Enterprise Distributed Application Service (EDAS) provides the resource search feature to help you find and access resources. You can use information such as resource IDs and names to search for resources. This topic describes how to use the resource search feature to quickly access resources.
Background information
EDAS resources include microservices namespaces, clusters, and applications. Each type of resource has multiple attributes or subresources. You may want to find microservices namespaces, clusters, or applications based on their attributes or subresources. For example, you may want to find the application on which a pod runs based on the IP address of the pod, or find the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) cluster in which an ECS instance resides based on the instance. These search operations are frequently required in day-to-day management, but rarely completed. EDAS provides the resource search feature that helps you quickly access resources.
You can search for the following resources:
Microservices namespace
Cluster: ECS clusters, Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) clusters, and serverless Kubernetes (ASK) clusters
Application: applications deployed in ECS clusters, ACK clusters, and ASK clusters
Limits
You must have the permissions to search for a resource. For more information, see Grant the search permissions on resources.
Grant the search permissions on resources
The resource search feature allows you to search for microservices namespaces, clusters, and applications in EDAS. When you use a Resource Access Management (RAM) user to search for resources, you must grant the search permissions on the resources to the RAM user. This ensures data security.
If you use your Alibaba Cloud account, you are granted the search permissions on resources by default.
Log on to the EDAS console with your Alibaba Cloud account and switch the account to a RAM user. For more information, see Step 4: Replace the EDAS-defined permissions with the RAM policy for the RAM user in the EDAS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Permission Assistant page, click Create Policy.
In the Create Custom Policy step of the Create Policy wizard, configure Policy Name and Remarks.
Add statements and click Next Step.
NoteYou can create multiple statements for a policy. If a permission is specified in statements that have different effects, the Deny statement prevails. For example, if a permission is specified in an Allow statement and a Deny statement, the Deny statement prevails.
When you add a statement, you can select only one statement type. Available statement types are Allow and Deny.
In the Create Custom Policy step, click Add Statement. In the Add Statement panel, add statements.
EDAS uses separate permissions to control whether the RAM user can search for resources and view the details of search results. For example, if a RAM user wants to view the application resources in a search result, the RAM user must have the permission to view the application. You can grant the search permissions on microservices namespaces, clusters, and applications to RAM users based on your business requirements.
The following section provides examples on how to add statements. In this example, statements that allow the RAM user to view a microservices namespace named test, view clusters in the microservices namespace, and manage applications in the microservices namespace are added.
Select Allow as Effect.
In the left-side directory tree of the Operation and Resource Permissions section, choose .
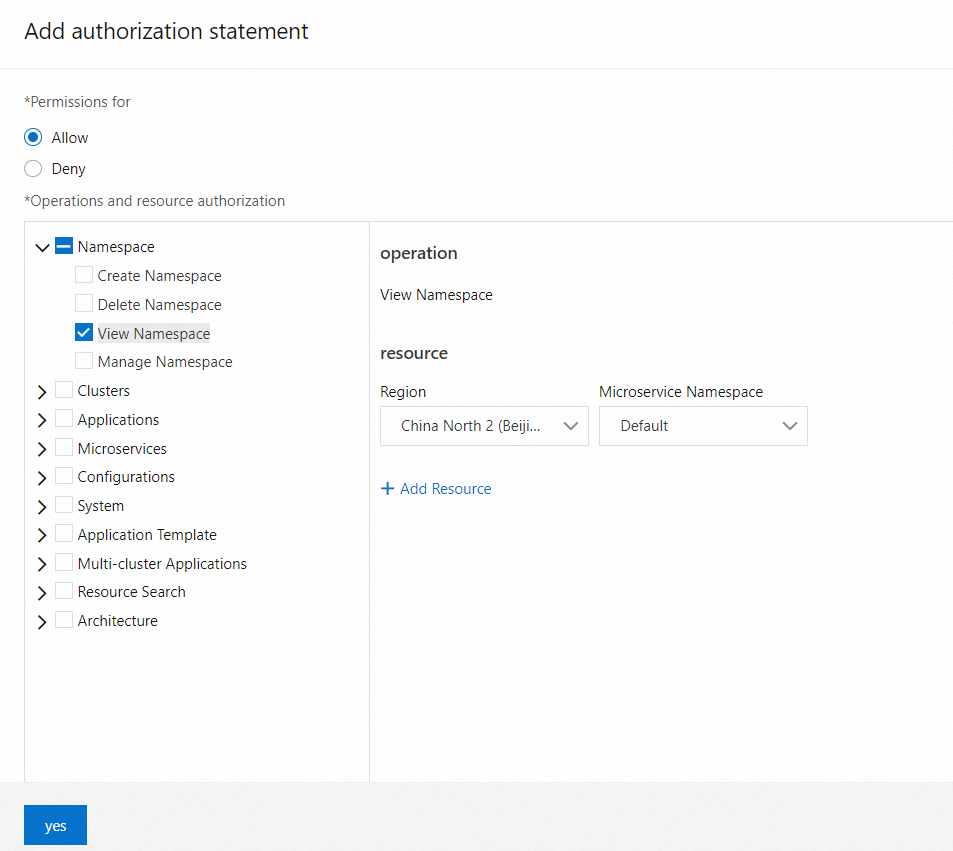
In the left-side directory tree of the Operation and Resource Permissions section, choose Namespace > View Namespace. From the drop-down lists on the right side, select China (Beijing) and test.
