In Function Compute, states are not shared between execution environment instances. You can use a database to persist structured data to enable state sharing. By accessing a cloud database from Function Compute, you can perform operations such as data queries and insertions. This topic uses a Python function as an example to describe how to access ApsaraDB for MongoDB from the same VPC or from different VPCs and regions.
Prerequisites
Create an ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. This topic uses a sharded cluster instance as an example. For more information about ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance types, see Create a standalone instance, Create a replica set instance, and Create a sharded cluster instance.
The sample code in `index.py` in this topic inserts a document into the `fc_col` collection of the `test-db` database. You can change the database and collection names as needed. For more information, see Create a database and a collection and write data.
Procedure
Step 1: Configure the database whitelist
Scenario 1: Access an ApsaraDB for MongoDB database in the same VPC
If you choose to access a database in the same VPC, make sure that the database instance and the function are in the same region. We recommend that you create the database instance in a zone that Function Compute supports. For more information, see Zones that Function Compute supports. If your database instance is not in a zone that is supported by Function Compute, you can create a vSwitch in your VPC in the same zone as Function Compute and use this vSwitch ID in the VPC configurations of the function. vSwitches in the same VPC can communicate with each other over the private network. Therefore, Function Compute can use the vSwitch to access resources in VPCs that reside in other zones. For more information, see What do I do if the vSwitch is in unsupported zone error occurs?.
Log on to the Function Compute console. Then, create a Python web function, enable VPC access for the function, and configure the target VPC resources.
NoteMake sure the VPC configured for the function is the same as the VPC to which the database instance is attached.
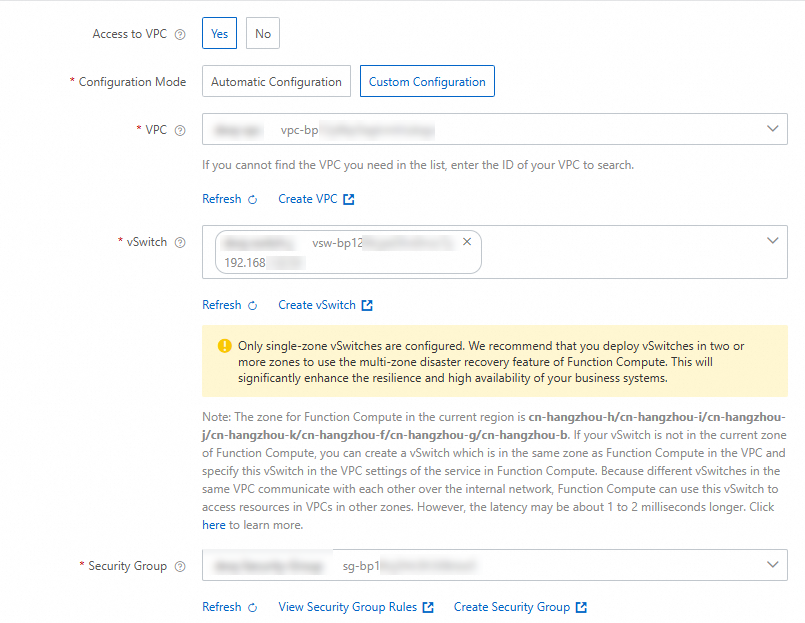
On the function details page, navigate to the tab. On the Network tab, obtain the vSwitch CIDR block from the function configuration.
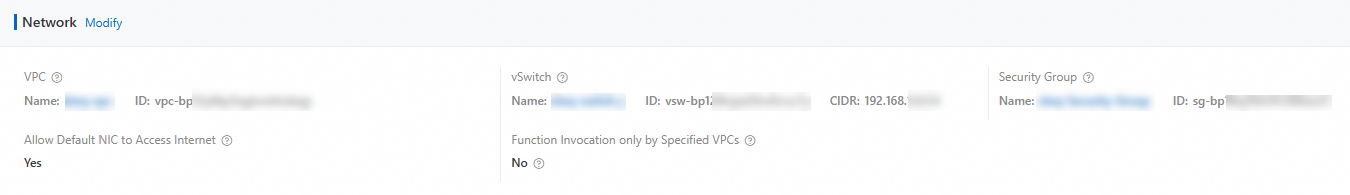
Add the vSwitch CIDR block obtained in the previous step to the database access whitelist.
ImportantUse an IP address whitelist to grant the function access to the database. Do not use security groups. Otherwise, the function may occasionally fail to connect to the database, which can affect your business.
