EMR Remote Shuffle Service (ESS) is an extension provided by E-MapReduce (EMR) to optimize shuffle operations of compute engines.
Background information
The current shuffle solution has the following disadvantages:
A data overflow occurs if a large amount of data exists in a shuffle write task. This causes write amplification.
A large number of small-size network packets exist in a shuffle read task. This causes connection reset.
A large number of small-size I/O requests and random reads exist in a shuffle read task. This causes high disk and CPU loads.
If thousands of mappers (M) and reducers (N) are used, a large number of connections are generated, which makes it difficult for jobs to run. The number of connections is calculated by using the following formula: M × N.
The Spark shuffle service runs on NodeManager. If the amount of data involved in shuffling is extremely large, NodeManager will be restarted. This affects the stability of YARN-based task scheduling.
The shuffle-based ESS service provided by EMR can optimize the shuffle solution. ESS has the following advantages:
Reduces the memory pressure that is caused by mappers by using push-style shuffle instead of pull-style shuffle.
Supports I/O aggregation, reduces the number of connections in a shuffle read task from M × N to N, and converts random read to sequential read.
Uses a two-replica mechanism to reduce the probability of fetch failures.
Supports compute-storage separation. The shuffle service can be deployed in a separated hardware environment.
Eliminates the dependency on local disks when Spark on Kubernetes is used.
The following figure shows the architecture of ESS. 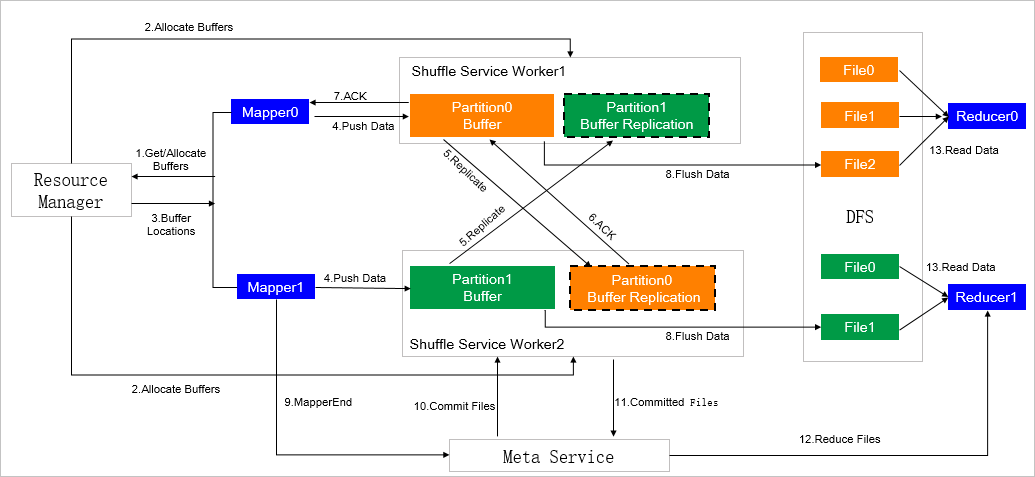
Limits
This topic applies only to EMR V4.X.X, a minor version earlier than EMR V3.39.1, or a minor version earlier than EMR V5.5.0. If you want to use ESS in EMR V3.39.1 or a later minor version, or EMR V5.5.0 or a later minor version, see RSS.
Create a cluster
EMR V4.5.0 is used as an example. You can create a cluster with ESS deployed by using one of the following methods:
Create an EMR Shuffle Service cluster.
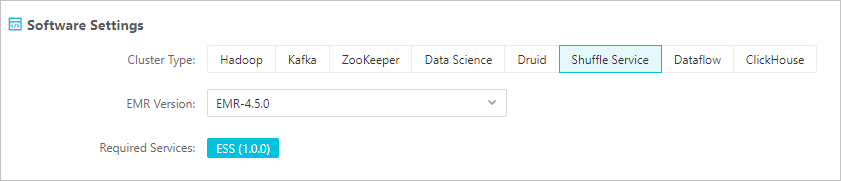
Create an EMR Hadoop cluster.
