The cache time-to-live (TTL) specifies the length of time that resources from an origin server are cached on DCDN nodes. After the TTL expires, the DCDN nodes mark these resources as expired. If a client requests an expired resource from a DCDN node, DCDN performs an origin fetch to retrieve the latest version of the resource and caches it on the DCDN node. You can configure the cache TTL for static resources based on file directories or file name extensions to meet your business requirements.
Precautions
You can modify the cache time after you add a domain name. The cache duration affects back-to-origin traffic and costs. The cache expiration time affects the frequency of origin fetches. Set the resource cache duration based on your business needs.
If the cache expiration time is too short, DCDN will frequently fetch data from the origin, which increases origin server traffic. If the cache expiration time is too long, data updates will be delayed.
A resource cached on a DCDN POP that is infrequently accessed (meaning the resource on the same DCDN POP is not requested often by clients) may be overwritten by other more popular resources on the DCDN POP before its cache expires.
When a DCDN point of presence receives a static file resource in a response from an origin server, it caches the resource according to the Alibaba Cloud DCDN Default Cache Rules and Priorities. For more information about the cache rules for dynamic file resources, see Overview of Acceleration Rules for Dynamic and Static Content.
Do not update content on your origin server using the same file name. Instead, use version numbers for synchronization.
To accurately distinguish between content before and after an update, synchronize your origin content using version numbers. This means using different file names when you update content. For example, you can use names such as img-v1.0.jpg and img-v2.1.jpg.
Procedure
Log on to the DCDN console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the domain name that you want to manage and click Configure.
In the left-side navigation tree of the domain name, click Caching.
On the Cache Duration tab, click Add.
You can configure cache rules in the Cache Duration dialog box.

Parameter
Description
Type
Supports Directory or Filename Extension to specify the resource scope:
Directory: Sets the same cache rule for all resources in a specific path.
Filename Extension: Sets the same cache rule for resources of a specific file type.
Content
The directory or file extension of the resources.
If you set Type to Directory, note the following:
Add only one directory at a time. Use a forward slash (/) to match all directories.
Enter the full path of the directory. The path must start with a forward slash (/). Example: /directory/aaa.
When you select Filename Extension as the type, note the following:
Enter one or more file extensions. Separate multiple extensions with commas (,). For example,
jpg,txt. The extensions are case-sensitive.The supported static file types are:
Images: GIF, PNG, BMP, JPEG, and JPG.
Webpages: HTML, HTM, and SHTML.
Audio and video files: MP3, WMA, FLV, MP4, WMV, OGG, and AVI.
Documents: DOC, DOCX, XLS, XLSX, PPT, PPTX, TXT, and PDF.
Other: ZIP, EXE, TAT, ICO, CSS, JS, SWF, APK, M3U8, TS, EJS, SVG, WOFF, and OTF.
You cannot use an asterisk (*) to match all file types.
Expire In
The time-to-live (TTL) for the cached resources. You can set the TTL to a maximum of 3 years. Follow these rules:
For static files that are not frequently updated, such as images and application packages, set the TTL to one month or longer.
For static files that are frequently updated, such as JS and CSS files, set the TTL as needed.
For dynamic files, such as PHP, JSP, and ASP files, set the TTL to 0s. This prevents the files from being cached.
Honor Origin TTL
If this feature is enabled and the origin server returns cache policy headers, such as Cache-Control and Pragma, the cache policy of the origin server takes precedence.
Ignore Origin No-Cache Header
When enabled, DCDN nodes will ignore the following cache policy headers from the origin server response (these headers are used to prevent caching).
Cache-Control: no-store
Cache-Control: no-cache
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Pragma: no-cache
Follow POP TTL
After you enable this feature, the DCDN node will respond to the client with the final effective cache policy.
Force Revalidation
This parameter takes effect only when the cache TTL is 0. The effects are as follows:
Off (default): When the time-to-live (TTL) for DCDN is set to 0, files are not cached on DCDN nodes, and each request must retrieve content from the origin server.
Enabled: When the time-to-live (TTL) for DCDN is set to 0, files are cached on DCDN nodes, and an origin fetch is required for each request to validate the cached content.
