This topic describes how to use the MySQL connector.
Background information
The MySQL connector supports all databases that are compatible with the MySQL protocol, such as RDS MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, OceanBase (MySQL mode), and self-managed MySQL.
When you use the MySQL connector to read from OceanBase, ensure that OceanBase binary logging (binlog) is enabled and correctly configured. For more information, see Binary logging operations. This feature is in public preview. We recommend that you evaluate it thoroughly and use it with caution.
The following table describes the support for the MySQL connector.
Category | Details |
Supported type | Source table, dimension table, sink table, and data ingestion source |
Runtime mode | Streaming mode only |
Data format | Not applicable |
Specific monitoring metrics | |
API type | DataStream, SQL, and data ingestion YAML |
Support for updating or deleting sink table data | Yes |
Features
A MySQL Change Data Capture (CDC) source table first reads the full historical data of a database and then seamlessly switches to reading binary log (binlog) events. This process ensures exactly-once semantics, which means no data is missed or duplicated, even if failures occur. The MySQL CDC source table supports concurrent reading of full data and implements lock-free reading and resumable data transfer using an incremental snapshot algorithm. For more information, see About MySQL CDC source tables.
Unified batch and streaming processing: Reads both full and incremental data without the need to maintain separate pipelines.
Concurrent full data reading: Horizontally scales performance.
Seamless switch from full to incremental reading: Automatically scales in to save computing resources.
Resumable data transfer: Supports resumable data transfer during full data reading for enhanced stability.
Lock-free reading: Reads full data without affecting online business operations.
Backup log reading: Supports reading backup logs from RDS MySQL.
Parallel binlog parsing: Reduces read latency by parsing binlog files in parallel.
Prerequisites
Before you use a MySQL CDC source table, you must configure your MySQL database as described in Configure MySQL. The following configurations are required.
RDS MySQL
Perform a network probe with Realtime Compute for Apache Flink to ensure network connectivity.
Supported MySQL versions: 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0.x.
Enable binary logging (binlog). This is enabled by default.
Set the binlog format to ROW. This is the default format.
Set binlog_row_image to FULL. This is the default setting.
Disable Binary Log Transaction Compression. This feature was introduced in MySQL 8.0.20 and is disabled by default.
A MySQL user has been created with the SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, and REPLICATION CLIENT permissions.
Create a MySQL database and table. For more information, see Create a database and account for RDS MySQL. We recommend that you use a privileged account to create the MySQL database to avoid operational failures that are caused by insufficient permissions.
Configure an IP whitelist. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for RDS MySQL.
PolarDB for MySQL
Perform a network probe with Realtime Compute for Apache Flink to ensure network connectivity.
Supported MySQL versions: 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0.x.
Enable binary logging (binlog). This is disabled by default.
Set the binlog format to ROW. This is the default format.
Set binlog_row_image to FULL. This is the default setting.
Disable Binary Log Transaction Compression. This feature was introduced in MySQL 8.0.20 and is disabled by default.
You have created a MySQL user and granted the SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, and REPLICATION CLIENT permissions.
Create a MySQL database and table. For more information, see Create a database and account for PolarDB for MySQL. We recommend that you use a privileged account to create the MySQL database to avoid operational failures that are caused by insufficient permissions.
Configure an IP whitelist. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for PolarDB for MySQL.
Self-managed MySQL
Perform a network probe with Realtime Compute for Apache Flink to ensure network connectivity.
Supported MySQL versions: 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0.x.
Enable binary logging (binlog). This is disabled by default.
Set the binlog format to ROW. The default format is STATEMENT.
Set binlog_row_image to FULL. This is the default setting.
Disable Binary Log Transaction Compression. This feature was introduced in MySQL 8.0.20 and is disabled by default.
A MySQL user has been created and granted the SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, and REPLICATION CLIENT permissions.
Create a MySQL database and table. For more information, see Create a database and account for a self-managed MySQL instance. We recommend that you use a privileged account to create the MySQL database to avoid operational failures that are caused by insufficient permissions.
Configure an IP whitelist. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for a self-managed MySQL instance.
Limits
General limits
The MySQL CDC source table does not support defining watermarks.
In CREATE TABLE AS SELECT (CTAS) and CREATE DATABASE AS SELECT (CDAS) jobs, the MySQL CDC source table can synchronize partial schema changes. For more information about supported change types, see Schema evolution synchronization policies.
The MySQL CDC connector does not support Binary Log Transaction Compression. Therefore, when you use the MySQL CDC connector to consume incremental data, you must ensure that this feature is disabled. Otherwise, incremental data may fail to be retrieved.
RDS MySQL limits
We do not recommend reading data from a secondary database or a read-only replica for RDS MySQL. By default, the binlog retention period for these instances is short. If binlogs expire and are cleared, the job may fail to consume binlog data and then report an error.
RDS MySQL enables parallel synchronization between primary and secondary databases by default but does not guarantee transaction order consistency. This may cause some data to be missed during a primary/secondary switchover and checkpoint recovery. To resolve this issue, you can manually enable the slave_preserve_commit_order option in RDS MySQL.
PolarDB for MySQL limits
MySQL CDC source tables do not support reading from Multi-master Clusters of PolarDB for MySQL version 1.0.19 or earlier. For more information, see What is a Multi-master Cluster?. Binlogs that are generated by these clusters may contain duplicate table IDs. This can cause schema mapping errors in the CDC source table and lead to binlog parsing errors.
Open-source MySQL limits
By default, MySQL maintains transaction order during primary-replica binary logging replication. If a MySQL replica enables parallel replication (slave_parallel_workers > 1) but does not have slave_preserve_commit_order=ON, its transaction commit order may differ from that of the primary database. When Flink CDC recovers from a checkpoint, it may miss data because of this order inconsistency. We recommend that you set slave_preserve_commit_order = ON on the MySQL replica or set slave_parallel_workers = 1. Note that setting slave_parallel_workers to 1 may reduce replication performance.
Notes
Sink table
Do not declare an auto-increment primary key in the DDL statement. MySQL automatically populates this field when it writes data.
You must declare at least one non-primary key field. Otherwise, an error occurs.
NOT ENFORCED in the DDL statement indicates that Flink does not enforce validity checks on the primary key. You must ensure the correctness and integrity of the primary key. For more information, see Validity Check.
Dimension table
To use indexes for query acceleration, the field order in the JOIN clause must match the index definition order. This is known as the leftmost prefix rule. For example, if the index is on
(a, b, c), the JOIN condition should beON t.a = x AND t.b = y.The Flink-generated SQL may be rewritten by the optimizer, which prevents the index from being used during actual database queries. To verify whether an index is used, you can check the execution plan (EXPLAIN) or slow query log in MySQL to view the actual SELECT statement that is executed.
SQL
You can use the MySQL connector in SQL jobs as a source table, dimension table, or sink table.
Syntax
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mysqlcdc_source (
order_id INT,
order_date TIMESTAMP(0),
customer_name STRING,
price DECIMAL(10, 5),
product_id INT,
order_status BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY(order_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql',
'hostname' = '<yourHostname>',
'port' = '3306',
'username' = '<yourUsername>',
'password' = '<yourPassword>',
'database-name' = '<yourDatabaseName>',
'table-name' = '<yourTableName>'
);How the connector writes to a sink table: For each record that is received, the connector constructs and executes a single SQL statement. The exact statement depends on the table structure:
For a sink table without a primary key, the system constructs and executes the following SQL statement:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);For a result table with a primary key, the system executes the following SQL statement:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE column1 = VALUES(column1), column2 = VALUES(column2), ...;Note: If the physical table has a unique index constraint in addition to the primary key, inserting two records with different primary keys but identical values in the columns that are covered by the unique index causes a unique index conflict. This conflict triggers a data overwrite, which results in data loss in the output data.
If you define an auto-increment primary key in the MySQL database, do not declare the auto-increment field in the Flink DDL statement. The database automatically populates this field during data insertion. The connector supports writing and deleting data with an auto-increment field but does not support updates.
