This topic describes how to use Express Connect and Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) to connect a data center to a virtual private cloud (VPC). The connection leverages active-standby Express Connect circuits that use Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Scenario
A company has a data center in Shanghai that hosts high-level business systems, such as database clusters. It has also created a VPC in the China (Shanghai) region and deployed applications, such as Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. To ensure stable connection between the cloud and on-premises environments, the company needs to purchase two Express Connect circuits to customer-premises equipment (CPE) in the data center and virtual border routers (VBRs) on Alibaba Cloud. Then, use CEN to connect the data center and the VPC. The two Express Connect circuits act as an active-standby pair. BGP dynamic routing and Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) are enabled between the data center and the VBRs. This setup ensures fast route convergence and high availability.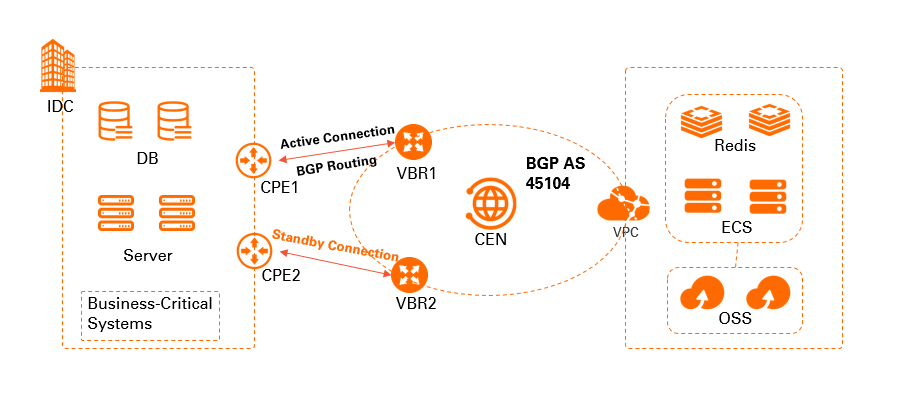
Prerequisites
Complete these prerequisites before you begin:
You have an Alibaba Cloud account. If you do not have one, Sign up for an account.
You have created a VPC in the China (Shanghai) region and deployed business applications on cloud resources, such as ECS instances, in the VPC. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
NoteBefore creating a VPC connection on an Enterprise Edition transit router, make sure the VPC has at least one vSwitch in a zone supported by the transit router. The vSwitch must have at least one idle IP address. In this topic, the transit router is created in the China (Shanghai) region, with the supported zones are Shanghai Zone F and Shanghai Zone G.
You understand the security group rules of the ECS instances in the VPC. Make sure that the rules allow the ECS instances to communicate with the data center. For more information, see View security group rules and Add a security group rule.
A CEN instance has been created. For more information, see Create a CEN instance.
An Enterprise Edition transit router has been created in the region where the VPC resides. For more information, see Create a transit router.
Two connections are created, either dedicated or shared circuits.
The following table lists the CIDR block planning for this example. Plan your own CIDR blocks and make sure they do not overlap.
Instance
CIDR block
Server or client address
Data center
10.1.1.0/24
Client address: 10.1.1.1
VPC
192.168.20.0/24
Server address: 192.168.20.161
VBR1
VLAN: 110
Alibaba Cloud-side IPv4 peer IP: 172.16.1.2/30
Customer-side IPv4 IP: 172.16.1.1/30
Not applicable
VBR2
VLAN: 120
Alibaba Cloud-side IPv4 IP: 172.16.2.2/30
Customer-side IPv4 IP: 172.16.2.1/30
Not applicable
Step 1: Create VBRs
Create a VBR for each Express Connect circuit to forward data between the VPC and the data center.
Log on to the Express Connect console.
In the top menu bar, select the region. In the navigation pane on the left, click Virtual Border Routers (VBRs).
In the Create VBR panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Account
The type of account that owns the VBR.
This topic uses Current Account.
Name
Enter a name for the VBR.
This topic uses VBR1.
Express Connect Circuit
Select Express Connect circuit 1.
VLAN ID
Enter the VLAN ID for the VBR.
