Enterprise Distributed Application Service (EDAS) allows you to deploy microservices applications. EDAS provides microservices application demos that use the following frameworks: Spring Cloud, Dubbo, and High-speed Service Framework (HSF). You can deploy application demos in the specified Kubernetes clusters. This topic describes how to deploy microservices applications in a Kubernetes cluster.
Prerequisites
EDAS is activated. For more information, see Activate EDAS.
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster is created and added to EDAS. This operation is required because you cannot create a Kubernetes cluster in EDAS. For more information, see Use the EDAS console to manage Kubernetes clusters.
NoteTo experience fast application deployment, we recommend that you add your ACK cluster to the default microservices namespace of the region that you use. If you want to isolate resources and services in EDAS, you can add the ACK cluster that you created to a specified microservices namespace based on your business requirements.
An application image is created. For more information, see Create an application image.
If you use an image from a repository of Container Registry Enterprise Edition to deploy applications as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, the RAM user must be authorized by the relevant Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see RAM authentication rules.
Background information
Kubernetes environment: A Kubernetes environment is a Kubernetes cluster that resides in a specified microservices namespace and region.
Application demo: You can use application demo images in the EDAS console to call simple services. A demo image contains a server-side application (service provider) and a client-side application (service consumer). EDAS also provides WAR and JAR packages of microservices application demos that use the Spring Cloud, Dubbo, and HSF frameworks. For more information about how to deploy applications by using JAR or WAR packages, see Use a JAR or WAR package to deploy an application in an ACK cluster and Use a JAR package or WAR package to deploy an application in an ACK Serverless cluster.
In this example, a demo image is used to describe how to deploy microservices applications. For more information about application demos, visit alibabacloud-microservice-demo.
For more information about how to implement the features of microservices applications, see Overview of application development.
Deploy a demo image
A demo image contains a server-side application (service provider) and a client-side application (service consumer). This topic describes how to deploy a server-side application. The procedures for deploying a server-side application and a client-side application are similar.
Log on to the EDAS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Applications page, select a region in the top navigation bar, select a microservices namespace, and then click Create Application.
In the Basic Information step of the Create Application wizard, configure the basic information of the application and click Next. The following table describes the configurations used in this example.
Parameter
Operation
Cluster Type
Select Kubernetes Clusters.