This permission allows the RAM user to view the test microservices namespace. You can determine whether to grant the permission to a RAM user based on your business requirements.
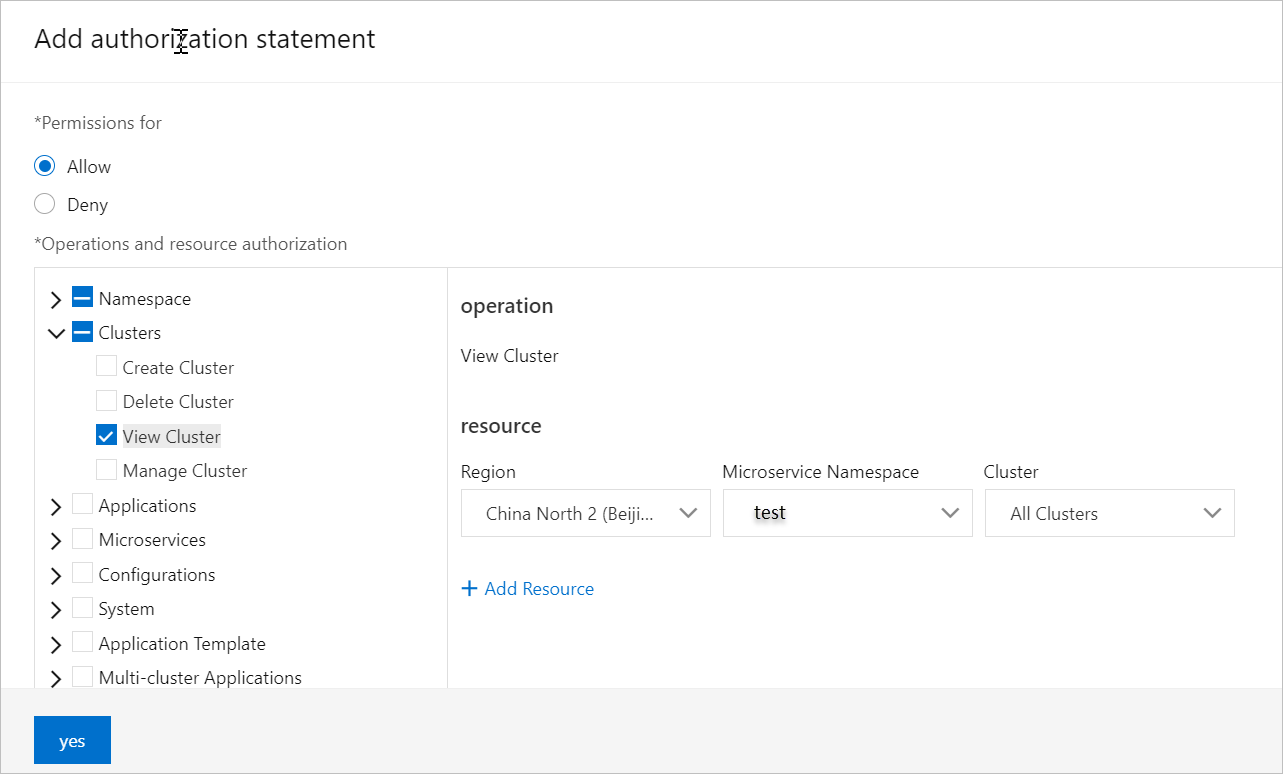
In the left-side directory tree of the Operation and Resource Permissions section, choose . From the drop-down lists on the right side, select China (Beijing), test, and All Clusters.
This permission allows the RAM user to view all clusters in the test microservices namespace. You can determine whether to grant the permission on specific clusters to a RAM user based on your business requirements.