This topic uses 110.
Set VBR Bandwidth Value
Set the bandwidth for the VBR.
This topic uses 200Mb.
Alibaba Cloud Side IPv4 Address
Enter the IPv4 address of the gateway on Alibaba Cloud.
This topic uses 172.16.1.2.
Data Center Side IPv4 Address
Enter the IPv4 address of the gateway in the data center.
This topic uses 172.16.1.1.
IPv4 Subnet Mask
The subnet mask for the Alibaba Cloud-side and customer-side IPv4 addresses.
This topic uses 255.255.255.252.
Repeat the preceding steps to create a VBR for the second Express Connect circuit.
The following parameters are used:
Parameter
Description
Account
The type of account that owns the VBR.
This topic uses Current Account.
Name
Enter a name for the VBR.
This topic uses VBR2.
Express Connect Circuit
Select Express Connect circuit 2.
VLAN ID
Enter the VLAN ID for the VBR.
This topic uses 120.
Set VBR Bandwidth Value
Set the bandwidth for the VBR.
This topic uses 200Mb.
Alibaba Cloud Side IPv4 Address
Enter the IPv4 address of the gateway on Alibaba Cloud.
This topic uses 172.16.2.2.
Data Center Side IPv4 Address
Enter the IPv4 address of the gateway in the data center.
This topic uses 172.16.2.1.
IPv4 Subnet Mask
The subnet mask for the Alibaba Cloud-side and customer-side IPv4 addresses.
This topic uses 255.255.255.252.
Step 2: Connect the VPC and VBR instances
To enable private communication between the on-premises data center and the VPC, create VPC and VBR connections on the Enterprise Edition transit router in the China (Shanghai) region after the Express Connect connections are established.
Log on to the CEN console.
On the Instances page, click the ID of the CEN instance that you want to manage.
Go to the tab, find the transit router that you want to manage, and then click Create Connection in the Actions column.
On the Connection with Peer Network Instance page, configure the following parameters and click OK.
NoteWhen you perform this operation for the first time, the system automatically creates a service-linked role named AliyunServiceRoleForCEN. This role allows the transit router to create an ENI in a vSwitch of the VPC. For more information, see AliyunServiceRoleForCEN.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
The type of network instance.
In this example, VPC is selected.
Region
The region in which the VPC is deployed.
In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
Transit Router
The system automatically displays the transit router in the selected region.
Resource Owner ID
The Alibaba Cloud account to which the VPC belongs.
In this example, Current Account is selected.
Billing Method
By default, transit routers use the pay-as-you-go billing method.
For more information, see Billing rules.
Network Instance
The ID of the VPC.
In this example, the VPC that you created is selected.
VSwitch
Select at least two vSwitches in a zone supported by the transit router.
Advanced Settings
By default, the following advanced features are selected: Associate with Default Route Table of Transit Router, Propagate System Routes to Default Route Table of Transit Router, and Automatically Creates Route That Points to Transit Router and Adds to All Route Tables of Current VPC.
In this example, the default settings are used.
On the Connection With Peer Network Instance page, click Create More Connections.
On the Connection With Peer Network Instance page, set the following parameters to create a connection for VBR1, and then click OK.
Parameter
Configuration
Instance Type
This topic uses Virtual Border Router (VBR).
Region
Select the region where the network instance is deployed.
This topic uses China (Shanghai).
Transit Router
The system automatically displays the transit router in the current region.
Resource Owner ID
Select the type of account that owns the network instance.
This topic uses the default value My Account.
Attachment Name
Enter a name for the VBR connection.
This topic uses VBR-test.
Network Instance
Select the ID of the VBR to connect.
This topic uses the created VBR1 instance.
Advanced Settings
By default, the following advanced features are enabled: Associate with Default Route Table of Transit Router, Propagate System Routes to Default Route Table of Transit Router, and Automatically Creates Route That Points to Transit Router and Adds to All Route Tables of Current VPC.
This topic uses the default configurations.
Repeat Step 5 and Step 6 to create a connection for VBR2.
