The outgoing response header from an Edge Security Acceleration (ESA) point of presence (POP) is part of the HTTP response message header. It carries specific response parameters and passes them to the client. You can configure the outgoing response headers of ESA POPs to control the response headers when resources are returned. ESA lets you add, modify, and delete outgoing response header rules to meet various business needs.
Overview
When a client requests a resource, the request first reaches ESA. If the resource is not found in the ESA POP cache, ESA sends an origin request to the origin server to retrieve the data. After the origin server returns the data, the ESA POP modifies the original response based on your configured response header rules. For example, it can add, replace, or delete specific fields. Finally, ESA returns the complete resource, including the modified response headers, to the client. This helps you implement cross-domain access control, cache policy optimization, and other business requirements.

Use cases
Inform the client of the resource type of the ESA response file: For example, you can add the
Content-Type: text/htmlresponse header. This tells the client that the ESA response file is in HTML format so it can be rendered correctly.Enable cross-origin resource access: When a user requests a resource from a domain name on ESA, you can configure the
Access-Control-Allow-Originresponse header in the response message from ESA. This enables cross-origin access. For more information, see Configure cross-origin resource sharing.Customize response behavior: You can add or modify custom headers to adjust the content and format of the response received by the client. This lets you implement specific features or use them for tracking purposes.
Notes
If you add multiple rules, they are executed sequentially from top to bottom in the rule list. A rule is overwritten by a subsequent rule with the same response header name. This may cause unexpected results.
Example 1
The response message contains the response header
test:123.A rule is added to set the response header
test:321.
If the response message hits the rule, the original response header test:123 is overwritten with test:321.
Example 2
The response message contains the response header
test:123.A rule is added to set the response header
test:321. Then, another rule is configured to delete thetestresponse header.
If the response message hits the rules, the original response header test:123 is deleted.
Procedure
After you add a rule, when a user requests a resource, ESA matches and executes rules sequentially based on the rule execution priority.
In the ESA console, select Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Select the Modify Response Header tab, click the ESA to Client section, and then click Create Rule.
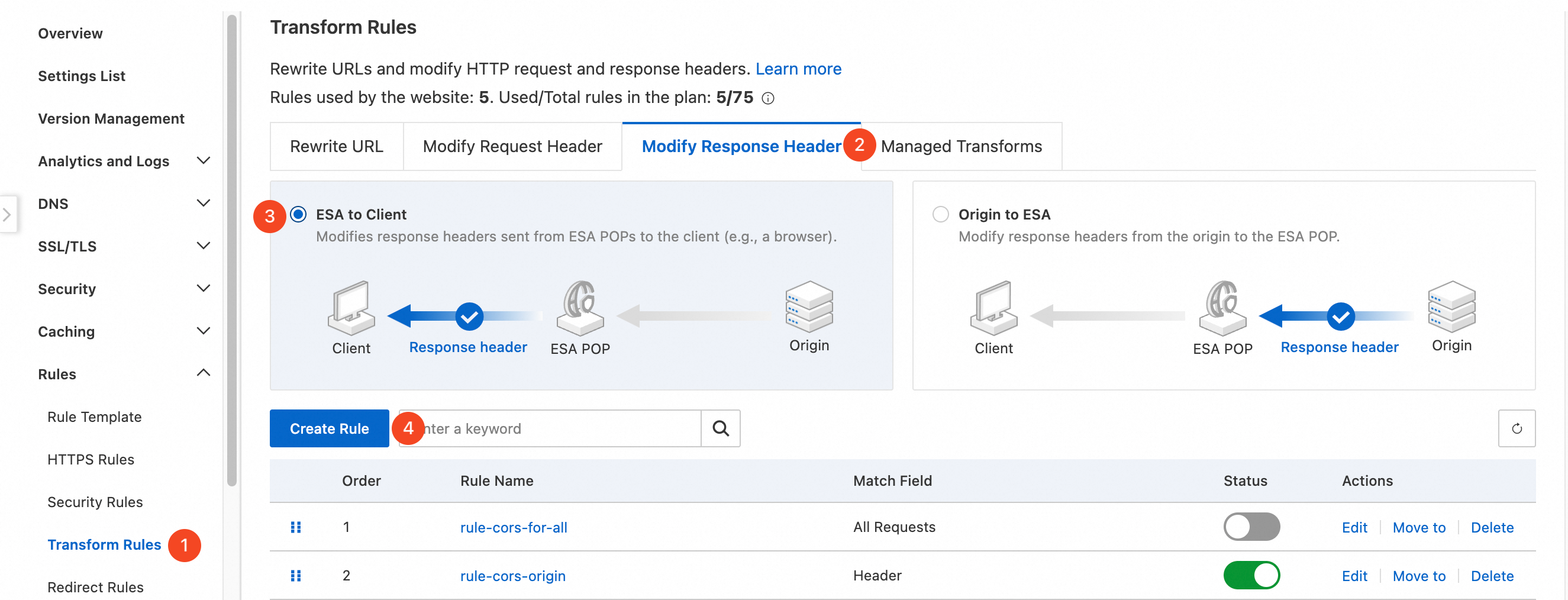
Click Create Rule. In the If requests match... section, set the user request features to match. For more information about how to configure rules, see Components of a rule expression.