Application Runtime Environment
Hosted Applications: Select Java.
Select Application: Select Custom.
In the Configurations step of the Create Application wizard, configure the application environment, select a demo image, and then click Next. The following table describes the configurations used in this example.
NoteIf you want to use an image from a repository of Container Registry Enterprise Edition to deploy the server-side application as a RAM user, the RAM user must be authorized by the relevant Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see RAM authentication rules.
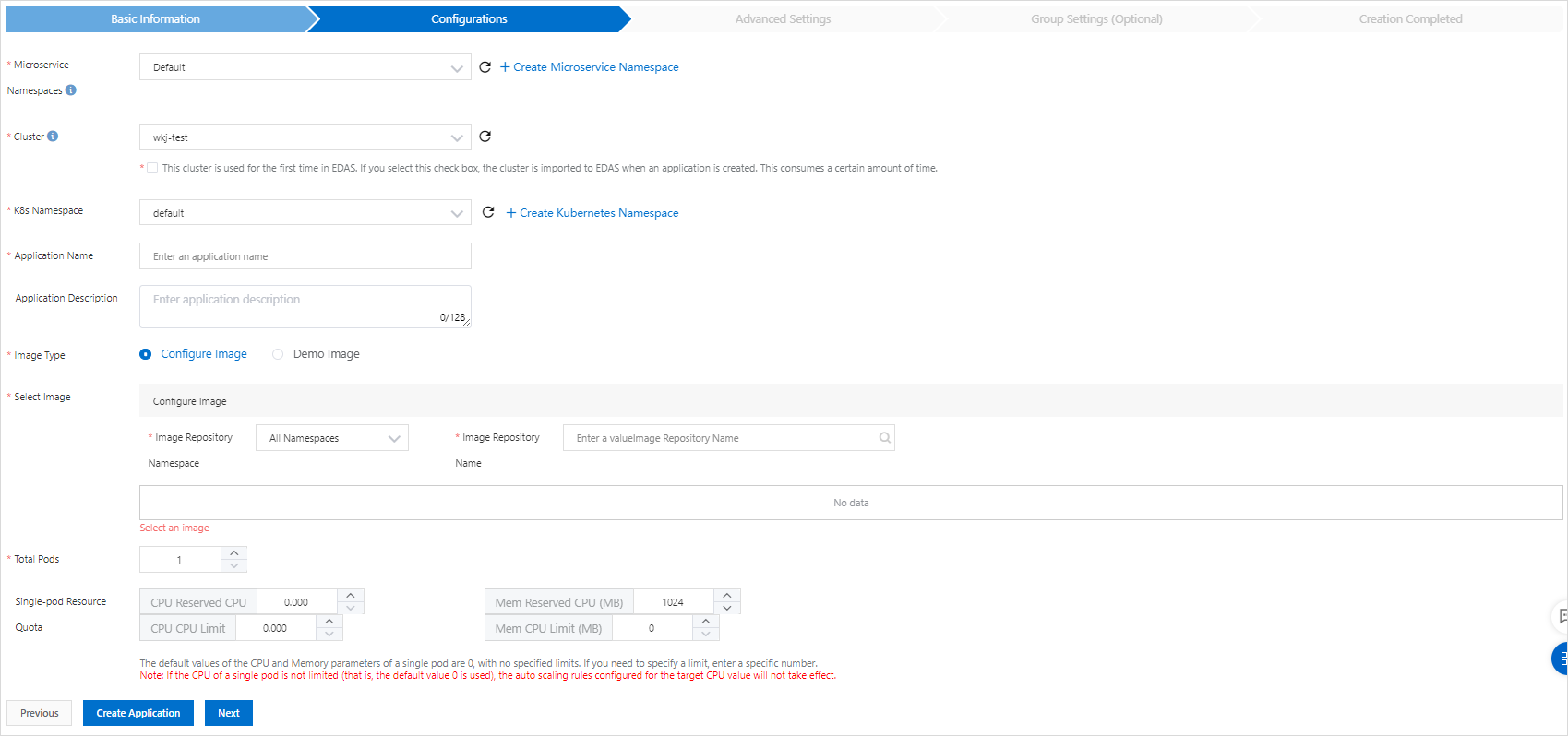
Parameter
Description
Microservices Namespace
Select Default.
NoteThis topic aims to show you how to deploy a microservices application demo in a Kubernetes cluster. We recommend that you use the default microservices namespace and do not create a microservices namespace. If you want to isolate resources and services in EDAS to meet your business requirements, you can create a microservices namespace. For more information, see Manage microservices namespaces.
Cluster
Select the desired Kubernetes cluster from the drop-down list.
K8s Namespace
Select default from the drop-down list.
If you want to create a custom Kubernetes namespace, click Create Kubernetes Namespace. In the dialog box that appears, enter a name for the Kubernetes namespace in the K8s Namespace field. The name can contain digits, lowercase letters, and hyphens (-), and can be 1 to 63 characters in length. It must start and end with a letter or a digit.
Application Name
Enter an application name in the text box.
Application Description
Enter a description for the application in the text box.
Image Type
Select Demo Image.
Image Repository Namespace
Select edas-demo-project from the drop-down list. Then, select 1.0 from the rightmost drop-down list of edas-demo-project/provider.
NoteThe demo image edas-demo-project/provider in the image repository edas-demo-project and the image version 1.0 are provided by EDAS. You are not allowed to change the settings.
Total Pods
Set the value to 1.
Single-pod Resource Quota
Set CPU Reserved CPU (Core) to 1 and Mem Reserved CPU (MB) to 2048.
In the Advanced Settings step of the Create Application wizard, click Create Application.
In the Advanced Settings step, you can configure the advanced settings based on your requirements. For more information, see Configure scheduling rules.
In the Creation Completed step of the Create Application wizard, confirm the information in the Basic Information, Configurations, and Advanced Settings steps. Then, click Create Application.
After EDAS starts to deploy the application, the message Application change in progress... is displayed in the upper part of the Basic Information tab. The deployment takes about 2 minutes.
You can also click View Details next to the message to go to the Change List page of the application. On this page, you can check the deployment progress and log data.
- Repeat the preceding steps to deploy the client-side application.
Verify the result
The service consumer can be a web service consumer. After a server-side application and a client-side application are deployed, you can access the web page of the client-side application to verify the result.