WITH parameters
General
Parameters
Description
Required
Data type
Default value
Remarks
connector
The type of the table.
Yes
STRING
None
When used as a source table, set this option to
mysql-cdcormysql. They are equivalent. When used as a dimension or sink table, set this option tomysql.hostname
The IP address or hostname of the MySQL database.
Yes
STRING
None
We recommend entering the VPC address.
NoteIf the MySQL database and Realtime Compute for Apache Flink are not in the same VPC, establish a cross-VPC network connection or use the Internet for access. For more information, see Manage and operate workspaces and How can a fully managed Flink cluster access the Internet?.
username
The username for the MySQL database service.
Yes
STRING
None
None.
password
The password for the MySQL database service.
Yes
STRING
None
None.
database-name
The name of the MySQL database.
Yes
STRING
None
When used as a source table, this option supports regular expressions to read data from multiple databases.
When using a regular expression, avoid using ^ and $ to match the start and end of strings. See the Remarks column for table-name for details.
table-name
The name of the MySQL table.
Yes
STRING
None
When used as a source table, this option supports regular expressions to read data from multiple tables.
When reading data from multiple MySQL tables, submit multiple CTAS statements as a single job. This avoids enabling multiple binlog listeners and improves performance and efficiency. For more information, see Multiple CTAS statements: Submit as a single job.
When using a regular expression, avoid using ^ and $ to match the start and end of strings. See the note below for details.
NoteWhen a MySQL CDC source table matches table names, it combines the database-name and table-name you specify into a full-path regular expression using the string \\. (In VVR versions before 8.0.1, the character . is used.) It then uses this regular expression to match the fully qualified names of tables in the MySQL database.
For example, if you set 'database-name'='db_.*' and 'table-name'='tb_.+', the connector uses the regular expression db_.*\\.tb_.+ (or db_.*.tb_.+ in versions before 8.0.1) to match fully qualified table names and determine which tables to read.
port
The port number of the MySQL database service.
No
INTEGER
3306
None.
Source-specific
Parameter
Description
Required
Data type
Default value
Remarks
server-id
A numeric ID for the database client.
No
STRING
A random value between 5400 and 6400 is generated.
This ID must be globally unique within the MySQL cluster. We recommend assigning a different ID for each job connecting to the same database.
This option also supports an ID range, such as 5400-5408. When incremental reading is enabled, concurrent reading is supported. In this case, we recommend specifying an ID range so that each concurrent reader uses a different ID. For more information, see Using server ID.
scan.incremental.snapshot.enabled
Specifies whether to enable incremental snapshots.
No
BOOLEAN
true
Incremental snapshots are enabled by default. Incremental snapshots are a new mechanism for reading full data snapshots. Compared to the legacy snapshot method, they offer several advantages:
Full data reading can be performed in parallel.
Full data reading supports chunk-level checkpoints.
Full data reading does not require acquiring a global read lock (FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK).
If you want the source to support concurrent reading, each concurrent reader needs a unique server ID. Therefore, the server-id must be a range like 5400-6400, and the range must be at least as large as the degree of parallelism.
NoteThis configuration item is removed in Ververica Runtime (VVR) 11.1 and later.
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.size
The size of each chunk in rows.
No
INTEGER
8096
When incremental snapshot reading is enabled, the table is split into multiple chunks for reading. Chunk data is buffered in memory until fully read.
The fewer rows each chunk contains, the larger the total number of chunks in the table. Although this reduces the granularity of fault recovery, it may lead to Out Of Memory (OOM) errors and a decrease in overall throughput. Therefore, you need to make a trade-off and set a reasonable chunk size.
scan.snapshot.fetch.size
The maximum number of records to fetch at a time when reading full table data.
No
INTEGER
1024
None.
scan.startup.mode
The startup mode for data consumption.
No
STRING
initial
Valid values:
initial (default): Scans full historical data first, then reads the latest binlog data on first startup.
latest-offset: Does not scan historical data on first startup. Starts reading from the end of the binlog, meaning it reads only the latest changes after the connector starts.
earliest-offset: Does not scan historical data. Starts reading from the earliest available binlog.
specific-offset: Does not scan historical data. Starts from a specific binlog offset you specify. You can specify the offset by configuring both scan.startup.specific-offset.file and scan.startup.specific-offset.pos, or configure only scan.startup.specific-offset.gtid-set to start from a specific GTID set.
timestamp: Does not scan historical data. Starts reading binlog events from a specified timestamp. Specify the timestamp using scan.startup.timestamp-millis, in milliseconds.
ImportantWhen using earliest-offset, specific-offset, or timestamp, ensure the table schema does not change between the specified binlog consumption position and job startup time to avoid errors caused by schema mismatches.
scan.startup.specific-offset.file
The binlog filename for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode.
No
STRING
None
When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. Example filename:
mysql-bin.000003.scan.startup.specific-offset.pos
The offset in the specified binlog file for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode.
No
INTEGER
None
When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset.
scan.startup.specific-offset.gtid-set
The GTID set for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode.
No
STRING
None
When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. Example GTID set:
24DA167-0C0C-11E8-8442-00059A3C7B00:1-19.scan.startup.timestamp-millis
The start offset as a millisecond timestamp when using the timestamp startup mode.
No
LONG
None
When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to timestamp. The timestamp is in milliseconds.
ImportantWhen using a timestamp, MySQL CDC attempts to read the initial event of each binlog file to determine its timestamp and locate the corresponding binlog file. Ensure the binlog file for the specified timestamp has not been cleared from the database and remains readable.
server-time-zone
The session time zone used by the database.
No
STRING
If you do not specify this option, the system uses the time zone of the Flink job's runtime environment as the database server time zone—the time zone of the zone you selected.
Example: Asia/Shanghai. This option controls how MySQL TIMESTAMP types convert to STRING types. For more information, see Debezium temporal values.
debezium.min.row.count.to.stream.results
Use batch reading mode when the number of rows in a table exceeds this value.
No
INTEGER
1000
Flink reads data from a MySQL source table in the following ways:
Full read: Loads the entire table's data directly into memory. This is fast but consumes memory proportional to the data volume. If the source table is very large, it may cause OOM issues.
Batch read: Reads data in batches, fetching a fixed number of rows per batch until all data is read. This avoids OOM risks for large tables but is slower.
connect.timeout
The maximum time to wait for a connection to the MySQL database server to time out before retrying.
No
DURATION
30s
None.
connect.max-retries
The maximum number of retries after a failed connection to the MySQL database service.
No
INTEGER
3
None.
connection.pool.size
The size of the database connection pool.
No
INTEGER
20
The database connection pool reuses connections to reduce the number of database connections.
jdbc.properties.*
Custom connection options in the JDBC URL.
No
STRING
None
You can pass custom connection options. For example, to disable SSL, set 'jdbc.properties.useSSL' = 'false'.
For more information about supported connection options, see MySQL Configuration Properties.
debezium.*
Custom Debezium options for reading binlogs.
No
STRING
None
You can pass custom Debezium options. For example, use 'debezium.event.deserialization.failure.handling.mode'='ignore' to specify how to handle parsing errors.
heartbeat.interval
The interval at which the source uses heartbeat events to advance the binlog offset.
No
DURATION
30s
Heartbeat events advance the binlog offset in the source. This is useful for slowly updated tables in MySQL. For such tables, the binlog offset does not advance automatically. Heartbeat events push the binlog offset forward, preventing issues where an expired binlog offset causes job failure and requires a stateless restart.
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.key-column
The column used to split chunks during the snapshot phase.
See Remarks.
STRING
None
Required for tables without a primary key. The selected column must be non-null (NOT NULL).
Optional for tables with a primary key. You can select only one column from the primary key.
rds.region-id
The region ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance.
Required when reading archived logs from OSS.
STRING
None
For region IDs, see Regions and zones.
rds.access-key-id
The AccessKey ID for the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL account.
Required when reading archived logs from OSS.