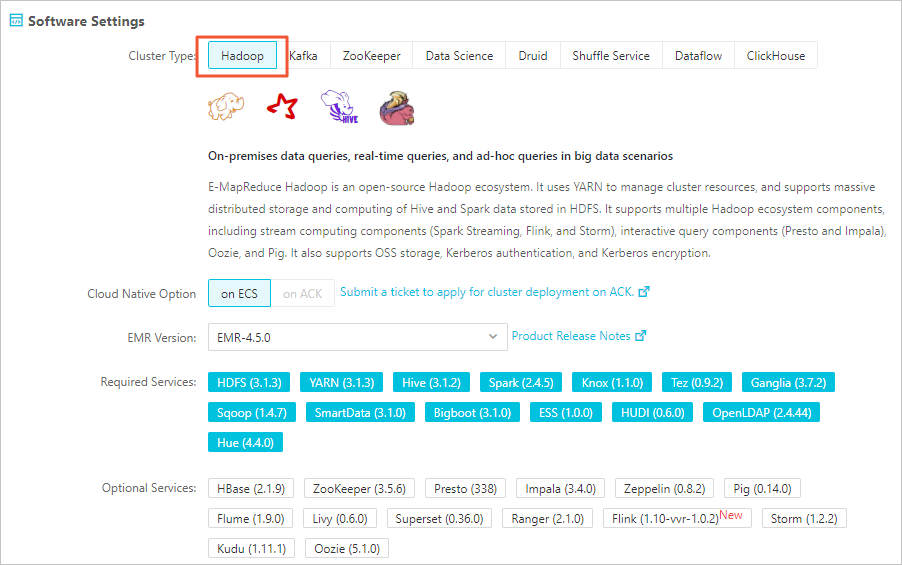
For more information about how to create a cluster, see Create a cluster.
Use ESS
If ESS is required when you use Spark, you must add the parameters that are described in the following table when you submit a Spark job. For more information about the parameter configurations, see Edit jobs.
For more information about Spark-related parameters, see Spark Configuration.
Parameter | Description |
spark.shuffle.manager | Set the value to org.apache.spark.shuffle.ess.EssShuffleManager. |
spark.ess.master.address | Specify this parameter in the format of <ess-master-ip>:<ess-master-port>. where:
|
spark.shuffle.service.enabled | Set the value to false. To use the ESS service provided by EMR, you must disable the original external shuffle service. |
spark.shuffle.useOldFetchProtocol | Set the value to true. ESS is compatible with the original shuffle protocol. |
spark.sql.adaptive.enabled | Set the value to false. ESS does not support adaptive execution. |
spark.sql.adaptive.skewJoin.enabled |
Parameters
You can view the settings of all parameters for ESS on the ESS service configuration page.
Parameter | Description | Default value |
ess.push.data.replicate | Specifies whether to enable the two-replica feature. Valid values:
Note We recommend that you enable the two-replica feature in the production environment. | true |
ess.worker.flush.queue.capacity | The number of flush buffers in each directory. Note You can configure multiple disks to improve performance. To improve the overall read and write throughput, we recommend that you configure a maximum of two directories on each disk. The heap memory used by flush buffers in each directory is calculated by using the following formula: ess.worker.flush.buffer.size × ess.worker.flush.queue.capacity. Example: | 512 |
ess.flush.timeout | The timeout period for flushing data to the storage layer. Unit: seconds. | 240s |
ess.application.timeout | The heartbeat timeout period of your application. Unit: seconds. After the heartbeat timeout period elapses, application-related resources are cleared. | 240s |
ess.worker.flush.buffer.size | The size of a flush buffer. Unit: KB. If the size of a flush buffer exceeds the upper limit, flushing is triggered. | 256k |
ess.metrics.system.enable | Specifies whether to enable monitoring. Valid values:
| false |
ess_worker_offheap_memory | The size of off-heap memory of a core node. Unit: GB. | 4g |
ess_worker_memory | The size of heap memory of a core node. Unit: GB. | 4g |
ess_master_memory | The size of heap memory of the master node. Unit: GB. | 4g |