The trash feature of Hadoop is an important feature for a Hadoop file system. You can use the feature to restore files and directories that are deleted. This topic describes how to use the trash feature of Hadoop.
Background information
The trash feature is implemented based on the client-side encapsulation of Hadoop FileSystem APIs by Hadoop Shell or specific services such as Hive. When you enable the trash feature for a client or a server, Hadoop Shell calls the rename operation of FileSystem to move the files or directories that you want to delete to the /user/<username>/.Trash/Current directory. If you do not enable the trash feature, Hadoop Shell calls the delete operation of FileSystem to delete the files or directories.
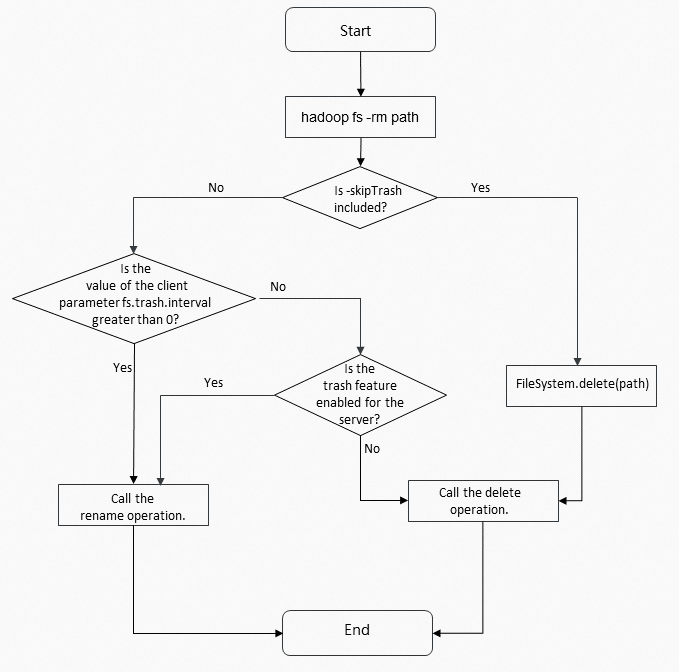
Enable the trash feature
To enable the trash feature, set the fs.trash.interval parameter to a value that is greater than 0. If you enable the trash feature, the related files and directories are moved to the trash directory when you run the rm command to delete files or directories from HDFS, Object Storage Service (OSS), OSS-HDFS, or JindoFS.
Disable the trash feature
If you disable the trash feature, you cannot restore the files and directories after you run the rm command. We recommend that you do not disable the trash feature. If you want to disable the trash feature, set the fs.trash.interval parameter to 0. This configuration takes effect for HDFS only after you restart the NameNode component of HDFS.
Access a trash directory
The default trash directory is /user/<username>/.Trash/Current. If you want to access the trash directory that corresponds to HDFS or other storage services, add the required prefix. Examples: hdfs://hdfs-cluster/user/<username>/.Trash/Current and oss://bucket/user/<username>/.Trash/Current.
Clear data in a trash directory
- HDFS: By default, EMR clears data that is stored in the trash directory of HDFS after the data is stored for one day (1,440 minutes). You can configure the fs.trash.interval parameter to specify the time period in minutes after which you want to delete the checkpoint.
- OSS-HDFS: The EMR server clears data that is stored in the trash directory of OSS-HDFS after the data is stored for seven days. This time period is fixed. We recommend that you monitor and manage the trash directory on a regular basis to prevent the retained data from occupying additional storage space due to unknown reasons.
- OSS: EMR cannot automatically clear data that is stored in the trash directory of OSS. To clear the data that is stored in the trash directory of OSS, configure a lifecycle rule for the trash directory. For more information about how to configure lifecycle rules, see Lifecycle rules based on the last modified time.
- JindoFS in block storage mode: You must manually clear data that is stored in the trash directory of JindoFS in block storage mode.