In the Modify Response Header section, select an Operation, enter a Response Header Name and Response Header Value, and then click OK.
Procedure
Type
Description
Example
Add
Static
Adds the specified response header to the response sent to the client.
If the response header already contains a header with the same name, the new header overwrites the existing one.
To add a response header with the name
x-codeand the valuekey1, specify the following:Response Header Name:
x-codeResponse Header Value:
key1
Dynamic
The response header value can be set to an expression.
To add a response header named
Client-Ip-Geo-Locationwith the valueip.geoip.countryto record the country or region of the client IP address, specify the following:Response Header Name:
Client-Ip-Geo-LocationResponse Header Value:
ip.geoip.country
Change
Static
Changes the value of the specified response header in the response sent to the client.
To modify the response header named
x-codeto the valuekey2, specify the following:Response Header Name:
x-codeResponse Header Value:
key2
Dynamic
The response header value can be set to an expression.
To modify the response header named
Client-Ip-Geo-Locationto the valueip.geoip.country, changing the header value to the country or region of the client IP address, specify the following:Response Header Name:
Client-Ip-Geo-LocationResponse Header Value:
ip.geoip.country
Delete
Deletes all parameter values that match the Response Header Name from the response sent to the client, regardless of whether there are duplicate response header parameters.
To delete the response header named
x-code, specify the Response Header Name:x-code.NoteDo not set a Response Header Name that starts with
ali-innerorali-swift.You can configure multiple values in the Response Header Value field. Separate them with commas (
,).The delete operation works the same for both static and dynamic schemas.
The modify operation changes an existing response header. The operation takes effect only if a response header with the specified name exists in the original response.
Configuration example
If you use OSS as the origin server and configure CORS in both the OSS and ESA consoles, the ESA configuration overwrites the OSS CORS settings.
Apply to all requests
Use case
This use case allows all requests from the current site, such as example.com, to access resources from any other origin.
