The ALTER TABLE statement modifies a table. Changes to a parent table of a partitioned table are automatically applied to its child tables. This topic describes how to use the ALTER TABLE statement.
Limits
Hologres supports the following table modifications:
-
Rename tables, add columns, and modify the time to live (TTL) of table data.
-
Modify the default value of a field and the dictionary_encoding_columns and bitmap_columns properties.
Notes
Modifying table properties such as dictionary_encoding_columns, bitmap_columns, and time_to_live_in_seconds can trigger a background asynchronous compaction. This process consumes CPU resources. The storage usage of the instance might increase before it decreases.
Modify data types
Starting from Hologres V3.0, you can modify the data types of columns in internal tables.
-
Limits
-
You can modify the column types of non-partitioned tables and parent tables of partitioned tables. You cannot modify the column types of child tables.
-
You cannot modify the data type of a partition key column in a parent table.
-
The COLLATE and USING clauses are not supported.
-
Only the following data type conversions are supported:
Source data type
Target type
Notes
VARCHAR(N)
VARCHAR(M)
M must be greater than N.
VARCHAR(N)
TEXT
None
CHAR(N)
CHAR(M)
M must be greater than N.
CHAR(N)
VARCHAR(M)
M must be greater than or equal to N.
CHAR(N)
TEXT
None
JSON
TEXT
None
VARCHAR(N)[]
VARCHAR(M)[]
M must be greater than N.
VARCHAR(N)[]
TEXT[]
None
-
-
Syntax
ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> ALTER [ COLUMN ] <column_name> TYPE <data_type>; -
Example
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS t; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t ( a varchar(5) ); INSERT INTO t VALUES ('holo'), ('gres'); ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS t ALTER COLUMN a TYPE text;
Rename
You can use the ALTER TABLE statement to rename a table. The system returns an error if the target table does not exist or if the new table name is already in use.
You cannot rename a table across schemas.
-
Syntax
-- Rename an internal table ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> RENAME TO <new_table_name>; -- Rename a foreign table ALTER FOREIGN TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<foreign_table_name> RENAME TO <new_foreign_table_name>; -
Example
-- Rename the holo_test table to holo_test_1 ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS public.holo_test RENAME TO holo_test_1 ; -- Rename the foreign_holo_test foreign table to foreign_holo_test_1 ALTER FOREIGN TABLE IF EXISTS public.foreign_holo_test RENAME TO foreign_holo_test_1;
Add a column
You can use the ALTER TABLE statement to add a column to a table. A new column can only be added after the last existing column.
-
Syntax
-- Add a column ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> ADD COLUMN <new_column> <data_type>; -- Add multiple columns ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> ADD COLUMN <new_column_1> <data_type>, ADD COLUMN <new_column_2> <data_type>; -
Example
-- Add the id column to the holo_test table ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS public.holo_test ADD COLUMN id int;
Delete a column (Beta)
Starting from Hologres V2.0, you can delete columns. The syntax is as follows.
-
Limits
-
This feature is available only in Hologres V2.0 and later. If your instance is earlier than V2.0, see Common errors when preparing for an upgrade or join the Hologres DingTalk group for feedback. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
-
If you use a partitioned table, you can only delete columns from the parent table, not directly from a child table. When a column is deleted from a parent table, it is automatically deleted from its child tables. This operation has high overhead. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
-
Only the table owner can delete columns. If your database uses the simple permission model, you must have the permissions of the developer user group.
-
You cannot delete columns that are set as a Primary Key, Distribution Key, Clustering Key, or Event_time_column.
-
You cannot delete columns from foreign tables.
-
When you delete a JSONB-related column, its associated JSONB indexes are also deleted.
-
When you delete a proxima_vector column, you must specify the
cascadeparameter. -
When you delete a Serial column, if a sequence was created based on this column, the sequence is also deleted.
-
If a materialized view is created for a table, you cannot delete the source table or any columns in the source table that are referenced by the materialized view.
