To allow IPv6 clients to access IPv4 services, enable the IPv6 translation service by setting the IP Protocol for your accelerated IP address to IPv6 in Global Accelerator (GA).
Limitations
Only standard GA instances support the IPv6 translation service.
For a list of acceleration regions that support IPv6 client access, see Acceleration areas.
Use cases
Some enterprises have existing IT systems deployed in on-premises data centers that use a pure IPv4 network. As business grows, these enterprises need to provide services to IPv6 clients. However, upgrading existing IT systems to support IPv6 is a complex and time-consuming engineering project, making it a major challenge for many companies. GA provides an IPv6 translation service that lets you quickly implement IPv6-to-IPv4 conversion without modifying your existing IT systems. GA converts access requests from an enterprise's IPv6 clients and sends them directly to the backend IPv4 servers for rapid service access. This solution also lets enterprises with IT systems deployed on the cloud quickly support IPv6 clients.
A company is headquartered in US (Silicon Valley), and has a self-managed server running an IPv4 web service. The company's office in China (Hong Kong) only uses IPv6 clients. Due to business expansion, the company requires that IPv6 clients in the Hong Kong office can access the IPv4 web service in Silicon Valley with reduced latency, jitter, and packet loss caused by unstable cross-border public networks.

Use GA to handle access requests from IPv6 clients in Hong Kong (China) that are accessing servers in Silicon Valley. Traffic from the clients enters the Alibaba Cloud acceleration network through an accelerated IP address via the nearest access point in Hong Kong (China). The service then converts the IPv6 network requests to IPv4 requests and uses smart routing to deliver the requests to the endpoint.
In this example, clients and servers are located in different regions. You can also use Global Accelerator to convert IPv6 requests from clients that access services deployed in the same region.
Step 1: Configure basic information about an instance
Log on to the GA console.
On the Instances page, click Create Standard Pay-as-you-go Instance.
In the Basic Instance Configuration step, configure the parameters based on the following table and click Next.
Parameter
Description
GA Instance Name
Enter a name for the GA instance.
Instance Billing Method
Pay-As-You-Go is selected by default.
You are charged instance fees, Capacity Unit (CU) fees, and data transfer fees for pay-as-you-go standard Global Accelerator instances.
For more information about instance fees and CU fees, see Billing of pay-as-you-go GA instances.
For more information about data transfer fees, see Pay-by-data-transfer.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the standard Global Accelerator instance belongs.
The resource group must be created by the current Alibaba Cloud account in Resource Management. For more information, see Create a resource group.
Step 2: Configure an acceleration area
By configuring an acceleration area for a Global Accelerator instance, you can specify the regions of your users and allocate bandwidth to accelerate their access to backend services.
In the Configure Acceleration Area step, configure an acceleration area and click Next.
Parameter | Description |
Acceleration Area | Select one or more regions from the drop-down list for access acceleration, and then click Add To List. In this topic, the China (Hong Kong) region is selected under the Asia Pacific area. Note If the acceleration area contains regions in the Chinese mainland and the service traffic uses HTTP or HTTPS, you must apply for an Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing for the service domain name. For more information, see Domain name management. |
Assign Bandwidth | |
Maximum Bandwidth | Specify the maximum bandwidth for the acceleration region. Each acceleration region supports a bandwidth range of 2 to 10,000 Mbit/s. The maximum bandwidth is used for bandwidth throttling. The data transfer fees are managed by CDT. In this example, the default value 200 Mbit/s is used. Important If you specify a small value for the maximum bandwidth, throttling may occur and packets may be dropped. Specify a maximum bandwidth based on your business requirements. |
IP Protocol | Select the IP version that is used to connect to Global Accelerator. In this topic, IPv6 is selected. |
ISP Line Type | Select an ISP line type for the Global Accelerator instance. In this topic, BGP (Multi-ISP) is selected. |
Step 3: Configure a listener
A listener listens for connection requests and distributes the requests to endpoints based on the port and the protocol that you specify. Each listener is associated with an endpoint group. You can associate an endpoint group with a listener by specifying the region to which you want to distribute network traffic. After you associate an endpoint group with a listener, network traffic is distributed to the optimal endpoint in the endpoint group.
In the Configure listeners step, configure a listener and click Next.
The following table describes only the parameters that are relevant to this topic. Use the default values for other parameters. For more information, see Add and manage smart routing listeners.
Parameter | Description |
Listener Name | Enter a name for the listener. |
Routing Type | Select a routing type. In this example, Intelligent Routing is selected. |
Protocol | Select a protocol for the listener. In this example, select HTTP. |
Port | Specify the listener port that is used to receive and forward requests to endpoints. The port number must be in the range of 1 to 65499. In this example, port 80 is used. |
Client Affinity | Specify whether to enable client affinity. If client affinity is enabled, requests from the same client are forwarded to the same endpoint when the client connects to a stateful application. In this example, Source IP is selected. |
Custom HTTP Headers | Select the HTTP headers that you want to add. In this example, the default settings are used. |
Step 4: Configure endpoint groups and endpoints
In the Configure an endpoint group step, configure an endpoint group, add endpoints to the endpoint group, and then click Next.
This topic describes only the key configuration items. For more information, see Add and manage endpoint groups for smart routing listeners.
Parameter
Description
Region
Select the region in which the endpoint group is deployed.
In this topic, US (Silicon Valley) is selected.
Endpoint Configuration
Client requests are routed to endpoints. To add an endpoint, configure the following parameters:
Backend Service Type: Select Custom Public IP Address.