Steps
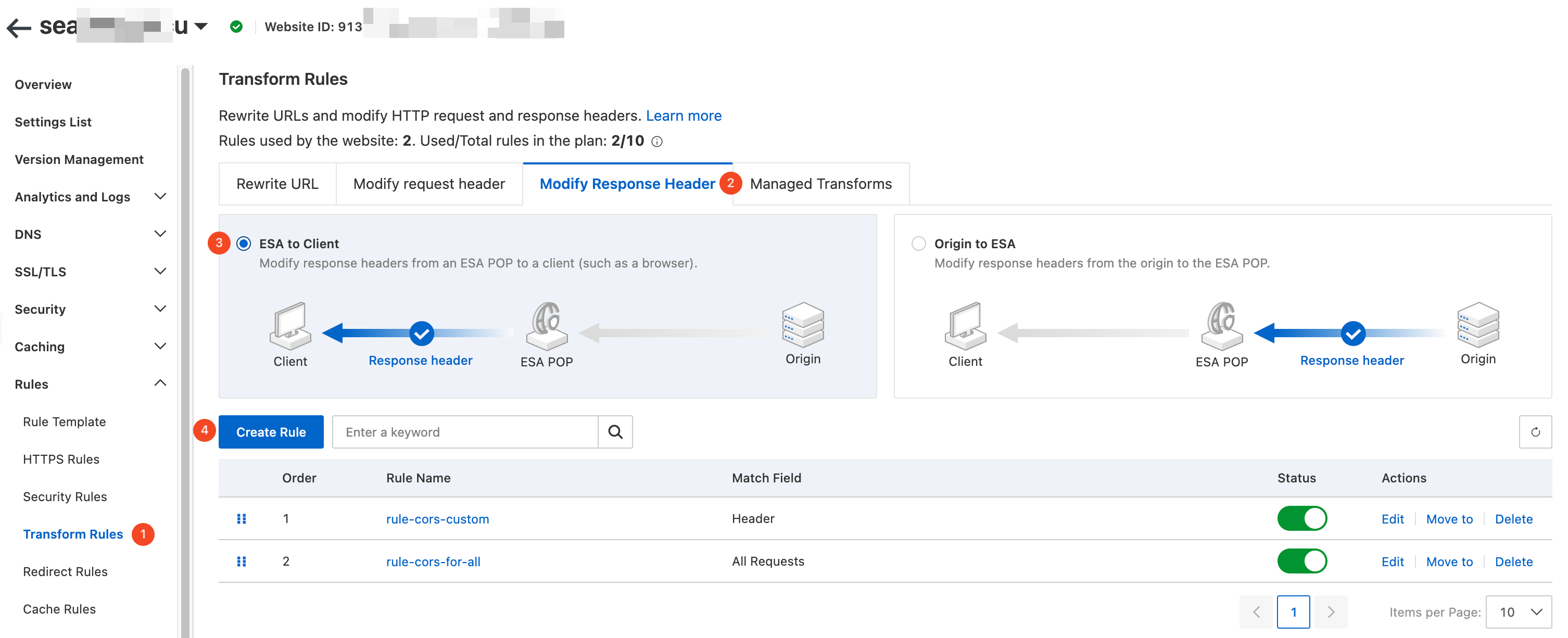
In the ESA console, select Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the Transform Rules page, click the Modify Response Header tab. Set Response Header Position to ESA to Client, and then click the Create Rule button.
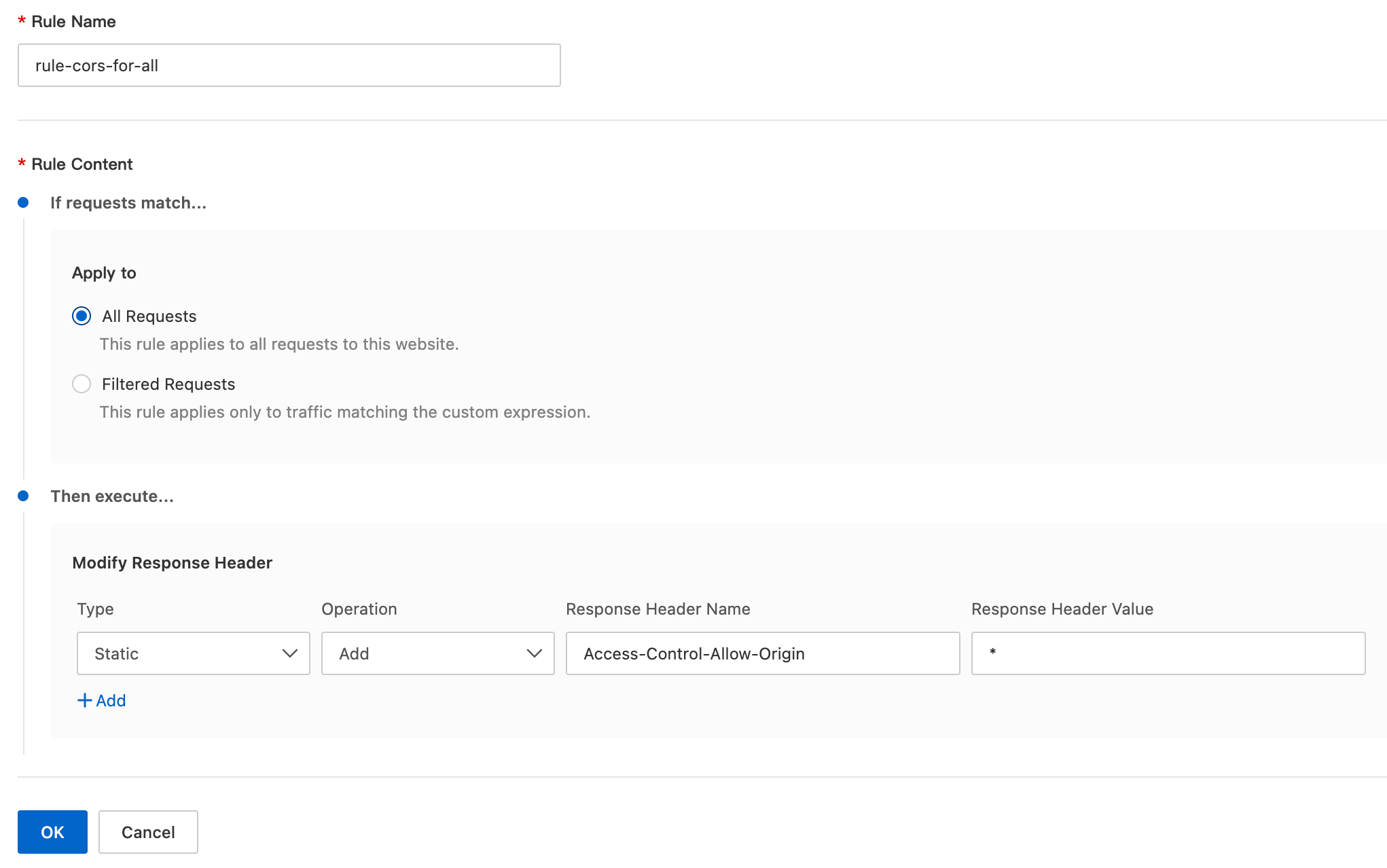
On the Create Response Header Modification Rule page, configure the parameters as follows:
Rule Name: Enter a custom rule name, such as
rule-cors-for-all.If requests match...: Set the rule conditions to filter client requests. For this example, select All Requests.