After the network connections are created, you can view information about the VPC and VBR connections on the Intra-region Connections tab. For more information, see View network instance connections.
Step 3: Configure routes
Configure BGP between your data center and the VBRs. Set the AS-Path length in your data center to determine route priorities.
Establish BGP peerings between the data center and the VBRs and advertise routes. For more information, see Configure and manage BGP.
The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of Alibaba Cloud is 45104. The data center can use a 2-byte or 4-byte ASN.
Configure BGP routes to be advertised from your data center to Alibaba Cloud (10.1.1.0/24). Use the AS-Path attribute to set weights and implement an active/standby mode for routes from Alibaba Cloud to your data center.
Set the Express Connect circuit connected to CPE1 as the primary link and the circuit connected to CPE2 as the standby link. You can set the AS-Path length to determine route priorities, with shorter AS-Path having a higher priority. The following table shows the BGP configurations for the two CPEs in the data center. For the specific commands, consult your device vendor.
Configuration | CPE1 | CPE2 |
VLAN Tag | 110 | 120 |
Network | 10.1.1.0/24 | 10.1.1.0/24 |
BGP ASN | 6***3 | 6***4 |
Interface IP | 172.16.1.1/24 | 172.16.2.1/24 |
AS-Path | B, A | C, B, A |
The CEN transit router can automatically learn and distribute routes. After you configure the routes, the transit router synchronizes the routes internally based on weights and other information. The following information describes how routes are learned at each node.
BGP routing information of the VBRs
Route table item
VBR1
VBR2
Destination CIDR block
10.1.1.0/24
10.1.1.0/24
Next hop
172.16.1.1
172.16.2.1
As shown in the table, you can view the routes and next hops learned from the peers in VBR1 and VBR2. Because a VBR connection is created on the transit router, the VBRs send the BGP routes learned from the data center, including the AS-Path, to the transit router.
Overall route configuration
CPE route configuration
Configuration
CPE1
CPE2
VLAN Tag
110
120
Network
10.1.1.0/24
10.1.1.0/24
BGP ASN
6***3
6***4
Interface IP
172.16.1.1/24
172.16.2.1/24
AS-Path
B, A
C, B, A
VBR Routes
Configuration
VBR1
VBR2
Destination CIDR block
10.1.1.0/24
10.1.1.0/24
Next hop
172.16.1.1
172.16.2.1
Data Center Routes
Destination CIDR block
192.168.20.0/24
Next hop
To create a symmetric traffic path for inbound and outbound traffic, set a higher weight for the route learned from the VBR1 peer. This ensures that traffic to the cloud preferentially uses CPE1:
172.16.1.2 (High weight)
172.16.2.2 (Low weight)
Transit Router Route Entries
Destination CIDR block
10.1.1.0/24
Next hop
VBR1
Because VBR and VPC connections are created on the transit router, BGP routes learned from the VBRs are also advertised to the transit router. The transit router synchronizes the routes internally based on weights.
The two VBRs learn BGP routes to the same destination CIDR block from the data center, but the routes have different weights. VBR1 is the primary link (shorter AS-Path) and VBR2 is the standby link (longer AS-Path). When the transit router learns these routes, it advertises their properties to other connected network instances, such as the VPC. The route table of the VPC then shows that routes to 10.1.1.0/24 point to VBR1.
The transit router also advertises its system routes through BGP. Therefore, the BGP route table of the data center shows the routes learned from the transit router. The next hops of these routes point to the interface IP addresses of the two VBRs that are BGP peers with the data center.
Similarly, to set up active/standby links from the data center to the VPC CIDR block 192.168.20.0/24, you can use BGP route selection attributes. In the data center, set different weights for the 192.168.20.0/24 route learned from the VBR1 and VBR2 peers. This lets you control the primary and standby paths from the data center to Alibaba Cloud.
Step 4: Configure health checks
When you use active/standby Express Connect circuits, you must configure health checks, which send probe packets at a specified interval. If all consecutive probe packets (the number you specify) are lost, CEN automatically switches traffic to the other Express Connect circuit.
Log on to the CEN console.