STRING
None
For more information, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?.
ImportantTo prevent your AccessKey information from leaking, manage your AccessKey ID using secrets management. For more information, see Variable management.
rds.access-key-secret
The AccessKey secret for the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL account.
Required when reading archived logs from OSS.
STRING
None
For more information, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?.
ImportantTo prevent your AccessKey information from leaking, manage your AccessKey secret using secrets management. For more information, see Variable management.
rds.db-instance-id
The instance ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance.
Required when reading archived logs from OSS.
STRING
None
None.
rds.main-db-id
The primary database ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance.
No
STRING
None
For more information about obtaining the primary database ID, see RDS MySQL log backup.
Supported only in VVR 8.0.7 and later.
rds.download.timeout
The timeout for downloading a single archived log from OSS.
No
DURATION
60s
None.
rds.endpoint
The service endpoint for retrieving OSS binlog information.
No
STRING
None
For valid values, see Service endpoints.
Supported only in VVR 8.0.8 and later.
scan.incremental.close-idle-reader.enabled
Specifies whether to close idle readers after the snapshot phase ends.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Supported only in VVR 8.0.1 and later.
This configuration takes effect only when execution.checkpointing.checkpoints-after-tasks-finish.enabled is set to true.
scan.read-changelog-as-append-only.enabled
Specifies whether to convert the changelog stream to an append-only stream.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Converts all message types (including INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE_BEFORE, UPDATE_AFTER) to INSERT messages. Enable only in special cases, such as preserving upstream table delete messages.
false (default): All message types are passed through unchanged.
NoteSupported only in VVR 8.0.8 and later.
scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled
During the incremental phase, specifies whether to deserialize change events only for specified tables.
No
BOOLEAN
The default value is false in VVR 8.x.
The default value is true in VVR 11.1 and later.
Valid values:
true: Deserializes change data only for target tables to accelerate binlog reading.
false (default): Deserializes change data for all tables.
NoteSupported only in VVR 8.0.7 and later.
In VVR 8.0.8 and earlier, rename this parameter to debezium.scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enable.
scan.parse.online.schema.changes.enabled
During the incremental phase, specifies whether to attempt parsing RDS lockless DDL events.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Parses RDS lockless DDL events.
false (default): Does not parse RDS lockless DDL events.
This is an experimental feature. Before performing online lockless changes, take a snapshot of the Flink job for recovery.
NoteSupported only in VVR 11.1 and later.
scan.incremental.snapshot.backfill.skip
Specifies whether to skip backfill during the snapshot reading phase.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Skips backfill during the snapshot reading phase.
false (default): Does not skip backfill during the snapshot reading phase.
If backfill is skipped, changes to the table during the snapshot phase are read in the subsequent incremental phase instead of being merged into the snapshot.
ImportantSkipping backfill may cause data inconsistency because changes during the snapshot phase might be replayed. Only at-least-once semantics are guaranteed.
NoteSupported only in VVR 11.1 and later.
scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled
Specifies whether to distribute unbounded chunks first during the snapshot reading phase.
No
BOOELEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Distributes unbounded chunks first during the snapshot reading phase.
false (default): Does not distribute unbounded chunks first during the snapshot reading phase.
This is an experimental feature. Enabling it reduces the risk of OOM errors when a TaskManager synchronizes the last chunk during the snapshot phase. We recommend adding this before the job's first startup.
NoteSupported only in VVR 11.1 and later.
binlog.session.network.timeout
The network timeout for binlog connection read/write operations.
No
DURATION
10m
Setting this to 0s uses the MySQL server's default timeout.
NoteSupported only in VVR 11.5 and later.
scan.rate-limit.records-per-second
Limits the maximum number of records emitted per second by the source.
No
LONG
None
Useful for limiting data reading. This limit applies to both full and incremental phases.
The
numRecordsOutPerSecondmetric reflects the number of records emitted per second across the entire data flow. Adjust this parameter based on that metric.During full reading, reduce the number of rows per batch by lowering the
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.sizevalue.NoteSupported only in VVR 11.5 and later.
Dimension table-specific
Parameter
Description
Required
Data type
Default value
Remarks
url
The MySQL JDBC URL.
No
STRING
None
The URL format is
jdbc:mysql://<endpoint>:<port>/<database_name>.lookup.max-retries
The maximum number of retries after a failed data read.
No
INTEGER
3
Supported only in VVR 6.0.7 and later.
lookup.cache.strategy
The cache policy.
No
STRING
None
Supports three cache policies: None, LRU, and ALL. For more information, see Background information.
NoteWhen using the LRU cache policy, you must also configure the lookup.cache.max-rows option.
lookup.cache.max-rows
The maximum number of cached rows.
No
INTEGER
100000
If you select the least recently used cache policy, you must specify the cache size.
Optional when selecting the ALL cache policy.
lookup.cache.ttl
The cache time-to-live (TTL).
No
DURATION
10 s
The configuration of lookup.cache.ttl depends on lookup.cache.strategy:
If lookup.cache.strategy is set to None, lookup.cache.ttl is optional and means the cache never expires.
If lookup.cache.strategy is set to LRU, lookup.cache.ttl is the cache TTL. By default, it never expires.
If lookup.cache.strategy is set to ALL, lookup.cache.ttl is the cache reload time. By default, it is not reloaded.
Specify time in formats such as 1min or 10s.
lookup.max-join-rows
The maximum number of results returned when querying the dimension table for each row in the primary table.
No
INTEGER
1024
None.
lookup.filter-push-down.enabled
Specifies whether to enable filter pushdown for the dimension table.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Enables filter pushdown for the dimension table. When loading data from the MySQL database table, the dimension table filters data in advance based on conditions set in the SQL job.
false (default): Disables filter pushdown for the dimension table. When loading data from the MySQL database table, the dimension table loads all data.
NoteSupported only in VVR 8.0.7 and later.
ImportantFilter pushdown should be enabled only when the Flink table is used as a dimension table. MySQL source tables do not support enabling filter pushdown. If a Flink table is used as both a source and dimension table, and filter pushdown is enabled for the dimension table, explicitly set this option to false for the source table using SQL hints. Otherwise, the job may run abnormally.
Sink-specific
Parameter
Description
Required
Data type
Default value
Remarks
url
The MySQL JDBC URL.
No
STRING
None
The URL format is
jdbc:mysql://<endpoint>:<port>/<database_name>.sink.max-retries
The maximum number of retries after a failed data write.
No
INTEGER
3
None.
sink.buffer-flush.batch-size
The number of records written in a single batch.
No
INTEGER
4096
None.
sink.buffer-flush.max-rows
The number of data records buffered in memory.
No
INTEGER
10000
This option takes effect only after a primary key is specified.
sink.buffer-flush.interval
The time interval for flushing the buffer. If data in the buffer does not meet output conditions after waiting for the specified time, the system automatically outputs all buffered data.
No
DURATION
1s
None.
sink.ignore-delete
Specifies whether to ignore DELETE operations.
No
BOOLEAN
false
When the stream generated by Flink SQL includes delete or update-before records, simultaneous updates to different fields of the same table by multiple output tasks may cause data inconsistency.
For example, after a record is deleted, another task updates only some fields. Unupdated fields become null or their default values, causing data errors.
Set sink.ignore-delete to true to ignore upstream DELETE and UPDATE_BEFORE operations and avoid such issues.
NoteUPDATE_BEFORE is part of Flink's retraction mechanism, used to "retract" the old value in an update operation.
When ignoreDelete = true, all DELETE and UPDATE_BEFORE records are skipped. Only INSERT and UPDATE_AFTER records are processed.
sink.ignore-null-when-update
When updating data, specifies whether to set the corresponding field to null or skip the update if the input field value is null.
No
BOOLEAN
false
Valid values:
true: Skips updating the field. Supported only when the Flink table has a primary key. When set to true:
In VVR 8.0.6 and earlier, batch execution is not supported for writing data to the sink table.
In VVR 8.0.7 and later, batch execution is supported for writing data to the sink table.