Then execute...: Set the action to modify the response header. For this example, configure the following parameters:
Type: Select Static.
Operation: Select Add.
Response Header Name: Enter
Access-Control-Allow-Origin.Response Header Value: Enter
*.
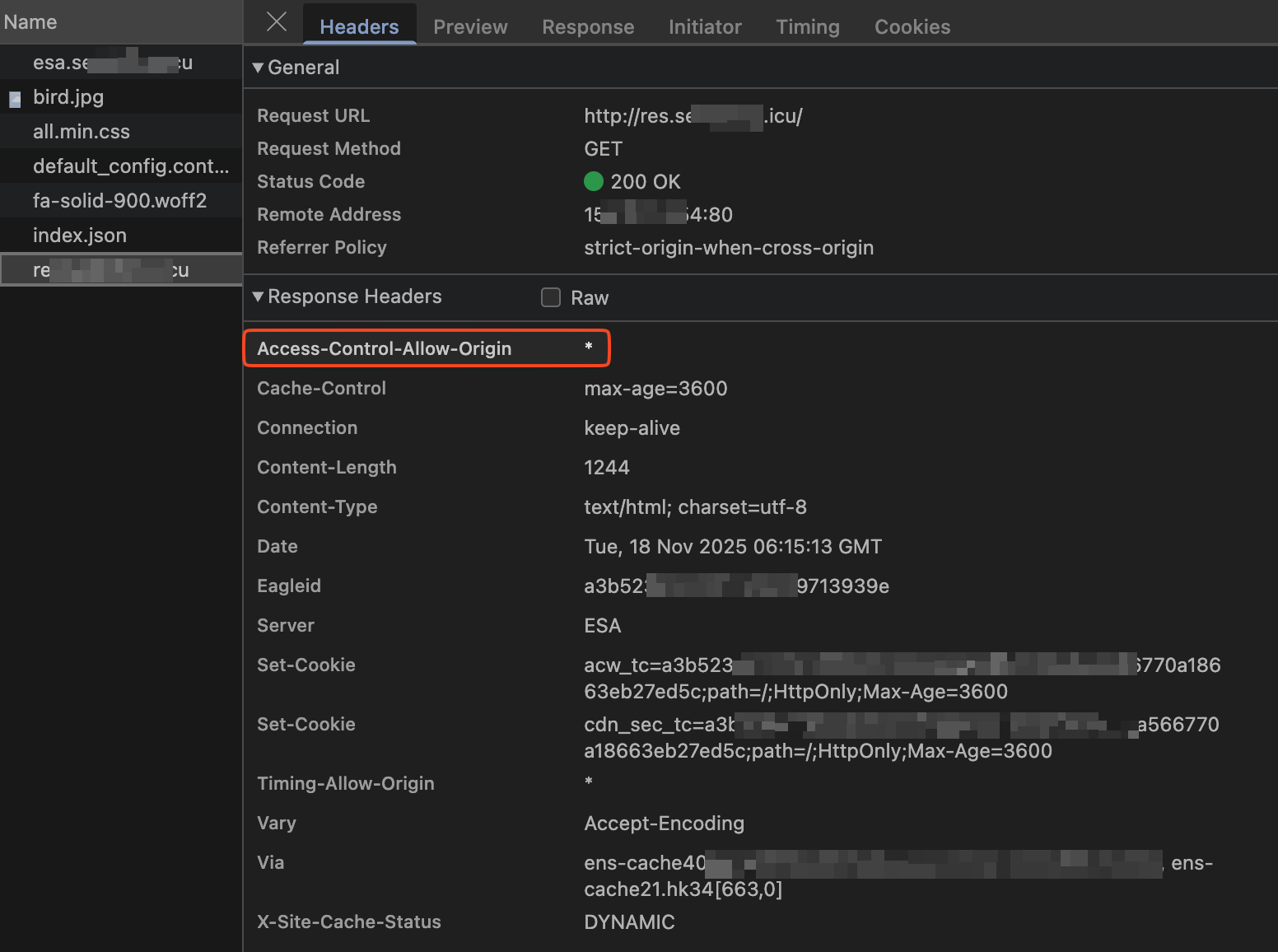
Result
For any cross-origin request, ESA adds the Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * header to the response. The browser can then process the response and display the cross-origin resource.
Apply to specific requests
Use case
This use case applies when the value of the origin header in a client request is a subdomain of example.com. It supports both the HTTP and HTTPS protocols. For example, cross-origin access is allowed for the following origins:
origin:http://www.example.comorigin:https://www.example.comorigin:http://image.example.comorigin:https://image.example.com
Add a CORS header to the response. The value of the CORS response header must be the same as the value of the origin header in the request.
Configuration steps
In the ESA console, select Websites. In the Website column, click the target site.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the Transform Rules page, click the Modify Response Header tab. Set Response Header Position to ESA to Client, and then click the Create Rule button.

