After you add your website to Alibaba Cloud Dynamic Content Delivery Network (DCDN), you can configure custom HTTP response headers to enable cross-origin access.
What is CORS?
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a standard cross-origin solution that is provided by HTML5 to allow web pages to access and load resources from different origin servers. This ensures the security of data transmission. For more information, see Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS).
Benefits
For security purposes, browsers use the same-origin policy. This restricts scripts from initiating requests to access and load resources from different domains or subdomains, or over different protocols or ports. For example, example.com cannot access resources on example.org. When you configure CORS, you can specify response headers that points of presence (POPs) return to clients. This way, if a request carries a header that is included in the allowed headers, the corresponding HTTP response header is returned, and the requested resources can be accessed and loaded even from a different origin.
How CORS works
CORS not enabled

A client sends a request for http://example.com/index.html to example.com. example.com returns the index.html file to the client, and a script in the index.html file initiates a request for http://example.org/api.
The client sends a request that contains the Origin:example.com header to example.org. By default, the POP does not return the cross-origin header because CORS is not enabled. Due to cross-origin restrictions, the browser blocks the response to this request, resulting in the error "No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource" displayed.

CORS enabled

A client sends a request for http://example.com/index.html to example.com. example.com returns the index.html file to the client, and a script in the index.html file initiates a request for http://example.org/api.
The client sends a request that contains the Origin:example.com header to example.org. After CORS is enabled, the POP checks whether the value of the Origin header in the request matches the value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. Exact match and wildcard domain name match of one or more values are supported. If the values match, the cross-origin header is returned, such as Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://example.com.
After the client receives the response, if the value of the cross-origin response header is http://example.com, which complies with the CORS policy, the result is displayed.
Usage notes
If the origin server is an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket and CORS is configured in both the OSS and DCDN consoles, the CORS settings in DCDN are used. For more information, see CORS.
If the origin server is an on-premises server or an ECS instance, we recommend that you separate dynamic content from static content. This way, the delivery of static content is accelerated by DCDN. The CORS settings in DCDN take effect only for static resources. For more information, see Dynamic and static content acceleration rules.
Enable CORS
Log on to the DCDN console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the domain name that you want to manage and click Configure.