While batch writes improve write efficiency and overall throughput, they introduce data latency and OOM risks. Balance these trade-offs based on your business scenario.
false: Sets the field to null.
NoteSupported only in VVR 8.0.5 and later.
Type mapping
CDC source table
MySQL CDC field type
Flink field type
TINYINT
TINYINT
SMALLINT
SMALLINT
TINYINT UNSIGNED
TINYINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
INT
INT
MEDIUMINT
SMALLINT UNSIGNED
SMALLINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
BIGINT
BIGINT
INT UNSIGNED
INT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
BIGINT UNSIGNED
DECIMAL(20, 0)
BIGINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
SERIAL
FLOAT [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
FLOAT
DOUBLE [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
DOUBLE
DOUBLE PRECISION [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
REAL [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
NUMERIC(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
DECIMAL(p, s)
DECIMAL(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
BOOLEAN
BOOLEAN
TINYINT(1)
DATE
DATE
TIME [(p)]
TIME [(p)] [WITHOUT TIME ZONE]
DATETIME [(p)]
TIMESTAMP [(p)] [WITHOUT TIME ZONE]
TIMESTAMP [(p)]
TIMESTAMP [(p)]
TIMESTAMP [(p)] WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE
CHAR(n)
STRING
VARCHAR(n)
TEXT
BINARY
BYTES
VARBINARY
BLOB
ImportantWe recommend that you do not use the TINYINT(1) type in MySQL to store values other than 0 and 1. When property-version=0, the MySQL CDC source table maps TINYINT(1) to Flink's BOOLEAN type by default. This may cause data inaccuracies. To use TINYINT(1) to store values other than 0 and 1, see the configuration option catalog.table.treat-tinyint1-as-boolean.
Dimension table and sink table
MySQL field type
Flink field type
TINYINT
TINYINT
SMALLINT
SMALLINT
TINYINT UNSIGNED
INT
INT
MEDIUMINT
SMALLINT UNSIGNED
BIGINT
BIGINT
INT UNSIGNED
BIGINT UNSIGNED
DECIMAL(20, 0)
FLOAT
FLOAT
DOUBLE
DOUBLE
DOUBLE PRECISION
NUMERIC(p, s)
DECIMAL(p, s)
Notep must be ≤ 38.
DECIMAL(p, s)
BOOLEAN
BOOLEAN
TINYINT(1)
DATE
DATE
TIME [(p)]
TIME [(p)] [WITHOUT TIME ZONE]
DATETIME [(p)]
TIMESTAMP [(p)] [WITHOUT TIME ZONE]
TIMESTAMP [(p)]
CHAR(n)
CHAR(n)
VARCHAR(n)
VARCHAR(n)
BIT(n)
BINARY(⌈n/8⌉)
BINARY(n)
BINARY(n)
VARBINARY(N)
VARBINARY(N)
TINYTEXT
STRING
TEXT
MEDIUMTEXT
LONGTEXT
TINYBLOB
BYTES
ImportantFlink supports MySQL BLOB records with a maximum size of 2,147,483,647 (2^31 - 1).
BLOB
MEDIUMBLOB
LONGBLOB
Data ingestion
You can use the MySQL connector as a data source in a data ingestion YAML job.
Syntax
source:
type: mysql
name: MySQL Source
hostname: localhost
port: 3306
username: <username>
password: <password>
tables: adb.\.*, bdb.user_table_[0-9]+, [app|web].order_\.*
server-id: 5401-5404
sink:
type: xxxConfiguration Item
Parameter | Description | Required | Data type | Default value | Remarks |
type | The type of the data source. | Yes | STRING | None | Set this option to mysql. |
name | The name of the data source. | No | STRING | None | None. |
hostname | The IP address or hostname of the MySQL database. | Yes | STRING | None | We recommend entering the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) address. Note If your MySQL database and Realtime Compute for Apache Flink are not in the same VPC, establish a cross-VPC network connection or use the Internet for access. For more information, see Manage and operate workspaces and How can a fully managed Flink cluster access the Internet?. |
username | The username for the MySQL database service. | Yes | STRING | None | None. |
password | The password for the MySQL database service. | Yes | STRING | None | None. |
tables | The MySQL data tables to synchronize. | Yes | STRING | None |
Note
|
tables.exclude | The tables to exclude from synchronization. | No | STRING | None |
Note A period separates the database name and table name. To match any character with a period, escape it with a backslash. Examples: db0.\.*, db1.user_table_[0-9]+, db[1-2].[app|web]order_\.*. |
port | The port number of the MySQL database service. | No | INTEGER | 3306 | None. |
schema-change.enabled | Specifies whether to send schema change events. | No | BOOLEAN | true | None. |
server-id | The numeric ID or range used by the database client for synchronization. | No | STRING | A random value between 5400 and 6400 is generated. | This ID must be globally unique within the MySQL cluster. We recommend assigning a different ID for each job connecting to the same database. This option also supports an ID range, such as 5400-5408. When incremental reading is enabled, concurrent reading is supported. In this case, we recommend specifying an ID range so that each concurrent reader uses a different ID. |
jdbc.properties.* | Custom connection parameters in the JDBC URL. | No | STRING | None | You can pass custom connection parameters. For example, to disable SSL, set 'jdbc.properties.useSSL' = 'false'. For more information about supported connection parameters, see MySQL Configuration Properties. |
debezium.* | Custom Debezium parameters for reading binary logs. | No | STRING | None | You can pass custom Debezium parameters. For example, use 'debezium.event.deserialization.failure.handling.mode'='ignore' to specify how to handle parsing errors. |
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.size | The size of each chunk in rows. | No | INTEGER | 8096 | A MySQL table is split into multiple chunks for reading. Chunk data is buffered in memory until fully read. The fewer rows each chunk contains, the greater the total number of chunks in the table. Although this reduces fault recovery granularity, it may cause out-of-memory (OOM) issues and reduce overall throughput. Therefore, you need to balance these factors and set an appropriate chunk size. |
scan.snapshot.fetch.size | The maximum number of records to fetch at a time when reading full table data. | No | INTEGER | 1024 | None. |
scan.startup.mode | The startup mode for data consumption. | No | STRING | initial | Valid values:
Important For earliest-offset, specific-offset, and timestamp, if the table schema differs between the startup time and the specified start offset time, the job fails due to schema mismatch. In other words, when using these three startup modes, ensure the table schema does not change between the specified binlog consumption position and job startup time. |
scan.startup.specific-offset.file | The binlog filename for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode. | No | STRING | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. Example filename: |
scan.startup.specific-offset.pos | The offset in the specified binlog file for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode. | No | INTEGER | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. |
scan.startup.specific-offset.gtid-set | The GTID set for the start offset when using the specific offset startup mode. | No | STRING | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. Example GTID set: |
scan.startup.timestamp-millis | The start offset as a millisecond timestamp when using the timestamp startup mode. | No | LONG | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to timestamp. The timestamp is in milliseconds. Important When using a timestamp, MySQL CDC attempts to read the initial event of each binlog file to determine its timestamp and locate the corresponding binlog file. Ensure the binlog file for the specified timestamp has not been cleared from the database and remains readable. |
server-time-zone | The session time zone used by the database. | No | STRING | If you do not specify this option, the system uses the time zone of the Flink job's runtime environment as the database server time zone—the time zone of the zone you selected. | Example: Asia/Shanghai. This option controls how MySQL TIMESTAMP types convert to STRING types. For more information, see Debezium temporal values. |
scan.startup.specific-offset.skip-events | The number of binlog events to skip when reading from a specific offset. | No | INTEGER | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. |
scan.startup.specific-offset.skip-rows | The number of row changes to skip when reading from a specific offset. A single binlog event may correspond to multiple row changes. | No | INTEGER | None | When using this configuration, set scan.startup.mode to specific-offset. |