Backend Service: Enter the public IP address of the IPv4 web service.
Weight: Enter the weight of the endpoint. Valid values: 0 to 255. Global Accelerator distributes network traffic to endpoints based on the configured weights. In this topic, the default value 255 is used.
WarningIf the weight of an endpoint is set to 0, Global Accelerator stops distributing traffic to that endpoint. Proceed with caution.
Preserve Client IP
By default, client IP address preservation is enabled. This feature lets you view client IP addresses on backend servers. HTTP listeners can retrieve client IP addresses from the X-Forwarded-For HTTP header. For more information, see Preserve client IP addresses.
Backend Service Protocol
Select the protocol that is used by backend servers.
The default configuration is HTTP.
Port Mapping
If the listener port is not the same port over which the endpoint provides services, you must set this parameter.
Listener Port: Enter the listener port.
Endpoint Port: Enter the port over which the endpoint provides services.
If the listener port and the port that is used by the endpoint to provide services are the same, you do not need to add a port mapping. Global Accelerator automatically forwards access requests to the listener port of the endpoint.
In this topic, no port mapping is required.
Traffic Distribution Ratio
Specify a traffic distribution ratio for the endpoint group.
The valid values are 0 to 100.
In this topic, the default value 100% is used.
Health Check
Specify whether to enable the health check feature.
After you enable this feature, you can use health checks to check the status of endpoints. For more information about health checks, see Enable and manage health checks.
This topic is disabled by default.
On the Configuration Review wizard page, confirm the information and click Submit.
NoteIt takes 3 to 5 minutes to create a GA instance.
Step 5: Configure DNS resolution
Configure DNS resolution to forward requests for the backend IPv4 service to GA for acceleration. You can choose one of the following methods:
Add a CNAME record that maps the accelerated domain name to the CNAME allocated by the Global Accelerator instance.
Add an AAAA record to point the accelerated domain name to the accelerated IPv6 address allocated by a Global Accelerator instance.
On the Public Zone page, find the target custom domain name, and in the Actions column, click Settings.
NoteIf your domain name is not registered with Alibaba Cloud, add the domain name to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console before you can configure its DNS settings.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add Record, configure the record, and then click OK.
Add a CNAME record
Parameter
Description
Record Type
Select CNAME.
A CNAME record is used to map a domain name to another domain name.
Hostname
Enter the prefix of the accelerated domain name.
If your accelerated domain name is
www.aliyun.com, the host record iswww.If your accelerated domain name is
aliyun.com, the host record is@.If your accelerated domain name is
*.aliyun.com, the host record is*.If your accelerated domain name is
mail.aliyun.com, the host record ismail.
Query Source
Keep the default setting.
TTL
Indicates the cache time of DNS records on DNS servers. The smaller the value, the faster the modified records take effect in various regions.
This topic uses the default value of 10 minutes.
Record Value
Enter the CNAME assigned by Global Accelerator.
You can view the CNAME assigned by the Global Accelerator instance on the Instances page.
Add an AAAA record
Parameter
Description
Record Type
Select AAAA.
The AAAA record is used to map the domain name to an IPv6 address.
Hostname
Enter the prefix of the accelerated domain name.
If your accelerated domain name is
www.aliyun.com, the host record iswww.If your accelerated domain name is
aliyun.com, the host record is@.If your accelerated domain name is
*.aliyun.com, the host record is*.If your accelerated domain name is
mail.aliyun.com, the host record ismail.
Query Source
Keep the default setting.
TTL
Indicates the cache time of DNS records on DNS servers. The smaller the value, the faster the modified records take effect globally.
This topic uses the default value of 10 minutes.
Record Value
Enter the accelerated IPv6 address that is allocated by Global Accelerator.
Step 6: Test network connectivity
In this example, a CNAME record is configured and the Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 operating system is used for testing. The command that is used to run the test may vary based on the operating system. For more information, refer to the user guide of the operating system.
Open the CLI of an IPv6 client in the acceleration region. In this example, the acceleration region is China (Hong Kong).
Run the following command to check whether the CNAME record takes effect:
ping -6 <accelerated domain name>If the result is the same as the accelerated IPv6 address assigned by the Global Accelerator instance, the CNAME record is in effect.
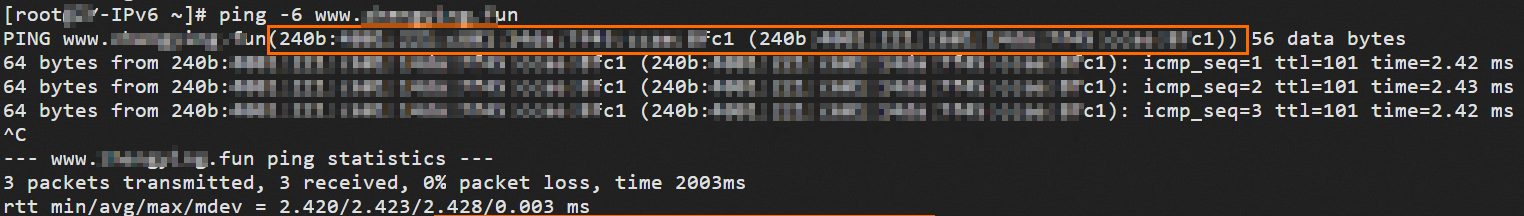
Run the following command to check whether the IPv6 client can access the IPv4 service as expected:
curl -6 -g http://[<The accelerated IP address allocated by GA>]The test result shows that the IPv6 client can access the IPv4 service in the US (Silicon Valley) region normally.