In the left-side navigation tree of the domain name, click Caching.
Click the Custom HTTP Response Header tab. Then click Add.
Configure the parameters according to the following table and click OK.
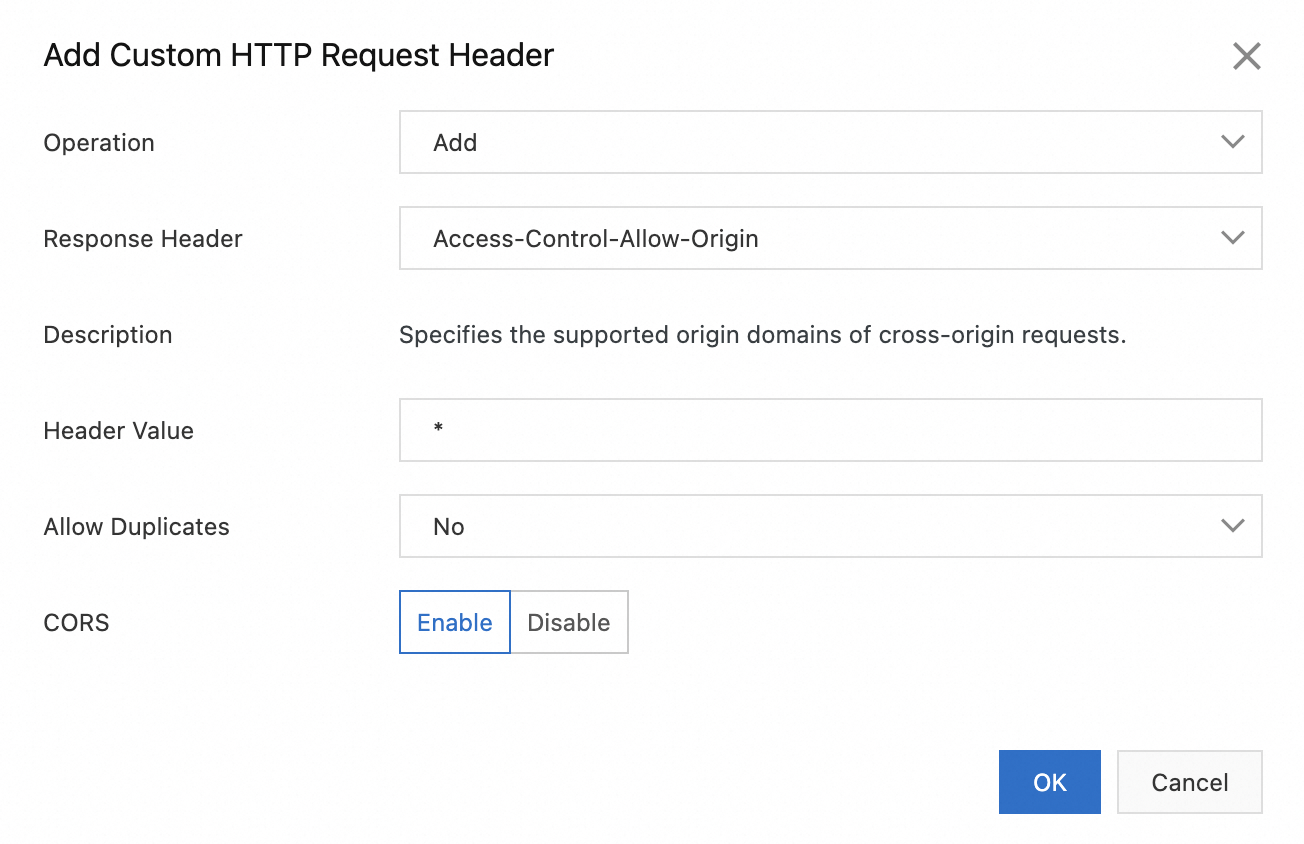
Parameter
Example
Operation
Add
Response Header
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
Header Value
*
NoteYou can set this header to an asterisk (*), which matches all origins.
If this header is not set to an asterisk (*), you can configure one or more IP addresses, domain names, or a combination of IP address and domain names. Separate multiple values with commas (,).
If you set Header Value to a value other than a wildcard character (*), the value must start with http:// or https://.
Port numbers are supported.
Wildcard domain names are supported.
Allow Duplicates
No
NoteYes: Duplicate headers are allowed. The header that is returned from the origin server and the header that is added to the response are returned to the client.
No: Duplicate headers are not allowed. The header that is returned from the origin server is overwritten by the header that is added to the response.
ImportantThe Allow Duplicates and CORS settings are mutually exclusive. If you set Allow Duplicates to Yes, CORS becomes invalid.
CORS
Enable
NoteYou can configure the CORS parameter only if you set Operation to Add and Response Header to Access-Control-Allow-Origin.
Valid values of CORS: Disable and Enable. Default value: Disable.
Disable: POPs do not check the Origin header in user requests. In this case, POPs return the configured value of Access-Control-Allow-Origin.
Enable: POPs check the Origin header in user requests and specify a value for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header based on the following rules:
Wildcard pattern match: If you set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to an asterisk (*), Access-Control-Allow-Origin:* is returned regardless of whether user requests contain the Origin header or the value that is specified for the Origin header.Response Header
Exact match: You can specify one or more values for the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header. Separate multiple values with commas (,).Response Header
If the value of the Origin header in a user request matches a value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, the matched value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is returned.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request does not match a value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is not returned.
Wildcard domain name match: If you set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to a wildcard domain name, the value of the Origin header is matched against the wildcard domain name.Response Header
If you set the CORS parameter to Enable and the value that you want to specify for the Header Value parameter contains a hyphen (
-), you need to escape the hyphen (-) to%-. Examples:Original response header value:
http://doc.aliyun-example.com.Escaped response header value:
http://doc.aliyun%-example.com.
Configure the parameters according to the following table and click OK.