-
-
Syntax
ImportantYou cannot delete columns in Hologres versions earlier than V2.0.
set hg_experimental_enable_drop_column = on; --Enable this feature using this GUC parameter. ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS <table_name> DROP COLUMN [ IF EXISTS ] <column> [ RESTRICT | CASCADE ] -
Example
-- Create a table begin; CREATE TABLE tbl ( "id" bigint NOT NULL, "name" text NOT NULL, "age" bigint, "class" text NOT NULL, "reg_timestamp" timestamptz NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id,age) ); call set_table_property('tbl', 'orientation', 'column'); call set_table_property('tbl', 'distribution_key', 'id'); call set_table_property('tbl', 'clustering_key', 'age'); call set_table_property('tbl', 'event_time_column', 'reg_timestamp'); call set_table_property('tbl', 'bitmap_columns', 'name,class'); call set_table_property('tbl', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', 'class:auto'); commit; -- Delete a specified column set hg_experimental_enable_drop_column = on;--This feature is in beta. You must enable it using this GUC parameter. ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS tbl DROP COLUMN name;Query the table:
SELECT*FROMtbl; -- The following result is returned: id age class reg_timestamp ----+-----+---------+--------------
Rename a column
Starting from Hologres V1.1, you can rename columns. The syntax is as follows.
-
If your instance is earlier than V1.1, see Common errors when preparing for an upgrade or join the Hologres DingTalk group for feedback. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
-
If you use a partitioned table, you can only rename columns in the parent table, not in a specific child table. The data structures of a parent table and its child tables must be consistent. When you rename a column in a parent table, the change is automatically applied to all child tables.
-
You cannot rename columns in multiple tables at the same time.
-
Only the table owner can rename columns. If your database uses the simple permission model, you must have the permissions of the developer user group.
-
Syntax
ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> RENAME COLUMN <old_column_name> TO <new_column_name>; -
Example
-- Rename the id column of the holo_test table to name ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS public.holo_test RENAME COLUMN id TO name;
Modify a default value
You can use the ALTER TABLE statement to modify the default value of a column. You can set the default value to a constant or a constant expression. The new default value applies only to data that is written or updated after the change. It does not affect existing data in the table. This feature is available only in Hologres V0.9.23 and later. The following section describes how to modify a default value.
-
Syntax
-- Modify the default value of a table field ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> ALTER COLUMN <column> SET DEFAULT <expression>; -- Delete the default value of a table field ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> ALTER COLUMN <column> DROP DEFAULT; -
Example
-- Set the default value of the id column in the holo_test table to 0 ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS holo_test ALTER COLUMN id SET DEFAULT 0; -- Delete the default value of the id column in the holo_test table ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS holo_test ALTER COLUMN id DROP DEFAULT;
Modify table properties
In Hologres, you can execute statements to modify parameters and change table properties. The following section describes how to modify table properties.
-
Modify the dictionary_encoding_columns property. Changing the dictionary encoding setting causes data files to be re-encoded. This process consumes CPU and memory resources for a period of time. We recommend that you perform this change during off-peak hours.
-
Syntax
-- Modify dictionary_encoding_columns (available from V2.1) ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> SET (dictionary_encoding_columns = '[columnName{:[on|off|auto]}[,...]]'); --Only full modification is supported. -- Modify dictionary_encoding_columns (all versions) --Full modification CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('[<schema_name>.]<table_name>', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', '[columnName{:[on|off|auto]}[,...]]'); --Incremental modification. Only the specified fields in the call are modified. Other fields remain unchanged. CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('[<schema_name>.]<table_name>', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', '[columnName{:[on|off|auto]}[,...]]');ImportantStarting from Hologres V2.0, the UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY syntax is optimized. When you run the following statement, the
dictionary_encoding_columnsproperty of the table remains unchanged. In versions earlier than Hologres V2.0, thedictionary_encoding_columnsproperty of the table is cleared.CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('<table_name>','dictionary_encoding_columns',''); -
Parameter description
Parameter
Description
table_name
The table name must be case-sensitive and can include the schema information.
on
Enables dictionary_encoding_columns for the current field.
off
Disables dictionary_encoding_columns for the current field.
auto
Automatic. If you set this parameter to auto, Hologres automatically determines whether to enable dictionary_encoding_columns based on the repetition rate of values in the column. A higher repetition rate provides greater benefits from dictionary encoding. In Hologres V0.8 and earlier, dictionary_encoding_columns is enabled by default for all text columns. In Hologres V0.9 and later, Hologres automatically determines whether to create a dictionary encoding based on data features.
