However, this database is allocated few resources. Create a new database for your business development. For more information, see Create a database.
Example:
mydb. -
-
Connection validation.
If you set PGSSLMODE to
require, the following prompt appears when you connect to Hologres. This indicates that an SSL-encrypted connection is used.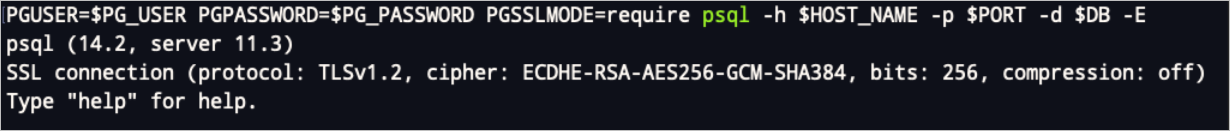
Use JDBC to connect to Hologres
When you use JDBC to connect to Hologres, you can use the ssl and sslmode connection configuration parameters to control whether to use SSL encryption in transit. The results in Hologres vary based on the values of these parameters, as shown in the following table.
|
Is encryption in transit enabled for the Hologres instance? |
ssl configuration |
sslmode configuration |
Result |
|
Yes |
true |
|
You can connect to the server and perform operations. Encryption in transit is used during data transmission. |
|
Yes |
false |
|
You can connect to the server and perform operations. Encryption in transit is not used during data transmission. |
|
No |
true |
|
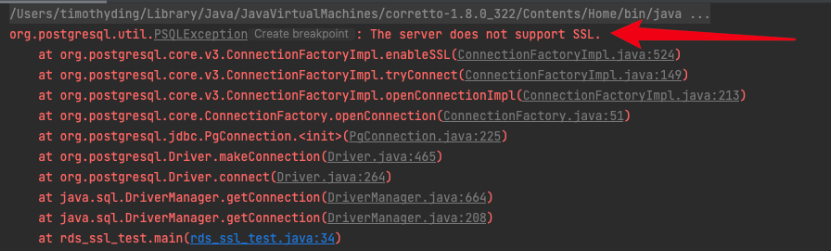
An error is reported. The error message is as follows:
|
|
No |
false |
|
You can connect to the server and perform operations. Encryption in transit is not used during data transmission. |
The following code provides an example.
// Set the endpoint of the Hologres instance.
String hostname = "hgxxxxxxx-cn-hangzhou-vpc.hologres.aliyuncs.com:80";
// Set the port of the Hologres instance.
String port = "80";
// Set the name of the database to connect to.
String dbname = "postgres";
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://" + hostname + ":" + port + "/" + dbname+"?binaryTransfer=true";
Properties properties = new Properties();
// Set the username for the database connection. Use an environment variable to reduce the risk of credential leaks.
properties.setProperty("user", "accessid");
// Set the password for the database connection. Use an environment variable to reduce the risk of credential leaks.
properties.setProperty("password", "accesskey");
// Configure access over SSL.
properties.setProperty("ssl", "true");
// Set the name of the public key of the certificate authority.
properties.setProperty("sslrootcert", path + "/" + "hologres_certificate.crt");
// Configure the SSL mode. Valid values are require, verify-ca, and verify-full.
properties.setProperty("sslmode", "verify-full");
try {
Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, properties);
// In this example, assume that a table named example exists in the postgres database. The following code queries data from the example table.
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from " +
"example");
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
Map map = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
map.put(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1).toLowerCase(), resultSet.getObject(i + 1));
}
System.out.println(map);
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}