This topic describes how to use a CLI to connect to Impala in the E-MapReduce (EMR) console.
Prerequisites
An EMR cluster is created, and Impala is selected when you create the cluster. For more information, see Create a cluster.
Use impala-shell to connect to Impala
Before you connect to Impala, you can run the impala-shell --help command to obtain help information.
Common cluster
Log on to the master node of your cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Run the following command to connect to Impala:
impala-shell -i <Node name of Impalad>To obtain the
name of an Impalad node, go to the Status tab of the Impala service page of your cluster in the EMR console. The nodes of Impalad are displayed in the Topology List section. For example, in the following figure, the nodes core-1-1 and core-1-2 are displayed. You can replace <Node name of Impalad> in the preceding command with core-1-1 or core-1-2.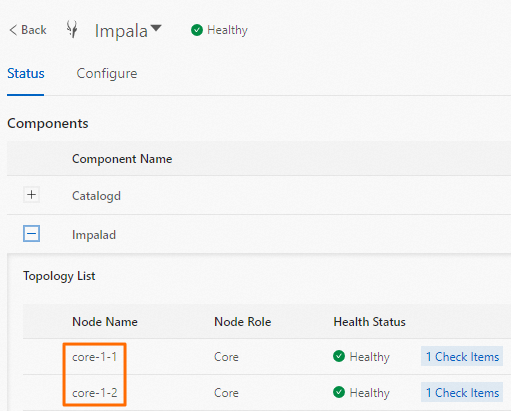
Optional. Run the
quit;command to exit the Impala CLI.
High-security cluster
Log on to the master node of your cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Initialize a Kerberos credential.
Run the following command to check whether Kerberos credentials are available:
klistIf the information
klist: No credentials cache foundis returned, initialize a Kerberos credential. If the returned information indicates that Kerberos credentials are available, run the impala-shell command to connect to Impala.Run the following command to view the information about a principal:
klist -k $IMPALA_CONF_DIR/impala.keytabSave the first row of the returned information, which needs to be used in the following step. For example, save
impala/master-1-1.c-45dcb9bbe234****.cn-hangzhou.emr.aliyuncs.com@EMR.C-45DCB9BBE23****.COMin the following figure.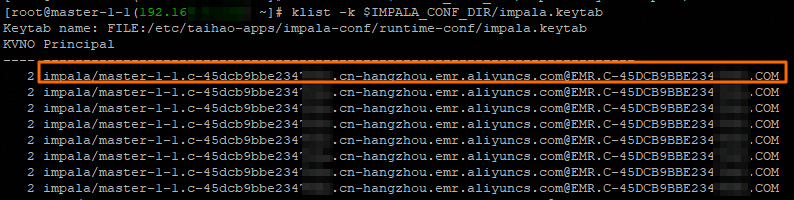
Run the following command to initialize a Kerberos credential:
kinit -k -t $IMPALA_CONF_DIR/impala.keytab <Principal information>NoteReplace
<Principal information>in the command with the row of information that you save in the previous step.
Run the following command to connect to Impala:
impala-shell -k -i <Node name of Impalad>Optional. Run the
quit;command to exit the Impala CLI.
Use Beeline to connect to Impala
Common cluster
Log on to the master node of your cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Run the following command to connect to Impala:
beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://<Node name of Impalad>:28000/default;transportMode=http;uauth=noSasl'Optional. Run the
quit;command to exit the Impala CLI.
High-security cluster
Log on to the core node of the cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Initialize a credential as the root user.
Run the following command to check whether Kerberos credentials are available:
klistIf the information
klist: No credentials cache foundis returned, initialize a Kerberos credential. If the returned information indicates that Kerberos credentials are available, run the impala-shell command to connect to Impala.Run the following command to view the information about a principal:
klist -k $IMPALA_CONF_DIR/impala.keytabSave the first row of the returned information, which needs to be used in the following step. For example, save
impala/master-1-1.c-45dcb9bbe234****.cn-hangzhou.emr.aliyuncs.com@EMR.C-45DCB9BBE23****.COMin the following figure.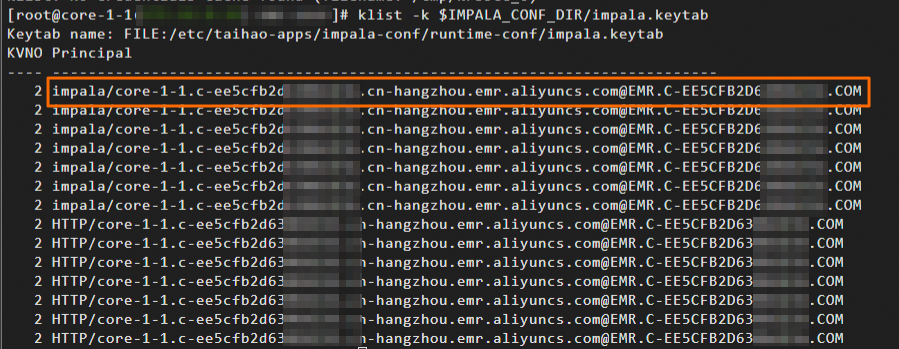
Run the following command to initialize a Kerberos credential:
kinit -k -t $IMPALA_CONF_DIR/impala.keytab <Principal information>NoteReplace
<Principal information>in the command with the row of information that you save in the previous step.
Run the following command as the root user to connect to Impala:
beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://<Node name of Impalad>:28000/default;principal=<Principal information>;transportMode=http'Optional. Run the
!quitcommand to exit the Impala CLI.