To accelerate the delivery of both static and dynamic resources, you can enable the dynamic acceleration feature and create custom acceleration rules for static resources by configuring static file types. This allows you to cache static resources on points of presence (POPs) and retrieve dynamic resources from the origin server over an optimal route.
Background information
The following acceleration rules apply to static and dynamic resources:
On
To accelerate the delivery of static and dynamic resources, you need to enable dynamic acceleration. You can configure acceleration rules for static resources by file type based on your business requirements. Then, static resources are distributed based on the custom acceleration rules. You can also configure the file types, URIs, and paths of static resources that you want to cache.
Off
If you no longer need to accelerate the delivery of dynamic resources, you can disable dynamic acceleration. Then, dynamic resources are distributed based on static content cache rules without acceleration. Only the default acceleration rules for static files remain valid. All custom acceleration rules for static files become invalid.
Procedure
Configure static file types.
Log on to the DCDN console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the domain name for which you want to configure static file types and click Configure.
In the left-side navigation tree of the domain name, click Acceleration Rules.
Turn on Dynamic Acceleration.
On the Static File Types tab, click Modify.
In the Static File Types dialog box, configure the Static File Types parameter. The following table describes the parameter:
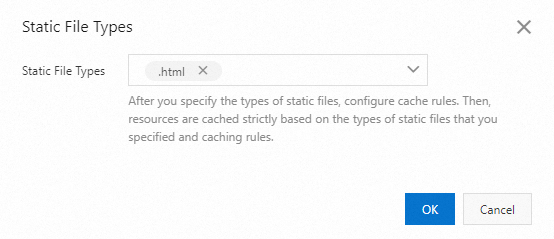
Parameter
Description
Static File Types
The following types of static files are supported:
Images: GIF, PNG, BMP, JPEG, and JPG.
Web pages: HTML, HTM, and SHTML.
Audio and video files: MP3, WMA, FLV, MP4, WMV, OGG, and AVI.
Text files: DOC, DOCX, XLS, XLSX, PPT, PPTX, TXT, and PDF.
Others: ZIP, EXE, TAT, ICO, CSS, JS, SWF, APK, M3U8, TS, EJS, SVG, WOFF, and OTF.
Click OK.
Create a cache expiration rule.
In the Cache Expiration section, click Add.
In the Cache Duration dialog box, select Directory or Filename Extension for the Type parameter and configure other required parameters.
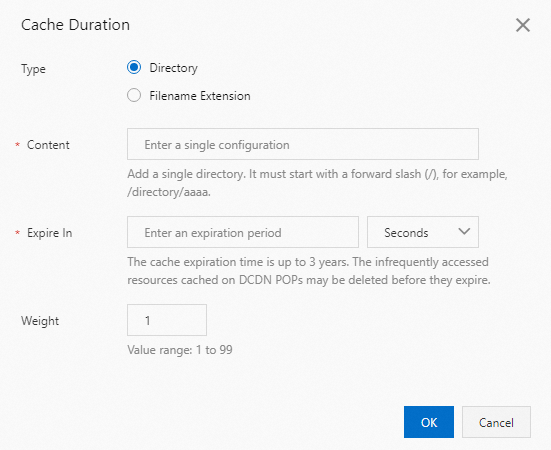
Parameter
Description
Type
Select Directory or Filename Extension.
Directory: adds a cache rule for resources in the same directory.
Filename Extension: adds a cache rule for resources that have the same file name extension.
Content
Specify the directory or filename extension for which you want to add the cache rule.
If you select Directory, take note of the following rules:
You can enter only one directory at a time. You can use a forward slash (/) to specify all directories.
You can enter a full path. The path must start with a forward slash (/). Example: /directory/aaa.
If you select Filename Extension, take note of the following rules:
You can enter one or more filename extensions. Separate the filename extensions with commas (,). Example:
jpg,txt. Filename extensions are case-sensitive.The following types of static files are supported:
Images: GIF, PNG, BMP, JPEG, and JPG.
Web pages: HTML, HTM, and SHTML.
Audio and video files: MP3, WMA, FLV, MP4, WMV, OGG, and AVI.
Text files: DOC, DOCX, XLS, XLSX, PPT, PPTX, TXT, and PDF.
Others: ZIP, EXE, TAT, ICO, CSS, JS, SWF, APK, M3U8, TS, EJS, SVG, WOFF, and OTF.
You cannot use the asterisk wildcard character (*) to specify all file types.
Expire In
Specify the TTL. The maximum TTL is three years. Take note of the following rules:
Specify a TTL of one month or longer for static files that are infrequently updated, such as images and application packages.
Specify a TTL for static files that are frequently updated, such as JavaScript and CSS files, based on your business requirements.
Specify a TTL of 0 seconds to disable caching for dynamic files, such as PHP, JSP, and ASP files.
Weight
Specify a weight for the cache rule. The weight indicates the priority of the cache rule. Valid values: 1 to 99. A larger value specifies a higher priority.
NoteIf you create multiple cache rules, we recommend that you specify a unique weight for each cache rule to define their priorities.
Cache rules that have the same weight are prioritized based on the creation time, regardless of the rule type. The rule that has the earliest creation time takes precedence.
If you have configured multiple cache rules for a cached resource, only the first matched rule takes effect.
Click OK.