-
Examples
-
Explicitly create a dictionary for column a, automatically determine whether to create a dictionary for column b, and do not create dictionaries for columns c or d.
CREATE TABLE dwd.holo_test ( a text NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL, c text NOT NULL, d text ); CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('dwd.holo_test','dictionary_encoding_columns','a:on,b:auto'); -
Explicitly disable the dictionary for column a. The system automatically adds dictionary indexes to columns b, c, and d.
CREATE TABLE dwd.holo_test ( a text NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL, c text NOT NULL, d text ); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('dwd.holo_test','dictionary_encoding_columns','a:off');
-
-
-
Modify the bitmap_columns property
Starting from Hologres V0.9, you can modify the bitmap_columns property by executing the following statements. You no longer need to recreate the table to modify this property.
-
Syntax
-- Modify bitmap_columns (available from V2.1) ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> SET (bitmap_columns = '[columnName{:[on|off]}[,...]]'); -- Modify bitmap_columns (all versions) --Full modification CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('[<schema_name>.]<table_name>', 'bitmap_columns', '[columnName{:[on|off]}[,...]]'); --Incremental modification. Only the specified fields in the call are modified. Other fields remain unchanged. CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('[<schema_name>.]<table_name>', 'bitmap_columns', '[columnName{:[on|off]}[,...]]');ImportantStarting from Hologres V2.0, the UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY syntax is optimized. When you run the following statement, the
bitmap_columnsproperty of the table remains unchanged. In versions earlier than Hologres V2.0, thebitmap_columnsproperty of the table is cleared.CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('<table_name>','bitmap_columns',''); -
Parameter description
Parameter
Description
table_name
The table name must be case-sensitive and can include the schema information.
on
Enables bitmap_columns for the current field.
off
Disables bitmap_columns for the current field.
-
Examples
-
Enable the bitmap index for column a, and disable it for columns b, c, and d.
CREATE TABLE dwd.holo_test ( a text NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL, c text NOT NULL, d text ); CALL UPDATE_TABLE_PROPERTY('dwd.holo_test','bitmap_columns','a:on'); -
Disable the bitmap index for column b. The system automatically creates bitmap indexes for columns a, c, and d.
CREATE TABLE dwd.holo_test_1 ( a text NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL, c text NOT NULL, d text ); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('dwd.holo_test_1','bitmap_columns','b:off');
-
-
-
Modify the TTL of table data
-
Syntax
call set_table_property('[<schema_name>.]<table_name>', 'time_to_live_in_seconds', '<non_negative_literal>'); -
Parameter description
Parameter
Description
time_to_live_in_seconds
Abbreviated as TTL. The time to live for table data, in seconds. The value must be a positive integer.
NoteThe TTL starts when data is written to Hologres. After the specified period, the data is deleted. The deletion is not precise to the second.
-
Example
call set_table_property('dwd.holo_test', 'time_to_live_in_seconds', '600');
-
Modify the schema of a table
Starting from Hologres V1.3, you can modify the schema of a table. For example, you can move a table from schema1 to schema2 without recreating the table and importing data. This lets you quickly switch the table path.
-
Syntax
ALTER TABLE [IF EXISTS] [<schema_name>.]<table_name> SET SCHEMA <new_schema>;schema_name is the name of the schema where the table resides. table_name is the name of the table to be modified. new_schema is the name of the new schema to which the table is moved.
-
Example
Move the table named tb1 from the public schema to the testschema schema.
ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS public.tbl SET SCHEMA testschema;
Modify a table using the HoloWeb visual editor
HoloWeb provides a visual editor for tables. You can modify table fields and some table properties without writing SQL commands. The steps are as follows.