connect.timeout | The maximum time to wait for a connection to the MySQL database server to time out before retrying. | No | DURATION | 30s | None. |
connect.max-retries | The maximum number of retries after a failed connection to the MySQL database service. | No | INTEGER | 3 | None. |
connection.pool.size | The size of the database connection pool. | No | INTEGER | 20 | The database connection pool reuses connections to reduce the number of database connections. |
heartbeat.interval | The interval at which the source uses heartbeat events to advance the binlog offset. | No | DURATION | 30s | Heartbeat events advance the binlog offset in the source. This is useful for slowly updated tables in MySQL. For such tables, the binlog offset does not advance automatically. Heartbeat events push the binlog offset forward, preventing issues where an expired binlog offset causes job failure and requires a stateless restart. |
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.key-column | The column used to split chunks during the snapshot phase. | No. | STRING | None | You can select only one column from the primary key. |
rds.region-id | The region ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance. | Required when reading archived logs from OSS. | STRING | None | For region IDs, see Regions and zones. |
rds.access-key-id | The AccessKey ID for the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL account. | Required when reading archived logs from OSS. | STRING | None | For more information, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?. Important To prevent your AccessKey information from leaking, manage your AccessKey ID using secrets management. For more information, see Variable management. |
rds.access-key-secret | The AccessKey secret for the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL account. | Required when reading archived logs from OSS. | STRING | None | For more information, see How do I view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret?. Important To prevent your AccessKey information from leaking, manage your AccessKey secret using secrets management. For more information, see Variable management. |
rds.db-instance-id | The instance ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance. | Required when reading archived logs from OSS. | STRING | None | None. |
rds.main-db-id | The primary database ID of the Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL instance. | No | STRING | None | For more information about obtaining the primary database ID, see RDS MySQL log backup. |
rds.download.timeout | The timeout for downloading a single archived log from OSS. | No | DURATION | 60s | None. |
rds.endpoint | The service endpoint for retrieving OSS binlog information. | No | STRING | None | For valid values, see Service endpoints. |
rds.binlog-directory-prefix | The directory prefix for storing binlog files. | No | STRING | rds-binlog- | None. |
rds.use-intranet-link | Specifies whether to use an internal network to download binlog files. | No | BOOLEAN | true | None. |
rds.binlog-directories-parent-path | The absolute path of the parent directory for storing binlog files. | No | STRING | None | None. |
chunk-meta.group.size | The size of the chunk metadata. | No | INTEGER | 1000 | If the metadata exceeds this size, it is transmitted in multiple parts. |
chunk-key.even-distribution.factor.lower-bound | The lower bound of the chunk distribution factor for even sharding. | No | DOUBLE | 0.05 | Chunk distribution factors less than this value result in uneven sharding. Chunk distribution factor = (MAX(chunk-key) - MIN(chunk-key) + 1) / Total number of rows. |
chunk-key.even-distribution.factor.upper-bound | The upper bound of the chunk distribution factor for even sharding. | No | DOUBLE | 1000.0 | Chunk distribution factors greater than this value result in uneven sharding. Chunk distribution factor = (MAX(chunk-key) - MIN(chunk-key) + 1) / Total number of rows. |
scan.incremental.close-idle-reader.enabled | Specifies whether to close idle readers after the snapshot phase ends. | No | BOOLEAN | false | For this configuration to take effect, set |
scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled | During the incremental phase, specifies whether to deserialize change events only for specified tables. | No | BOOLEAN |
| Valid values:
|
scan.parallel-deserialize-changelog.enabled | During the incremental phase, specifies whether to use multithreading to parse change events. | No | BOOLEAN | false | Valid values:
Note Supported only in VVR 8.0.11 and later. |
scan.parallel-deserialize-changelog.handler.size | The number of event handlers when using multithreading to parse change events. | No | INTEGER | 2 | Note Supported only in VVR 8.0.11 and later. |
metadata-column.include-list | The metadata columns to pass downstream. | No | STRING | None | Available metadata includes Note The MySQL CDC YAML connector does not need to and does not support adding database name, table name, and Important The
|
scan.newly-added-table.enabled | When restarting from a checkpoint, specifies whether to synchronize newly added tables that were not matched in the previous run or remove currently unmatched tables saved in the state. | No | BOOLEAN | false | This takes effect when restarting from a checkpoint or savepoint. |
scan.binlog.newly-added-table.enabled | During the incremental phase, specifies whether to send data from newly added tables that match the pattern. | No | BOOLEAN | false | This cannot be enabled simultaneously with |
scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.key-column | Specify a column for certain tables to use as the chunk-splitting key during the snapshot phase. | No | STRING | None |
|
scan.parse.online.schema.changes.enabled | During the incremental phase, specifies whether to attempt parsing RDS lockless DDL events. | No | BOOLEAN | false | Valid values:
This is an experimental feature. Before performing online lockless changes, take a snapshot of the Flink job for recovery. Note Supported only in VVR 11.0 and later. |
scan.incremental.snapshot.backfill.skip | Specifies whether to skip backfill during the snapshot reading phase. | No | BOOLEAN | false | Valid values:
If backfill is skipped, changes to the table during the snapshot phase are read in the subsequent incremental phase instead of being merged into the snapshot. Important Skipping backfill may cause data inconsistency because changes during the snapshot phase might be replayed. Only at-least-once semantics are guaranteed. Note Supported only in VVR 11.1 and later. |
treat-tinyint1-as-boolean.enabled | Specifies whether to treat the TINYINT(1) type as a Boolean type. | No | BOOLEAN | true | Valid values:
|
treat-timestamp-as-datetime-enabled | Specifies whether to process TIMESTAMP as DATETIME. | No | BOOLEAN | false | Valid values:
MySQL TIMESTAMP stores UTC time and is affected by time zones. MySQL DATETIME stores literal time and is unaffected by time zones. Enabling this converts MySQL TIMESTAMP data to DATETIME based on server-time-zone. |
include-comments.enabled | Specifies whether to sync table and column comments. | No | BOOELEAN | false | Valid values:
Enabling this increases job memory usage. |
scan.incremental.snapshot.unbounded-chunk-first.enabled | Specifies whether to distribute unbounded chunks first during the snapshot reading phase. | No | BOOELEAN | false | Valid values:
This is an experimental feature. Enabling it reduces the risk of OOM errors when a TaskManager synchronizes the last chunk during the snapshot phase. We recommend adding this before the job's first startup. Note Supported only in VVR 11.1 and later. |
binlog.session.network.timeout | The network timeout for binlog connections. | No | DURATION | 10m | Setting this to 0s uses the MySQL server's default timeout. Note Supported only in VVR 11.5 and later. |
scan.rate-limit.records-per-second | Limits the maximum number of records emitted per second by the source. | No | LONG | None | Useful for limiting data reads. This limit applies to both full and incremental phases. The During full reading, reduce the number of rows per batch by lowering the Note Supported only in VVR 11.5 and later. |
Type mapping
The following table shows the type mappings for data ingestion.