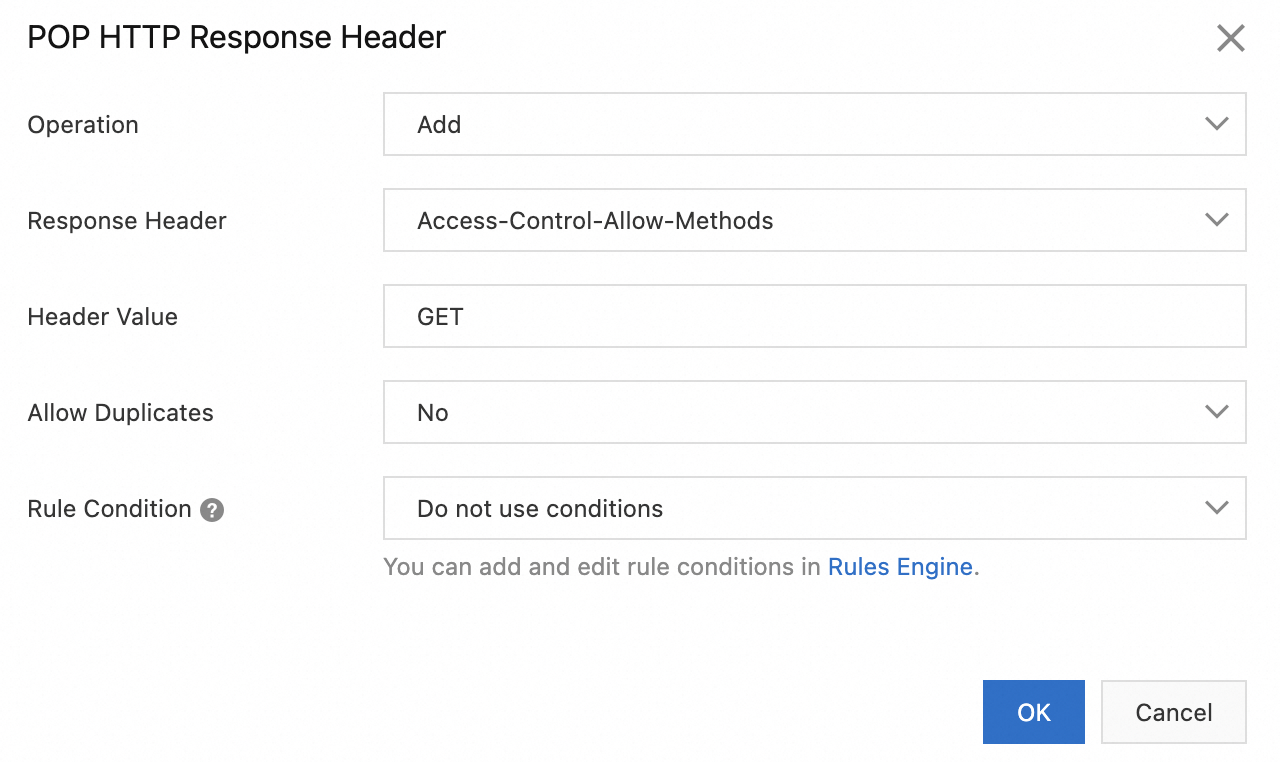
Parameter
Example
Operation
Add
Response Header
Access-Control-Allow-Methods
Header Value
GET, POST, or PUT
NoteIf you want to add GET, POST, and PUT at the same time, separate them with commas (,).
Allow Duplicates
No
NoteYes: Duplicate headers are allowed. The header that is returned from the origin server and the header that is added to the response are returned to the client.
No: Duplicate headers are not allowed. The header that is returned from the origin server is overwritten by the header that is added to the response.
In this example, the value No is used. You can configure this parameter based on your business requirements.
Examples
Example 1
If you set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to one or more values that are separated by commas (,):
If the value of the Origin header in a user request matches a value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, the matched value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is returned.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request does not match a value of the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is not returned.
In the DCDN console, the response header is set to Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://example.com,https://aliyundoc.com.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is http://example.com, POPs return Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://example.com.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is https://aliyundoc.com, POPs return Access-Control-Allow-Origin:https://aliyundoc.com.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is http://aliyun.com, POPs do not return Access-Control-Allow-Origin because the domain names do not match.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is http://aliyundoc.com, POPs do not return Access-Control-Allow-Origin because the request uses HTTP and POPs respond to HTTPS requests in this case.
Example 2
If you set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin parameter to a wildcard domain name, POPs check whether the value of the Origin header in a user request matches the wildcard domain name.
In the DCDN console, the response header is set to Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://*.aliyundoc.com.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is http://demo.aliyundoc.com, POPs return Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://demo.aliyundoc.com.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is http://demo.example.com, POPs do not return Access-Control-Allow-Origin because the domain names do not match.
If the value of the Origin header in a user request is https://demo.aliyundoc.com, POPs do not return Access-Control-Allow-Origin because the request uses HTTPS and POPs respond only to HTTP requests in this case.