-
Go to the HoloWeb page. For more information, see Connect to HoloWeb and run a query.
-
In the top menu bar of the HoloWeb page, click Metadata Management.
-
In the Logged-in Instances list on the left side of the Metadata Management page, double-click the target table that you want to modify.
-
On the table details page, you can visually modify the table fields and some table properties.
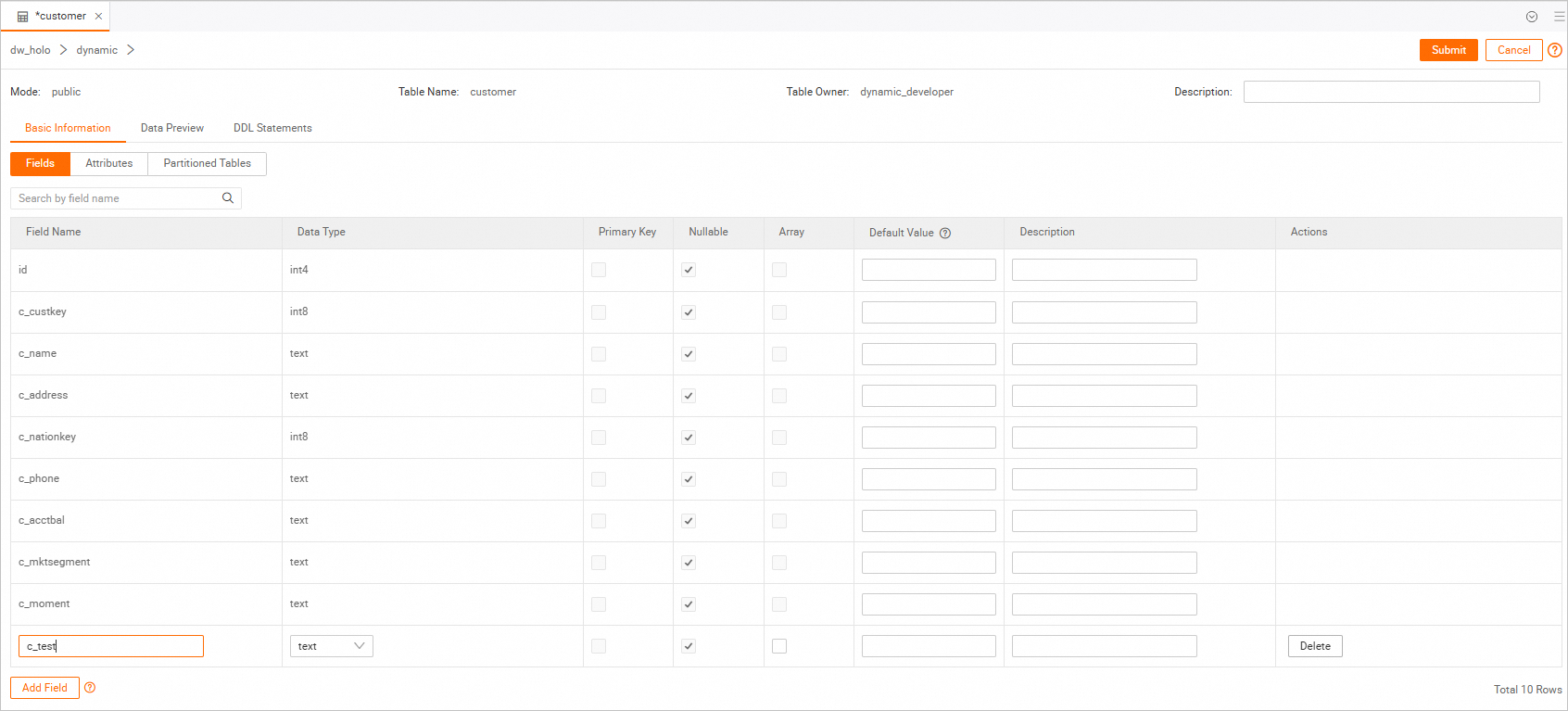
-
In the upper-right corner, click Submit to complete the modification.