MySQL CDC field type | CDC field type |
TINYINT(n) | TINYINT |
SMALLINT | SMALLINT |
TINYINT UNSIGNED | |
TINYINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL | |
YEAR | |
INT | INT |
MEDIUMINT | |
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | |
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL | |
SMALLINT UNSIGNED | |
SMALLINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL | |
BIGINT | BIGINT |
INT UNSIGNED | |
INT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL | |
BIGINT UNSIGNED | DECIMAL(20, 0) |
BIGINT UNSIGNED ZEROFILL | |
SERIAL | |
FLOAT [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] | FLOAT |
DOUBLE [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] | DOUBLE |
DOUBLE PRECISION [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] | |
REAL [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] | |
NUMERIC(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where p ≤ 38 | DECIMAL(p, s) |
DECIMAL(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where p ≤ 38 | |
FIXED(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where p ≤ 38 | |
BOOLEAN | BOOLEAN |
BIT(1) | |
TINYINT(1) | |
DATE | DATE |
TIME [(p)] | TIME [(p)] |
DATETIME [(p)] | TIMESTAMP [(p)] |
TIMESTAMP [(p)] | Field mapping depends on the
|
CHAR(n) | CHAR(n) |
VARCHAR(n) | VARCHAR(n) |
BIT(n) | BINARY(⌈(n + 7) / 8⌉) |
BINARY(n) | BINARY(n) |
VARBINARY(N) | VARBINARY(N) |
NUMERIC(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where 38 < p ≤ 65 | STRING Note In MySQL, decimal precision can reach up to 65. Flink limits decimal precision to 38. If you define a decimal column with precision > 38, map it to a string to avoid precision loss. |
DECIMAL(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where 38 < p ≤ 65 | |
FIXED(p, s) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] where 38 < p ≤ 65 | |
TINYTEXT | STRING |
TEXT | |
MEDIUMTEXT | |
LONGTEXT | |
ENUM | |
JSON | STRING Note The JSON data type is converted to a JSON-formatted string in Flink. |
GEOMETRY | STRING Note MySQL spatial data types are converted to strings with a fixed JSON format. For more information, see MySQL spatial data type mapping. |
POINT | |
LINESTRING | |
POLYGON | |
MULTIPOINT | |
MULTILINESTRING | |
MULTIPOLYGON | |
GEOMETRYCOLLECTION | |
TINYBLOB | BYTES Note MySQL supports BLOBs with a maximum length of 2,147,483,647 (2**31-1) bytes. |
BLOB | |
MEDIUMBLOB | |
LONGBLOB |
Examples
CDC source table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mysqlcdc_source ( order_id INT, order_date TIMESTAMP(0), customer_name STRING, price DECIMAL(10, 5), product_id INT, order_status BOOLEAN, PRIMARY KEY(order_id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql', 'hostname' = '<yourHostname>', 'port' = '3306', 'username' = '<yourUsername>', 'password' = '<yourPassword>', 'database-name' = '<yourDatabaseName>', 'table-name' = '<yourTableName>' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE blackhole_sink( order_id INT, customer_name STRING ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'blackhole' ); INSERT INTO blackhole_sink SELECT order_id, customer_name FROM mysqlcdc_source;Dimension table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE datagen_source( a INT, b BIGINT, c STRING, `proctime` AS PROCTIME() ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'datagen' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mysql_dim ( a INT, b VARCHAR, c VARCHAR ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql', 'hostname' = '<yourHostname>', 'port' = '3306', 'username' = '<yourUsername>', 'password' = '<yourPassword>', 'database-name' = '<yourDatabaseName>', 'table-name' = '<yourTableName>' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE blackhole_sink( a INT, b STRING ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'blackhole' ); INSERT INTO blackhole_sink SELECT T.a, H.b FROM datagen_source AS T JOIN mysql_dim FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF T.`proctime` AS H ON T.a = H.a;Sink table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE datagen_source ( `name` VARCHAR, `age` INT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'datagen' ); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mysql_sink ( `name` VARCHAR, `age` INT ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql', 'hostname' = '<yourHostname>', 'port' = '3306', 'username' = '<yourUsername>', 'password' = '<yourPassword>', 'database-name' = '<yourDatabaseName>', 'table-name' = '<yourTableName>' ); INSERT INTO mysql_sink SELECT * FROM datagen_source;Data ingestion source
source: type: mysql name: MySQL Source hostname: ${mysql.hostname} port: ${mysql.port} username: ${mysql.username} password: ${mysql.password} tables: ${mysql.source.table} server-id: 7601-7604 sink: type: values name: Values Sink print.enabled: true sink.print.logger: true
About MySQL CDC source tables
How it works
A MySQL CDC source table scans the full table at startup and splits it into multiple chunks based on the primary key. It records the current binlog offset and then uses the incremental snapshot algorithm to read each chunk's data using SELECT statements. The job performs periodic checkpoints to record completed chunks. If a failover occurs, the job continues to read only unfinished chunks. After all chunks are read, the job reads incremental change records from the previously recorded binlog offset. The Flink job continues to perform periodic checkpoints to record the binlog offset. If a failover occurs, the job resumes processing from the last recorded binlog offset. This process achieves exactly-once semantics.
For more details about the incremental snapshot algorithm, see MySQL CDC Connector.
Metadata
Metadata is highly useful in sharded database and table merging scenarios. After merging, businesses often still need to identify the source database and table for each row of data. Metadata columns allow you to access this information. Therefore, you can easily merge multiple sharded tables into a single destination table using metadata columns.
The MySQL CDC Source supports metadata column syntax. You can access the following metadata through metadata columns.
Metadata key
Metadata type
Description
database_name
STRING NOT NULL
The name of the database containing the row.
table_name
STRING NOT NULL
The name of the table containing the row.
op_ts
TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) NOT NULL
The time when the row was changed in the database. If the record comes from the table's existing historical data rather than the binlog, this value is always 0.
op_type
STRING NOT NULL
The change type of the row.
+I: INSERT message
-D: DELETE message
-U: UPDATE_BEFORE message
+U: UPDATE_AFTER message
NoteSupported only in Ververica Runtime (VVR) 8.0.7 and later.
query_log
STRING NOT NULL
Read the MySQL query log record corresponding to this row.
NoteMySQL must have the binlog_rows_query_log_events parameter enabled to record query logs.
The following example shows how to merge multiple orders tables from different sharded databases in a MySQL instance and synchronize them to the holo_orders table in Hologres.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mysql_orders ( db_name STRING METADATA FROM 'database_name' VIRTUAL, -- Read the database name. table_name STRING METADATA FROM 'table_name' VIRTUAL, -- Read the table name. operation_ts TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) METADATA FROM 'op_ts' VIRTUAL, -- Read the change timestamp. op_type STRING METADATA FROM 'op_type' VIRTUAL, -- Read the change type. order_id INT, order_date TIMESTAMP(0), customer_name STRING, price DECIMAL(10, 5), product_id INT, order_status BOOLEAN, PRIMARY KEY(order_id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql-cdc', 'hostname' = 'localhost', 'port' = '3306', 'username' = 'flinkuser', 'password' = 'flinkpw', 'database-name' = 'mydb_.*', -- Match multiple sharded databases using a regular expression. 'table-name' = 'orders_.*' -- Match multiple sharded tables using a regular expression. ); INSERT INTO holo_orders SELECT * FROM mysql_orders;Based on the preceding code, if you set scan.read-changelog-as-append-only.enabled to true in the WITH clause, the output varies based on the primary key configuration of the downstream table:
If the primary key of the downstream table is order_id, the output contains only the last change for each primary key in the upstream table. For example, if the last change for a primary key is a delete operation, you see a record in the downstream table with the same primary key and an op_type of -D.
If the primary key of the downstream table is order_id, operation_ts, and op_type, the output contains the complete change history for each primary key in the upstream table.
Regular expression support
The MySQL CDC source table supports using regular expressions in the table name or database name to match multiple tables or databases. The following example shows how to specify multiple tables using a regular expression.
CREATE TABLE products ( db_name STRING METADATA FROM 'database_name' VIRTUAL, table_name STRING METADATA FROM 'table_name' VIRTUAL, operation_ts TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) METADATA FROM 'op_ts' VIRTUAL, order_id INT, order_date TIMESTAMP(0), customer_name STRING, price DECIMAL(10, 5), product_id INT, order_status BOOLEAN, PRIMARY KEY(order_id) NOT ENFORCED ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql-cdc', 'hostname' = 'localhost', 'port' = '3306', 'username' = 'root', 'password' = '123456', 'database-name' = '(^(test).*|^(tpc).*|txc|.*[p$]|t{2})', -- Match multiple databases using a regular expression. 'table-name' = '(t[5-8]|tt)' -- Match multiple tables using a regular expression. );Explanation of the regular expressions in the preceding example:
^(test).* is a prefix match example. This expression matches database names that start with test, such as test1 or test2.
.*[p$] is a suffix match example. This expression matches database names that end with p, such as cdcp or edcp.
txc is an exact match. It matches the specific database name txc.