Log on to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Sharded Cluster Instances and click the ID of the target instance.
On the instance details page, in the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Click Manually Modify to the right of the default group. In the Manually Modify panel, add the vSwitch IPv4 CIDR block to the whitelist, and then click OK.
After the configuration is complete, the function can access the ApsaraDB for MongoDB database using the private endpoint of the database.
Scenario 2: Access an ApsaraDB for MongoDB database across VPCs or regions
Different VPCs and regions are completely logically isolated from each other. In general, you cannot access databases across VPCs and regions. If you need to access a database across VPCs or regions, you can configure a static public IP address for the function. In this case, the system creates a public NAT gateway in the VPC to which the function is attached. You can use the public gateway to access the database through the public IP address.
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Functions, select a region, and then follow the prompts to create a function.
On the function details page, navigate to the tab. On the Network tab, configure a static public IP address for the function, and then click Deploy.
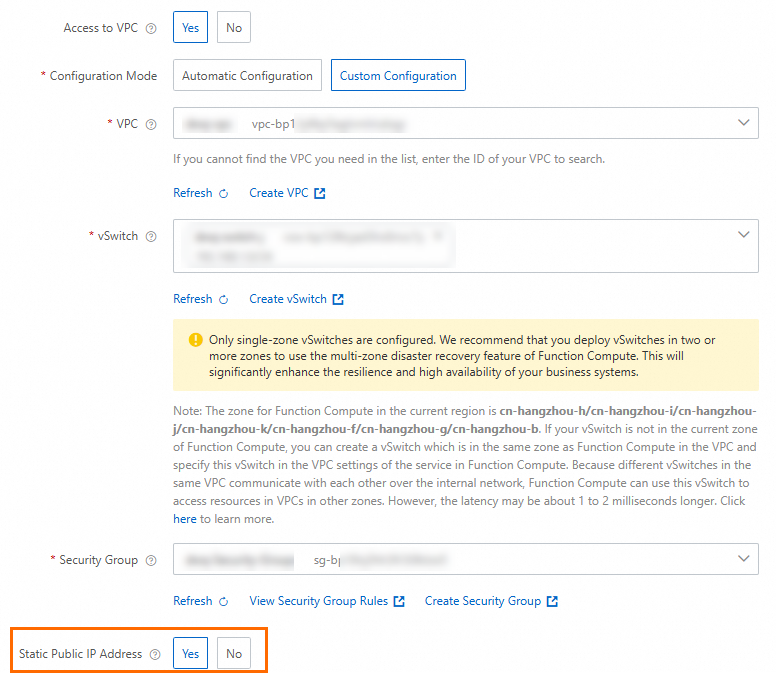
In the Static Public IP Configuration dialog box, select the checkbox and click OK. After the configuration is complete, set Allow functions to access the Internet through the default network interface card to No to activate the static public IP address.
On the function details page, navigate to the tab. On the Network tab, obtain the static public IP address configured for the function.
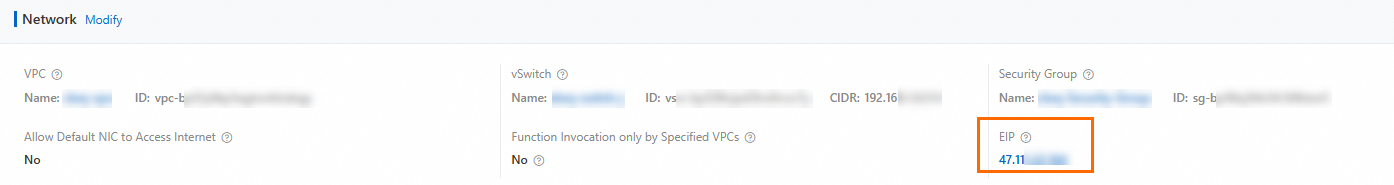
Add the static public IP address obtained in the previous step to the database access whitelist.
ImportantUse an IP address whitelist to grant the function access to the database. Do not use security groups. Otherwise, the function may occasionally fail to connect to the database, which can affect your business.
Log on to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Sharded Cluster Instances and click the ID of the target instance.
On the instance details page, in the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Click Manual Modification to the right of the default group. In the Manual Modification panel, add the vSwitch IPv4 CIDR block to the whitelist and click OK.