On the Create Response Header Modification Rule page, configure the parameters as follows:
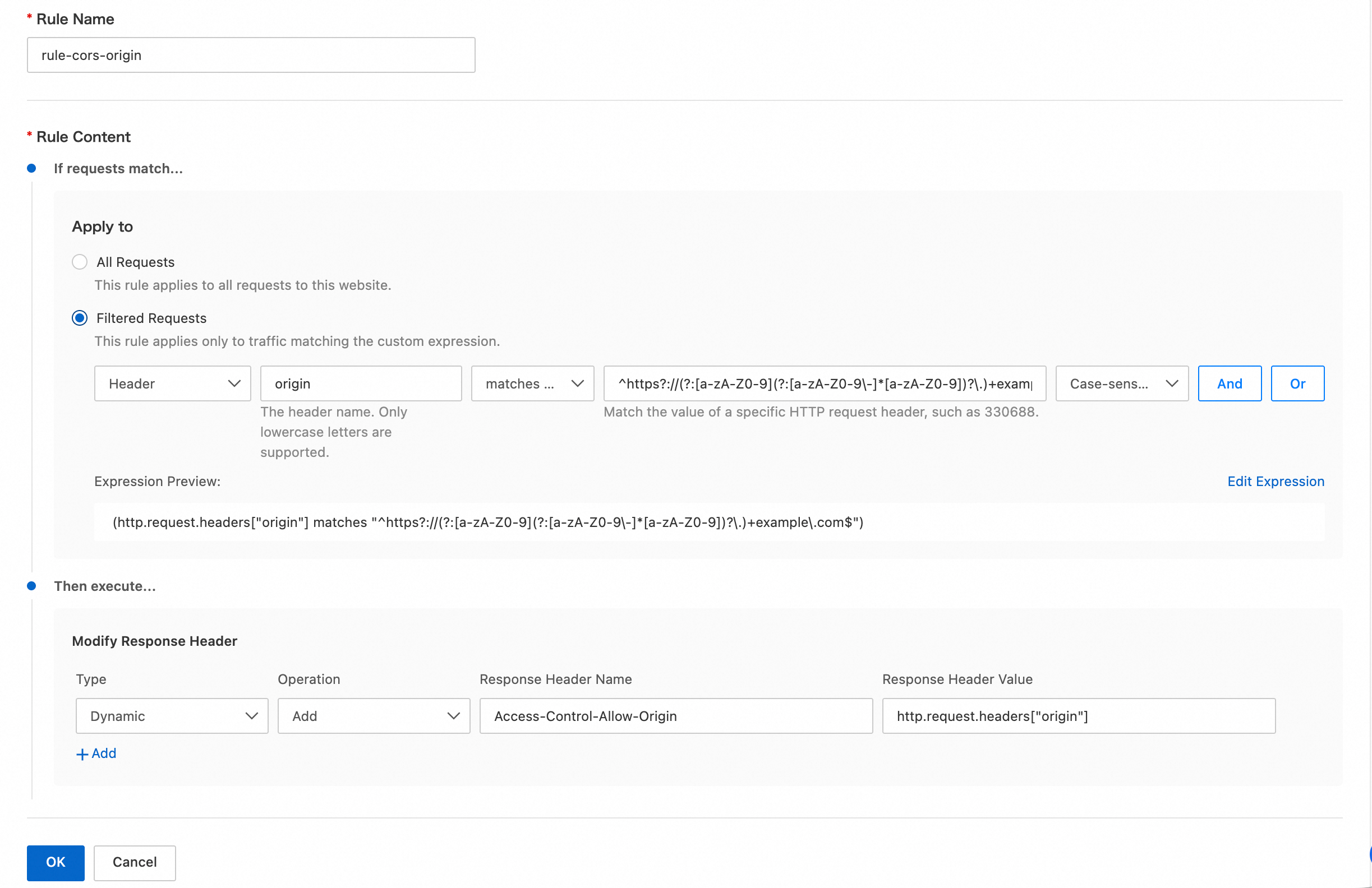
Rule Name: Enter a custom rule name, such as
rule-cors-origin.If requests match...: Set the rule conditions to filter client requests. This ensures that the action is executed only for requests that meet specific criteria. For this example, set the condition to
Header Value of origin matches regex ^https?://(?:[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9\-]*[a-zA-Z0-9])?\.)+example\.com$.You can also directly edit the expression as follows:
(http.request.headers["origin"] matches "^https?://(?:[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9\-]*[a-zA-Z0-9])?\.)+example\.com$")NoteIf your plan does not support matching with regular expressions, use the
is inoperator and list the allowed origin header values.You can also directly edit the expression as follows:
(http.request.headers["origin"] in {"http://www.example.com" "https://www.example.com" "http://image.example.com" "https://image.example.com"})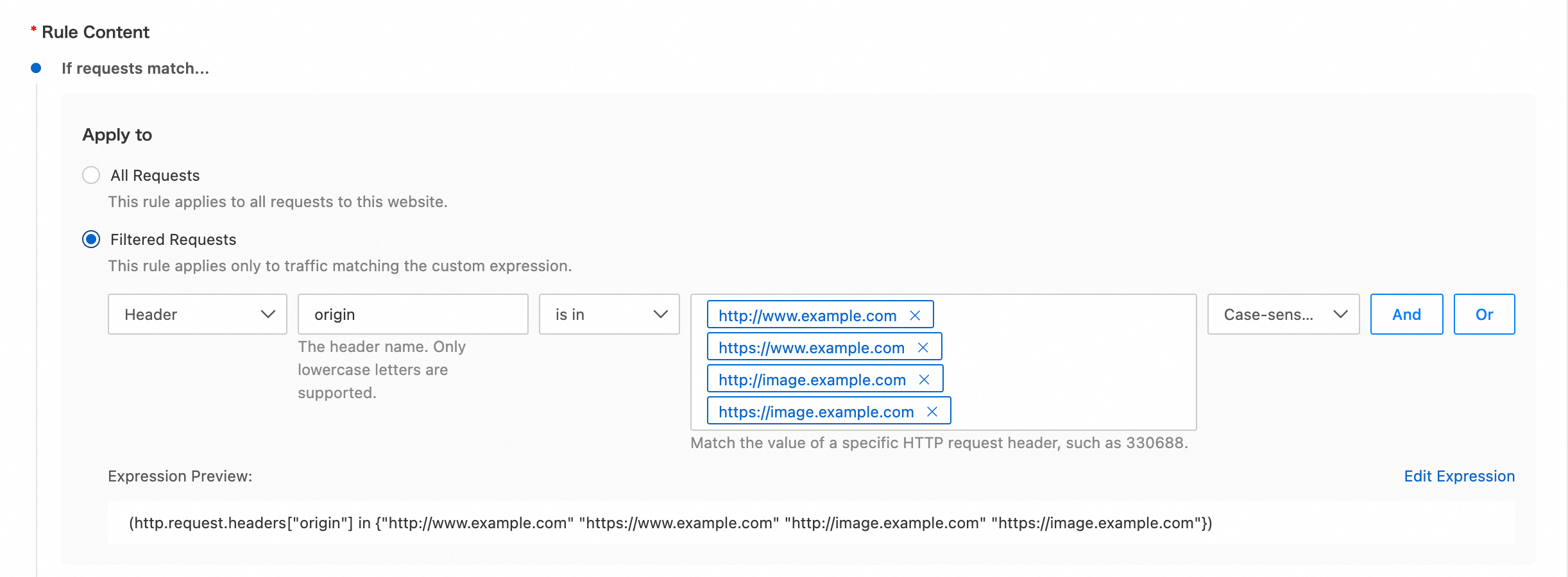
Then execute...: Set the action to modify the response header. For this example, configure the following parameters:
Type: Select Dynamic.
Operation: Select Add.
Response Header Name: Enter
Access-Control-Allow-Origin.Response Header Value: Enter
http.request.headers["origin"].
Result
When a cross-origin request is made, if the origin header in the request matches the rule, ESA adds the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the response. The value of this header is the same as the value of the Origin header from the client request. The browser can then process the response and display the cross-origin resource.