Weight
The priority of the cache rule. Valid values: 1 to 99. A larger value indicates a higher priority. The rule with the highest priority takes precedence.
NoteIf multiple cache rules are configured, set a different weight for each rule to control their execution priority.
If multiple rules have the same weight, the rule that was created earlier has a higher priority, regardless of the rule type.
If multiple cache policies are configured, DCDN stops matching other policies after one policy takes effect.
Rule Condition
Rule conditions can identify parameters in a request to determine whether a configuration applies to the request.
Do not use conditions
If you want to add or edit rules conditions, see Rules engine.
Click OK to complete the configuration.
After you create a cache rule, you can click Modify or Delete in the Cache Duration list.
Default Alibaba Cloud DCDN cache rules and priorities
For origin responses with the HTTP status codes 200, 203, 206, 300, 301, 308, or 410, the cache expiration time is determined by the following rules.
When a DCDN POP receives a file resource from an origin server, it applies cache rules in the following order of priority. A smaller number indicates a higher priority.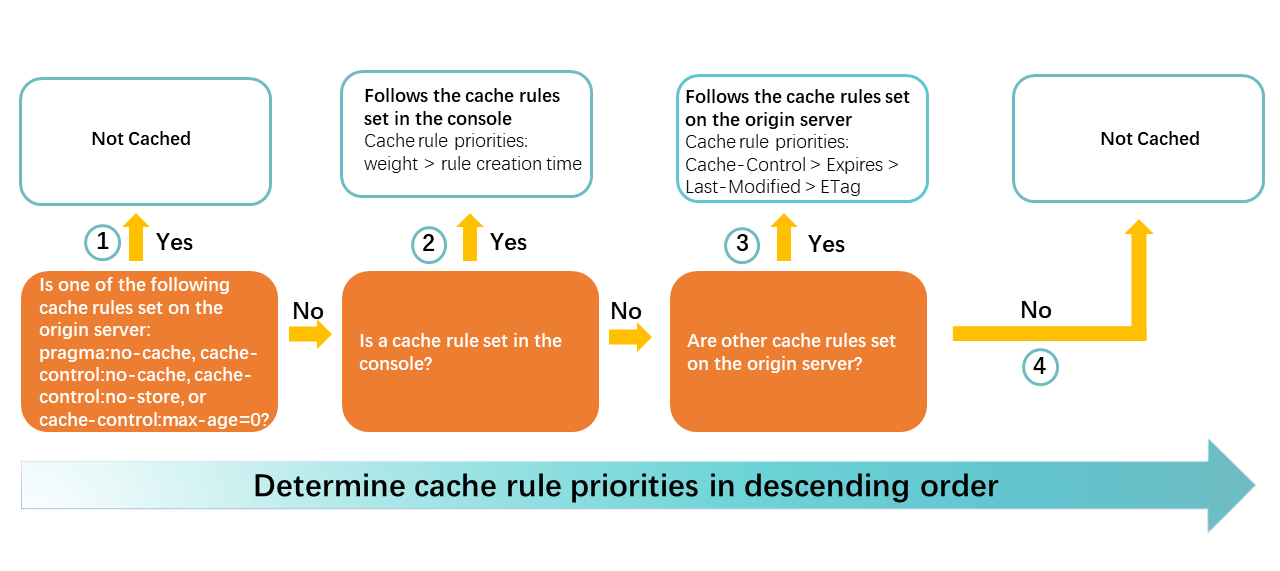
If the origin server responds with
pragma:no-cache,cache-control:no-cache(orno-store, ormax-age=0), DCDN does not cache the resource.The cache expiration time or status code expiration time that is set in the DCDN console.
NoteIf a DCDN request matches multiple rules, only one rule is applied. The priority is determined first by weight and then by creation time.
If you have multiple cache rules, you can set a different weight for each rule to control its execution priority. A larger weight indicates a higher priority.
For rules with the same weight, the rule that was created earlier has a higher priority, regardless of the rule type.
