This topic covers the structure, sample code, and FAQ of event handlers in a Custom Container runtime.
Background
For a Custom Container function Function Compute forwards the common request headers, request body, POST method, and the /invoke and /initialize paths to the HTTP server in the container. You can use function signatures, such as context and event, from runtimes supported by Function Compute, such as a Go runtime. You can also use the request headers and body as input parameters to define the service logic of a function. For more information, see Event handlers in a custom runtime.
Function invocation
If a Custom Container function uses an event handler, the HTTP server needs to implement logic only for the /invoke path and the POST method.
Path | Request | Expected response |
POST |
| Response body: the return value of the function handler, which includes the response code and response headers.
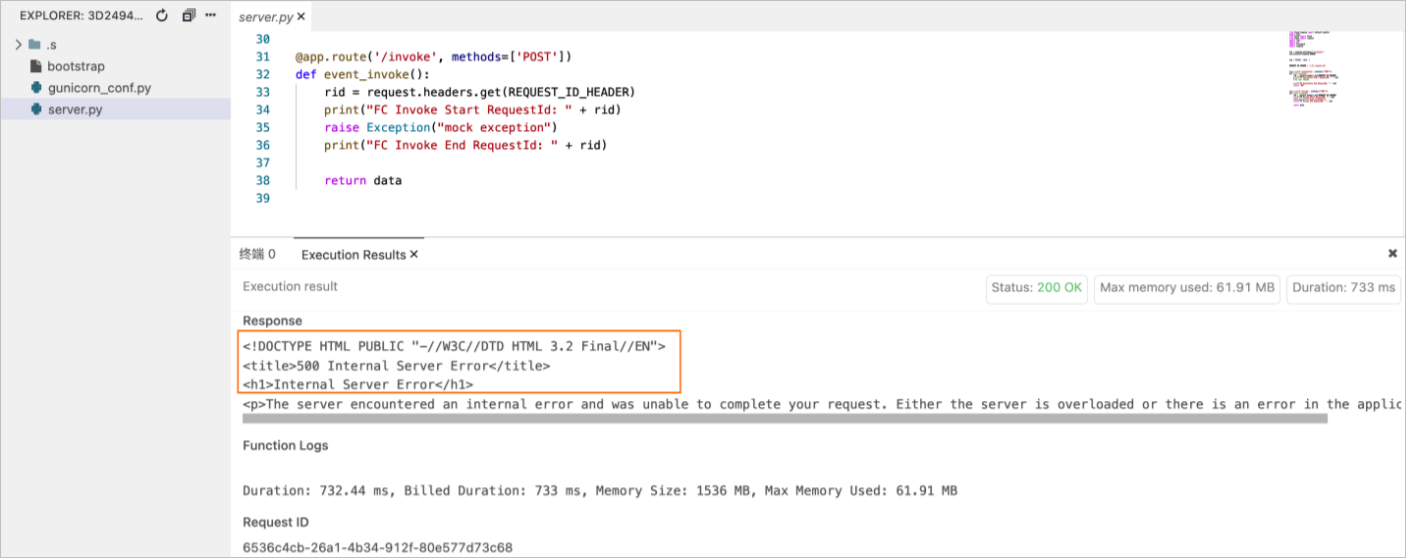
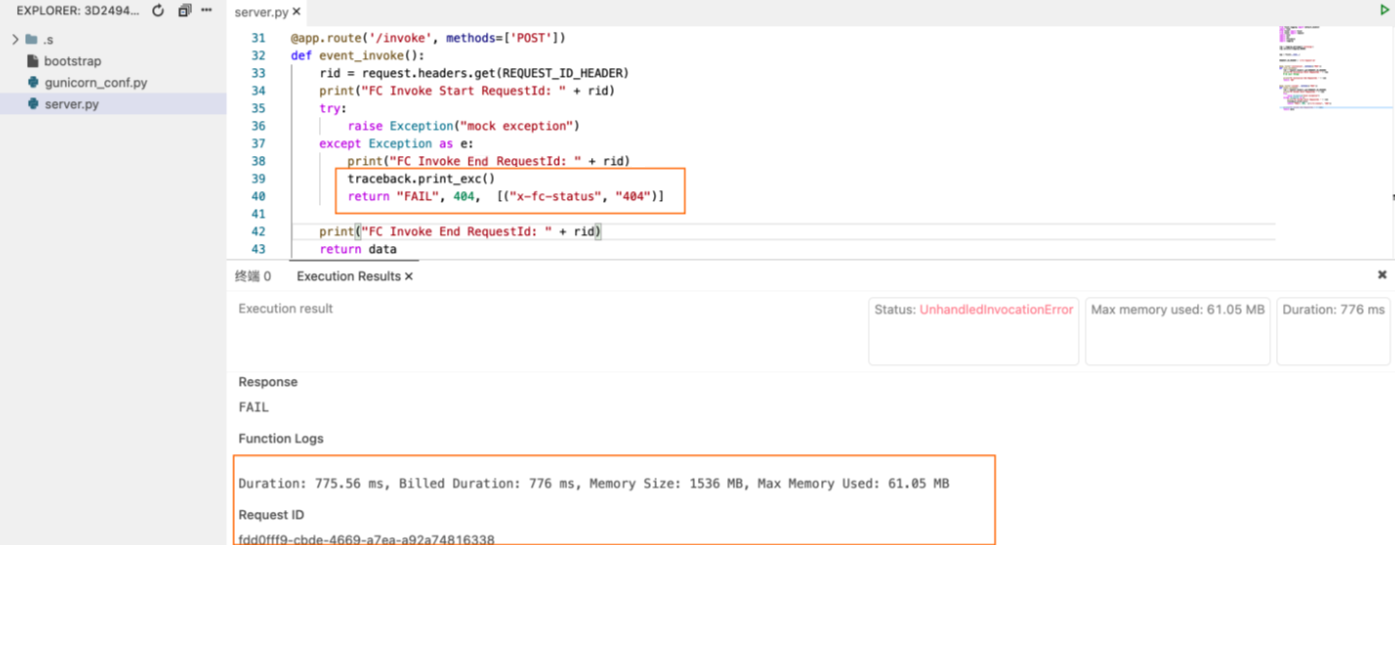
You can include the x-fc-status field in response headers to report to Function Compute whether the local function is successfully invoked.
Note We recommend that you specify the StatusCode and x-fc-status fields in the HTTP response. |
Sample code
In the following Node.js Express example, the POST method and /initialize path are called by Function Compute when a function instance is initialized. The POST method and /invoke path serve as handlers when Function Compute is called. The context and event parameters are obtained from req.headers and req.body, and the results of the invocation are then returned as an HTTP response.
'use strict';
const express = require('express');
// The constants.
const PORT = 9000;
const HOST = '0.0.0.0';
const app = express();
// Parse the JSON-formatted request body.
app.use(express.json({type:['application/json', 'application/octet-stream']}))
// The example of the Initializer hook. You must configure the initializer hook when you create the function.
app.post('/initialize', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.body)
res.send('Hello FunctionCompute, /initialize\n');
});
// Invoke the event function.
app.post('/invoke', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.body)
res.send('Hello FunctionCompute, event function\n');
});
var server = app.listen(PORT, HOST);
console.log(`Running on http://${HOST}:${PORT}`);
server.timeout = 0; // Never time out.
server.keepAliveTimeout = 0; // keepalive, never timeoutExamples for other programming languages
You can use Serverless Devs to migrate your applications to Function Compute with a few clicks. The following example shows how to use Serverless Devs to deploy and invoke a function in an efficient manner. You can modify the sample code based on your business requirements.