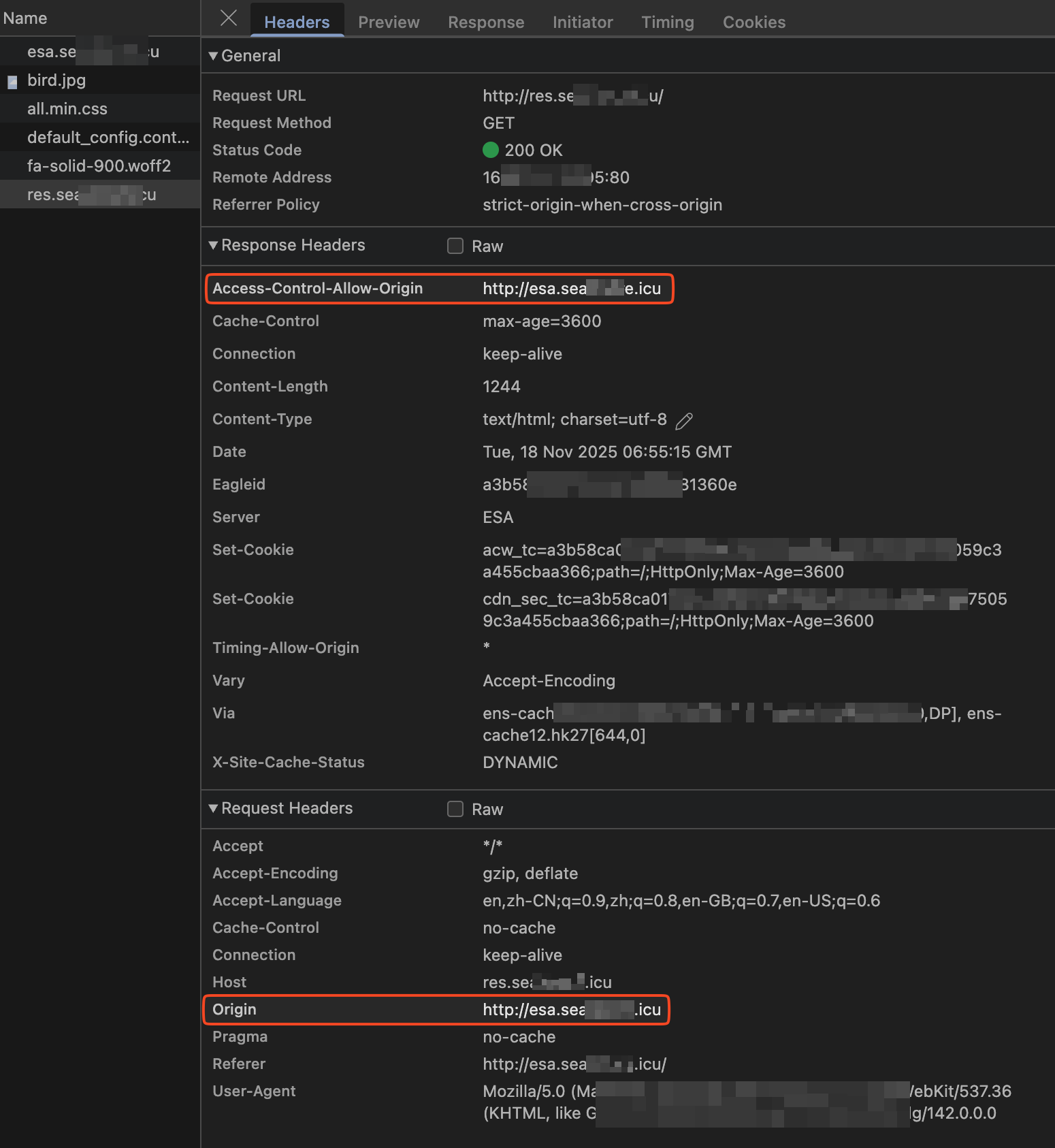
Response header parameter descriptions
Response header parameter | Description | Example |
Custom | You can add custom response headers. The custom response header name must meet the following requirements:
| Test-Header |
Cache-Control | Specifies the caching mechanism that the client program's requests and responses must follow. | no-cache |
Content-Disposition | Specifies the default filename when the client program saves the requested content as a file. | examplefile.txt |
Content-Type | Specifies the content type of the response object for the client program. | text/plain |
Pragma | Pragma is a general header defined in HTTP/1.0. This header is typically used in server responses to define the client's caching behavior for files. | no-cache |
Access-Control-Allow-Origin | Specifies which origins can access the resource. It is part of the cross-origin resource sharing (
|
|
Access-Control-Allow-Methods | Specifies the allowed methods for cross-origin requests. Separate multiple methods with commas ( | POST,GET |
Access-Control-Allow-Headers | Specifies the allowed fields for cross-origin requests. | X-Custom-Header |
Access-Control-Expose-Headers | Specifies the custom headers that can be accessed. | Content-Length |
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials | This response header indicates whether the response to the request can be exposed to the page.
| true |
Access-Control-Max-Age | Specifies the cache duration for the preflight request result of a specific resource for the client program, in seconds. | 600 |
References
Rule-related features vary in execution priority, rule behavior, and configuration scope. For more information, see How ESA rules take effect.