Other cache rules that are configured on the origin server. The priority from high to low is:
cache-control>expires>last-modified>ETag.If the
cache-controlheader in the response from the origin server specifies amax-ageors-maxagevalue greater than 0, thecache-controlheader is used to set the time-to-live. For example: cache-control:max-age=3600. If bothmax-ageands-maxageare present,s-maxagetakes precedence.If the origin response does not contain a
cache-controlheader but contains anExpiresheader, the cache expiration time is determined by theExpiresheader. For example: expires:Tue, 25 Nov 2031 17:25:43 GMT.If the origin response does not contain
cache-controlorExpiresbut containslast-modified, the cache time is calculated using the formula: (Current Time -last-modified) × 0.1. If the result is between 10 seconds and 3600 seconds, that result is used. If the result is less than 10 seconds, the cache time is 10 seconds. If the result is greater than 3600 seconds, the cache time is 3600 seconds.If the origin response does not contain
cache-control,Expires, orlast-modifiedbut containsETag, the resource is cached for 10 seconds.
If the data returned from the origin server does not contain any of the cache-related response headers (
cache-control,expires,last-modified, orETag), the resource is not cached by default.
Description of cache response information
Date:Indicates the time when the origin server sent the resource in a response to the DCDN POP.
When the DCDN POP revalidates the resource with the origin server by including the
If-Modified-SinceorIf-None-Matchheader in the origin request, the Date information is updated if the origin server returns a 304 status code.The format is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), for example:
Sat, 19 Apr 2025 08:58:31 GMT.
X-Cache:Indicates whether the requested resource hit the cache on the DCDN POP. The following table describes the possible values.
Status
Description
HITThe requested resource hit the cache on the DCDN POP.
MISSThe requested resource did not hit the cache on the DCDN POP. The resource was provided by the origin server.
X-Swift-Cachetime:Indicates the remaining cache time of the resource on the DCDN POP, in seconds.
X-Swift-Cachetime=Ali-Swift-Global-Savetime+ Cache expiration time set for CDN -X-Swift-SaveTime.X-Swift-Cachetimeis not always equal to the cache expiration time set for DCDN. The following three situations may occur:X-Swift-Cachetime= Cache expiration time set for DCDN, for example, 3600 seconds.X-Swift-Cachetimeis slightly less than the cache expiration time set for DCDN. For example, the cache expiration time for DCDN is set to 300 seconds, butX-Swift-Cachetimeis 295 seconds. This may be because of the following reasons:High latency occurs when a Layer 1 POP fetches data from a Layer 2 POP.
The clocks on the Layer 1 and Layer 2 POPs are not synchronized.
The value of
X-Swift-Cachetimeis negative. This may be because the cache expiration time for DCDN was changed. When the client sends a request, the cache on the Layer 1 POP has expired, but the cache on the Layer 2 POP has not. For example, the cache expiration time for DCDN was originally 3600 seconds and was later changed to 300 seconds. If a client sends a request 600 seconds after the first request, the response header isX-Swift-Cachetime:-300. To resolve this issue, you can refresh the cache.
X-Swift-SaveTime:Indicates the time when the resource was first cached on the DCDN POP that the client directly accessed. This is typically a Layer 1 POP.
The format is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), for example:
Sat, 19 Apr 2025 08:58:31 GMT.
Ali-Swift-Global-Savetime:Indicates the time when the resource was first cached on a DCDN POP. This could be a Layer 2 POP or a POP at another cache layer, depending on the site's cache architecture.
The format is a UNIX timestamp, for example:
1745053111, which represents2025-04-19 16:58:31.
HTTP cache control mechanisms
The HTTP protocol defines three types of cache control mechanisms:
Configuration examples
Example 1: To cache .txt files for seven days, you can add a cache rule for the .txt file extension in the DCDN console and set the cache TTL to 7 days.

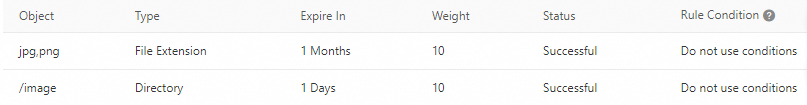
Example 2: The following cache policies are configured for the accelerated domain name demo.aliyun.com. When a DCDN node retrieves the resource http://demo.aliyun.com/image/example.png from the origin server, both rules are matched. Because the two rules have the same weight, the rule that was created earlier has a higher priority. The rule for the /image directory was created earlier and therefore takes effect.