When matching fully qualified table names, MySQL CDC uses both the database name and table name to uniquely identify a table. It uses the pattern database-name.table-name for matching. For example, the pattern (^(test).*|^(tpc).*|txc|.*[p$]|t{2}).(t[5-8]|tt) matches tables such as txc.tt and test2.test5 in the database.
ImportantIn SQL job configurations, the table-name and database-name options do not support using commas (,) to specify multiple tables or databases.
To match multiple tables or use multiple regular expressions, you can separate them with a VERTICAL LINE (|) and enclose them in parentheses. For example, to read the user and product tables, you can configure table-name as
(user|product).If a regular expression contains a comma, you must rewrite it using the VERTICAL LINE (|) operator. For example, the regular expression
mytable_\d{1, 2}must be rewritten as the equivalent(mytable_\d{1}|mytable_\d{2})to avoid using a comma.
Concurrency control
The MySQL connector supports the concurrent reading of full data, which improves data loading efficiency. When combined with Autopilot in the Realtime Compute for Apache Flink console, the connector automatically scales in during the incremental phase after the concurrent reading is complete. This saves computing resources.
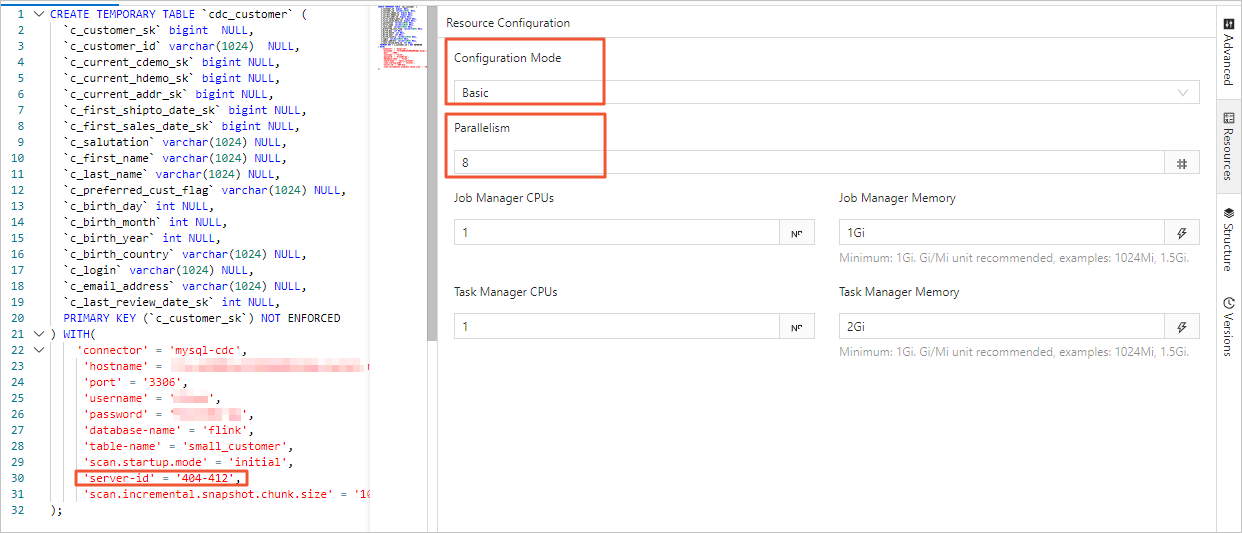
In the Realtime Compute development console, you can set the job's parallelism on the Resource Configuration page in either Basic mode or Expert mode. The differences are as follows:
The parallelism set in Basic mode is the global parallelism for the entire job.
Expert mode lets you set the parallelism for a specific VERTEX as needed.
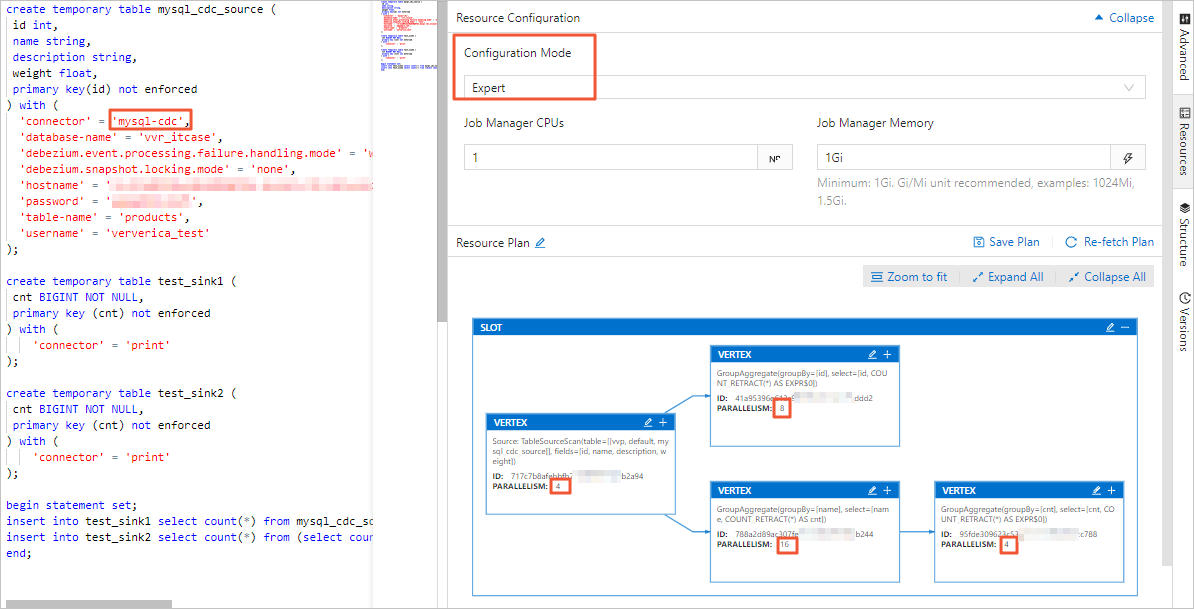
For more information about resource configuration, see Configure job deployment information.
ImportantRegardless of whether you use Basic mode or Expert mode, the server-id range that is declared in the table must be greater than or equal to the job's parallelism. For example, if the server-id range is 5404-5412, there are eight unique server IDs. Therefore, the job can have a maximum of eight parallel tasks. Different jobs for the same MySQL instance must have non-overlapping server-id ranges. Each job must explicitly configure a different server-id.
Autopilot Auto Scale-in
The full data phase accumulates large amounts of historical data. To improve reading efficiency, historical data is typically read concurrently. In the incremental binlog phase, however, a single concurrency is usually sufficient because the binlog data volume is small and global ordering must be maintained. Autopilot automatically balances performance and resources to meet these differing requirements between the full and incremental phases.
Autopilot monitors traffic for each task in the MySQL CDC Source. When entering the binlog phase, if only one task handles binlog reading while others remain idle, Autopilot automatically reduces the Source's CU count and parallelism. To enable Autopilot, set the Autopilot mode to Active on the job's Operations and Maintenance page.
NoteThe default minimum trigger interval for scaling down parallelism is 24 hours. For more information about Autopilot parameters and details, see Configure Autopilot.
Startup modes
You can use the scan.startup.mode option to specify the startup mode for the MySQL CDC source table. The valid values are described as follows:
initial (default): Performs a full read of the database table on first startup, then switches to incremental mode to read the binlog.
earliest-offset: Skips the snapshot phase and starts reading from the earliest available binlog offset.
latest-offset: Skips the snapshot phase and starts reading from the end of the binlog. In this mode, the source table reads only changes that are made after the job starts.
specific-offset: Skips the snapshot phase and starts reading from a specified binlog offset. You can specify the offset by binlog filename and position or by GTID set.
timestamp: Skips the snapshot phase and starts reading binlog events from a specified timestamp.