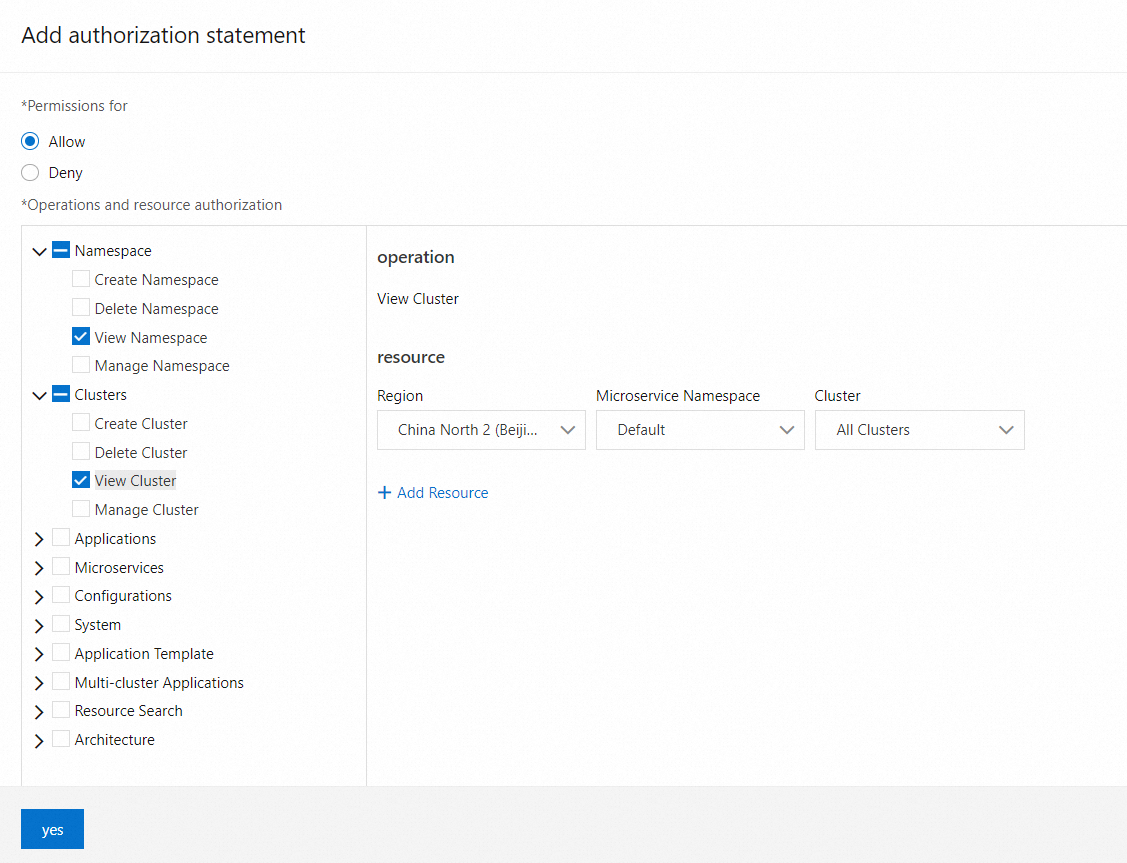
In the left-side directory tree of the Operation and Resource Permissions section, select Applications to select all permissions on applications. From the drop-down lists on the right side, select China (Beijing) and test.
This permission allows the RAM user to view all applications in the test microservices namespace. You can determine whether to grant the permission on specific applications to a RAM user based on your business requirements.
Follow the on-screen instructions in the Preview Policy step to create a custom policy in the RAM console and attach the policy to the RAM user. After you create the custom policy, preview the permissions and click Complete. For more information, see Step 3: Create a RAM user and attach the policy to the RAM user.
The New policy authorization succeeded message appears. Click Back to Policy List to return to the Permission Assistant page. On this page, view the created policy.
Search for a resource
Log on to the EDAS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click . In the search box that appears, enter the keyword of the resource that you want to query.
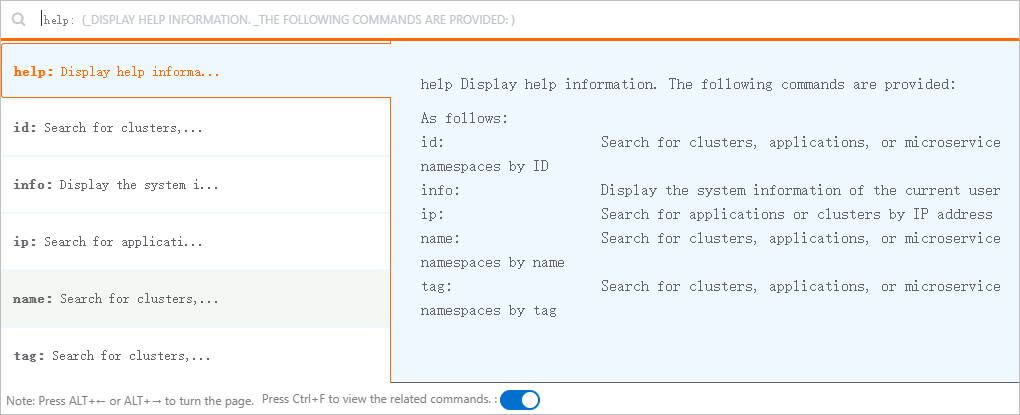
You can also perform fine-grained searches by selecting the attribute prefix of the keyword. The following attribute prefixes are supported:
id: the unique identifier of the resource.name: the name of the resource.ip: the IP address of the resource.tag: the tag of the resource.
You can enter the following commands in the search box to obtain the help information:
help: provides the help information.
info: provides information about the current account.
NoteIn the EDAS console, you can press Ctrl+F on your keyboard to open the resource search box for real-time queries.
The resource is displayed on the right side of the search box. Click the resource ID to go to the resource details page.