Set the minimum number of instances for a function to a value greater than 0 to pre-allocate elastic resources. This helps prevent request latency caused by cold starts during peak hours. You can also configure policies to automatically scale the minimum number of instances based on a schedule or metric thresholds. This ensures high performance and improves instance utilization.
Setting the minimum number of instances to a value greater than 0 helps mitigate cold starts and provides improved service responses for latency-sensitive online businesses. You are charged for these instances regardless of their usage. When these instances process requests, they are billed at the rate of active elastic instances. When they are idle, they are billed at the rate of idle elastic instances. For more information about how active and idle elastic instances are billed, see Billing overview.
You can configure elastic policies for the minimum number of instances only for a function alias or the LATEST version.
Set the minimum number of instances
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click Create Function.
On the Create Function page, in the Elastic Configuration section, set the Minimum Number Of Instances parameter. Configure the other required parameters, and then click Create.
Configure elastic policies
On the details page of the target function, click the Elastic Configuration tab. In the Elastic Policies section, click Edit in the row of the target policy.
In the Edit Elastic Policy panel, configure a dynamic elastic policy for the minimum number of instances.
NoteIf you configure multiple auto scaling policies, the system calculates the Minimum Number Of Instances for each policy when it is triggered, and sets the current minimum number of instances to the highest Minimum Number Of Instances value among the policies that are currently in effect. For more information, see How is the current minimum number of instances calculated?.
While an elastic policy is active, the initial Minimum Number Of Instances setting is ignored. If no elastic policy is active, the current minimum number of instances reverts to the initial value that you configured for Minimum Number Of Instances.
Configure a Scheduled Scaling or Threshold-based Scaling policy
Scheduled scaling
A scheduled scaling policy is suitable for functions with clear periodic patterns or predictable traffic peaks. When the number of concurrent function invocations exceeds the minimum number of instances, the excess requests are automatically handled by on-demand elastic instances. For more information, see Scheduled scaling.

As shown in the figure, this example sets the Time Zone to Asia/Shanghai (UTC+8). The policy is long-term and scales out the minimum number of instances to 50 at 10:00 from Monday to Friday, and scales it in to 5 at 22:00.
Threshold-based scaling
The system periodically collects metrics such as Instance Concurrency Utilization, Memory Utilization, or resource utilization for GPU-accelerated instances. When the conditions are met, the Minimum Number Of Instances is scaled accordingly. For more information, see Threshold-based scaling.
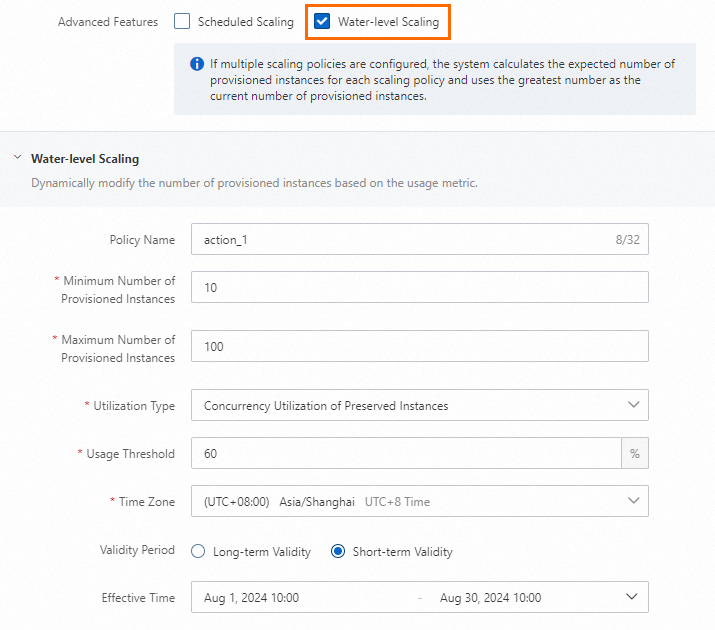
As shown in the figure, this example sets the Time Zone to Asia/Shanghai (UTC+8). The policy is active from 00:00 on July 15, 2025, to 00:00 on July 31, 2025, and tracks the Instance Concurrency Utilization metric. When the utilization exceeds the tracking value of 60%, the system scales out up to a maximum of 100 instances. When the utilization falls below 60%, the system scales in to a minimum of 10 instances.
For CPU functions, threshold-based scaling for the minimum number of instances monitors the Instance Concurrency Utilization and Memory Utilization metrics. For GPU functions, the policy supports monitoring Instance Concurrency Utilization and GPU-related resource utilization metrics, as shown in the following figures.
CPU functions
GPU functions


Configure periodic elastic scaling using a CRON Expression
If your business has clear periodic patterns, you can also use a CRON expression to periodically scale the minimum number of instances. As shown in the following figure, the Time Zone is set to Asia/Shanghai (UTC+8). The minimum number of instances is scaled out to 10 at 10:00 every Monday and scaled in to 1 at 22:00 every Friday.

Modify or delete an elastic policy for the minimum number of instances
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the Elastic Policies page, find the target policy. In the Actions column, click Edit or Delete to modify or delete the policy.
Deleting an elastic policy for the minimum number of instances of an alias releases all pre-allocated instances for that alias. The function then automatically switches to on-demand scaling, which may involve a cold start. For CPU-based services, the average cold start time is typically hundreds of milliseconds, depending on the application's startup speed. For GPU-based services, the average cold start time can be several minutes, depending on the model size and loading speed.
References
To limit the number of instances for a specific function, you can configure function quotas. If the total number of running instances for the function exceeds the configured limit, Function Compute returns a throttling error.