In the navigation pane on the left, click VBR Health Check.
On the VBR Health Check page, select the region where the VBR is deployed, and click Set Health Check.
This topic uses China (Shanghai), which is the region where VBR1 is deployed.
In the Set Health Check dialog box, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Instances
The CEN instance to which the VBR is attached.
Virtual Border Router (VBR)
The VBR that you want to monitor.
In this example, VBR1 is selected.
Source IP
The source IP address. You can select one of the following methods to specify the source IP address:
Automatic IP Address: The system automatically assigns an IP address from the 100.96.0.0/16 CIDR block. We recommend that you select this option.
NoteIf you select this option and an ACL policy is configured on the peer , you must modify the ACL policy to allow this CIDR block. Otherwise, the health check fails.
Custom IP Address: You need to specify an idle IP address within the 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.0.0/16, or 172.16.0.0/12 CIDR block. The specified IP address cannot be the IP address with which you want to communicate, the IP address of the VBR on the Alibaba Cloud side, or the IP address of the VBR on the user side.
Destination IP
The IP address of the VBR on the user side.
Probe Interval (Seconds)
The interval at which probe packets are sent for the health check. Unit: seconds.
Default value: 2. Valid values: 2 to 3.
Probe Packets
The number of probe packets that are sent for health checks. Unit: packet.
Default value: 8. Valid values: 3 to 8.
Change Route
Specifies whether to allow the health check feature to switch to the redundant route.
By default, Change Route is turned on. This indicates that the health check feature can switch to the redundant route. If a redundant route is configured on the CEN instance, the health check feature immediately switches to the redundant route if an error is detected on the Express Connect circuit.
If you turn off Change Route, the health check feature does not switch to the redundant route. Only probing is performed. The health check feature does not switch to the redundant route even if an error is detected on the Express Connect circuit.
WarningBefore you turn off Change Route, make sure that the system can switch to a redundant route by using other mechanisms. Otherwise, network connections are interrupted if the Express Connect circuit is down.
NoteHealth checks send probe packets at the interval you specify. The health check fails if all consecutive probe packets (the number you specify) are lost.
Repeat Step 3 to Step 4 to configure a health check for VBR2.
Step 5: Enable BFD on the VBRs
Enable BFD on the VBRs to implement fast route convergence.
Log on to the Express Connect console.
In the top menu bar, select the destination region. In the navigation pane on the left, click Virtual Border Routers (VBRs).
On the Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) page, find the VBR that you want to manage and click Edit in the Actions column.
In the Edit VBR panel, set the BFD parameters and click OK.
This section describes only the BFD parameters. Keep the default values for other parameters.
Parameter
Description
Interval for Sending
The interval at which BFD packets are sent. Unit: ms.
This topic uses the default value 1000 ms.
Interval for Receiving
The interval at which BFD packets are received. Unit: ms.
This topic uses the default value 1000 ms.
Detection Time Multiple
The maximum number of BFD packets that can be lost before the connection is considered down.
This topic uses the default value 3.
Return to the Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) page and click the ID of the VBR.
On the VBR details page, click the BGP Peers tab.
Find the BGP peer that you want to manage and click Edit in the Actions column.
In the Modify BGP Peer panel, select the Enable BFD check box, configure BFD Hop Count, and then click OK.
NoteBFD supports custom single-hop or multi-hop sessions. You can configure the number of hops based on your physical link.
Step 6: Test the connectivity
Perform the following steps to test the connectivity of the active/standby Express Connect circuits.
Before you begin, make sure you the security rules of ECS instances allow access from the on-premises data center. For more information, see View security group rules.
- Open the Command Prompt window of your computer at the on-premises data center.
- Run the
pingcommand to connect to an ECS instance that belongs to the 192.168.0.0/24 CIDR block in the VPC. If the ping request is successful, the connection between the on-premises data center and Alibaba Cloud is established. - Disconnect a leased line (for example, from VBR1 to CPE1) and run the
tracertcommand. You can see that the CEN instance switches routes and that all traffic from Alibaba Cloud to the on-premises data center is forwarded over VBR2.