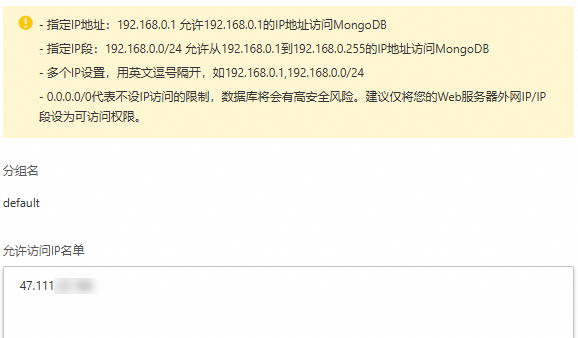
After the configuration is complete, the function can access the ApsaraDB for MongoDB database using the public endpoint of the database.
Step 2: Access ApsaraDB for MongoDB from the function
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the function list, find the target function. On the function details page, click the Code tab. In the code editor, add the following sample code.
from flask import Flask import os from pymongo import MongoClient app = Flask(__name__) # Use a global variable to store the MongoDB singleton connection. _mongo_client = None # Create a database connection (singleton pattern). def getConnection(): global _mongo_client try: # If the connection already exists and is not disconnected, return it directly. if _mongo_client is not None: try: # Test if the connection is valid. _mongo_client.admin.command('ping') # Use the ping command of the admin database to test the connection status. return _mongo_client except Exception: # If the connection is disconnected, reset it. _mongo_client = None # If the connection does not exist or is disconnected, create a new one. url = os.environ['MONGO_URL'] _mongo_client = MongoClient(url) return _mongo_client except Exception as e: print(f"ERROR: Failed to connect to MongoDB instance: {e}") raise @app.route('/', defaults={'path': ''}) @app.route('/<path:path>', methods=['GET', 'POST', 'PUT', 'DELETE']) def hello_world(path): dbName = os.environ['MONGO_DATABASE'] # Get the MongoDB connection. client = getConnection() # Operate on the collection. Change fc_col as needed. col = client[dbName]['fc_col'] col.insert_one(dict(DEMO="FC", MSG="Hello FunctionCompute For MongoDB")) doc = col.find_one(dict(DEMO="FC")) print('find documents:' + str(doc)) return str(doc) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=9000)On the Code tab, in the WebIDE interface, choose . In the terminal window, run the following command to install the `pymongo` library.
pip install -t . pymongoOn the function details page, navigate to the tab. Click Edit. In the Environment Variables panel, configure the following environment variables.
Environment Variable Name
Environment Variable Value
Description
MONGO_DATABASE
test-db
The name of the database created in the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.
NoteIf you use the root account, versions later than MongoDB 7.0.4 do not have write permissions on the default `admin` database. We recommend that you use a manually created database.
MONGO_URL
mongodb://root:password@s-bp132a4e334e****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717,s-bp1b486e9aa4****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717
The endpoint of the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.
If you chose to access the database within the same VPC, set this environment variable to the private endpoint of the database.
If you chose to access the database across VPCs or regions, set this environment variable to the public endpoint of the database.
Log on to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB console and click the target instance. In the navigation pane on the left of the instance details page, choose Database Connection. On the Database Connection page, obtain the private or public endpoint of the database.
On the function details page, navigate to the Code tab and click Test Function. After the function is executed, view the returned result. The following figure shows that a data record is successfully inserted into the ApsaraDB for MongoDB database.
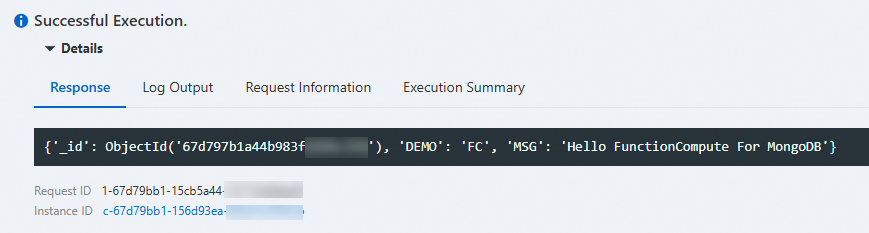
More information
For more sample code for accessing an ApsaraDB for MongoDB database, see Python code for accessing an ApsaraDB for MongoDB database from Function Compute.
If you cannot access the database, troubleshoot the issue based on the symptoms. For more information, see Common causes of database access failures.
Follow these steps to create a function and access an RDS MySQL database using the Serverless Devs command line interface.