Example:
CREATE TABLE mysql_source (...) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql-cdc', 'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset', -- Start from the earliest offset. 'scan.startup.mode' = 'latest-offset', -- Start from the latest offset. 'scan.startup.mode' = 'specific-offset', -- Start from a specific offset. 'scan.startup.mode' = 'timestamp', -- Start from a specific timestamp. 'scan.startup.specific-offset.file' = 'mysql-bin.000003', -- Specify the binlog filename for the specific-offset mode. 'scan.startup.specific-offset.pos' = '4', -- Specify the binlog position for the specific-offset mode. 'scan.startup.specific-offset.gtid-set' = '24DA167-0C0C-11E8-8442-00059A3C7B00:1-19', -- Specify the GTID set for the specific-offset mode. 'scan.startup.timestamp-millis' = '1667232000000' -- Specify the startup timestamp for the timestamp mode. ... )ImportantThe MySQL source logs the current position at the INFO level during a checkpoint. The log prefix is
Binlog offset on checkpoint {checkpoint-id}. This log helps you restart the job from a specific checkpoint position.If the schema of the table that is being read has changed in the past, starting from earliest-offset, specific-offset, or timestamp may cause errors. This is because the Debezium reader internally stores the latest schema, and older data with mismatched schemas cannot be parsed correctly.
Keyless CDC source tables
To use a keyless table, you must set scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.key-column and select only a non-null field.
The processing semantics of a keyless CDC source table depend on the behavior of the column that is specified in scan.incremental.snapshot.chunk.key-column:
If the specified column is never updated, exactly-once semantics are guaranteed.
If the specified column is updated, only at-least-once semantics are guaranteed. However, you can ensure data correctness by combining it with downstream systems, specifying a downstream primary key, and using idempotent operations.
Read backup logs from RDS MySQL
The MySQL CDC source table supports reading backup logs from Alibaba Cloud RDS MySQL. This feature is especially useful when the full snapshot phase takes a long time. In this case, local binlog files may be automatically cleaned up, while manually or automatically uploaded backup files still exist.
Example:
CREATE TABLE mysql_source (...) WITH ( 'connector' = 'mysql-cdc', 'rds.region-id' = 'cn-beijing', 'rds.access-key-id' = 'xxxxxxxxx', 'rds.access-key-secret' = 'xxxxxxxxx', 'rds.db-instance-id' = 'rm-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx', 'rds.main-db-id' = '12345678', 'rds.download.timeout' = '60s' ... )Enable CDC source reuse
A single job with multiple MySQL CDC source tables launches multiple binlog clients. If all source tables read from the same MySQL instance, this practice increases the pressure on the database. For more information, see MySQL CDC FAQ.
Solutions
VVR 8.0.7 and later versions support MySQL CDC source reuse. Reuse merges compatible MySQL CDC source tables. Merging occurs when source tables share identical configurations except for the database name, table name, and
server-id. The engine automatically merges MySQL CDC sources within the same job.Procedure
You can use the
SETcommand in an SQL job:SET 'table.optimizer.source-merge.enabled' = 'true'; # (VVR 8.0.8 and 8.0.9 versions) Also set this: SET 'sql-gateway.exec-plan.enabled' = 'false';VVR 11.1 and later versions enable reuse by default.
Start the job statelessly. Modifying the source reuse configuration changes the job topology. You must start the job without states. Otherwise, the job may fail to start or lose data. If a source is merged, you can see a
MergetableSourceScannode in the job topology.
ImportantAfter you enable reuse, do not set
pipeline.operator-chainingtofalse. Disabling operator chaining adds serialization and deserialization overhead. The more sources that are merged, the greater the overhead.In VVR 8.0.7, disabling operator chaining causes serialization issues.
Accelerate binlog reading
When you use the MySQL connector as a source table or data ingestion source, it parses binlog files to generate various change messages during the incremental phase. Binlog files record all table changes in a binary format. You can accelerate binlog file parsing in the following ways:
Enable parsing filter configuration
Use the
scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabledoption to parse change events only for specified tables.
Optimize Debezium options
debezium.max.queue.size: 162580 debezium.max.batch.size: 40960 debezium.poll.interval.ms: 50debezium.max.queue.size: The maximum number of records that the blocking queue can hold. When Debezium reads an event stream from the database, it places events in a blocking queue before it writes them downstream. The default value is 8192.debezium.max.batch.size: The maximum number of events that are processed per iteration. The default value is 2048.debezium.poll.interval.ms: The number of milliseconds that the connector waits before it requests new change events. The default value is 1000 ms (1 second).
Example:
CREATE TABLE mysql_source (...) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql-cdc',
-- Debezium configuration
'debezium.max.queue.size' = '162580',
'debezium.max.batch.size' = '40960',
'debezium.poll.interval.ms' = '50',
-- Enable parsing filter
'scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled' = 'true', -- Parse change events only for specified tables.
...
)source:
type: mysql
name: MySQL Source
hostname: ${mysql.hostname}
port: ${mysql.port}
username: ${mysql.username}
password: ${mysql.password}
tables: ${mysql.source.table}
server-id: 7601-7604
# Debezium configuration
debezium.max.queue.size: 162580
debezium.max.batch.size: 40960
debezium.poll.interval.ms: 50
# Enable parsing filter
scan.only.deserialize.captured.tables.changelog.enabled: trueThe enterprise version of MySQL CDC consumes binlogs at a rate of 85 MB/s, which is about twice the rate of the open-source community version. If the binlog generation rate exceeds 85 MB/s (equivalent to one 512 MB file every 6 seconds), the Flink job latency continuously increases. The latency gradually decreases after the binlog generation rate slows down. When binlog files contain large transactions, the processing latency may temporarily increase and then decrease after the transaction's log is read.
MySQL CDC DataStream API
To read and write data using the DataStream API, you must use the corresponding DataStream connector to connect to Flink. For instructions on how to set up the DataStream connector, see DataStream connector usage.
The following examples show how to create a DataStream API program and use MySqlSource, including the required pom dependencies.
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import com.ververica.cdc.debezium.JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema;
import com.ververica.cdc.connectors.mysql.source.MySqlSource;
public class MySqlSourceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MySqlSource<String> mySqlSource = MySqlSource.<String>builder()
.hostname("yourHostname")
.port(yourPort)
.databaseList("yourDatabaseName") // Set captured database.
.tableList("yourDatabaseName.yourTableName") // Set captured table.
.username("yourUsername")
.password("yourPassword")
.deserializer(new JsonDebeziumDeserializationSchema()) // Converts SourceRecord to JSON String.
.build();
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// Enable checkpointing.
env.enableCheckpointing(3000);
env
.fromSource(mySqlSource, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), "MySQL Source")
// Set 4 parallel source tasks.
.setParallelism(4)
.print().setParallelism(1); // Use parallelism 1 for sink to maintain message ordering.
env.execute("Print MySQL Snapshot + Binlog");
}
}<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-core</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-streaming-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-base</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-common</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-clients</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-api-java-bridge</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.ververica</groupId>
<artifactId>ververica-connector-mysql</artifactId>
<version>${vvr.version}</version>
</dependency>When you build MySqlSource, you must specify the following parameters in your code:
Parameter | Description |
hostname | The IP address or hostname of the MySQL database. |
port | The port number of the MySQL database service. |
databaseList | The name of the MySQL database. Note The database name supports regular expressions to read data from multiple databases. Use |
username | The username for the MySQL database service. |
password | The password for the MySQL database service. |
deserializer | A deserializer that converts SourceRecord objects to a specified type. Valid values:
|
Your pom dependencies must specify the following parameters:
${vvr.version} | The engine version of Alibaba Cloud Realtime Compute for Apache Flink—for example, Note Use the version number displayed on Maven. We periodically release hotfix versions, and these updates may not be announced through other channels. |
${flink.version} | The Apache Flink version—for example, Important Use the Apache Flink version corresponding to your Realtime Compute for Apache Flink engine version to avoid compatibility issues during job runtime. For version mapping details, see Engine. |
FAQ
For information about issues that you might encounter when you use a CDC source table, see CDC issues.