This topic describes the causes of and solutions to the issue that a general fault occurs when you ping the public IP address of a Windows Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Problem description
When you ping the public IP address of a Windows instance, you are prompted with a general fault or a common issue.
Causes
The preceding issue may occur due to different causes. The following table describes the causes and the corresponding solutions.
Cause | Solution |
Cause | Solution |
Third-party antivirus software or security protection software is installed on the Windows instance. | Check third-party antivirus software or security protection software |
The internal gateway and route configurations of the Windows instance are incorrect. | Check the gateway and route configurations of the Windows instance |
Other causes. |
Solutions
Check third-party antivirus software or security protection software
Third-party antivirus software or security protection software may have network protection capabilities to control traffic similar to a firewall.
If third-party antivirus software or security protection software is installed on the Windows instance, uninstall or temporarily disable the software. Then, ping the public IP address of the instance again.
Check the gateway and route configurations of the Windows instance
You must configure the correct default gateway address and default route for an instance to communicate with the Internet. If the configurations are incomplete or incorrect, the instance may be unable to access the Internet. To troubleshoot the issue, perform the following steps:
Step 1: Check the default gateway configuration
Run the ipconfig command to view the default gateway configuration.
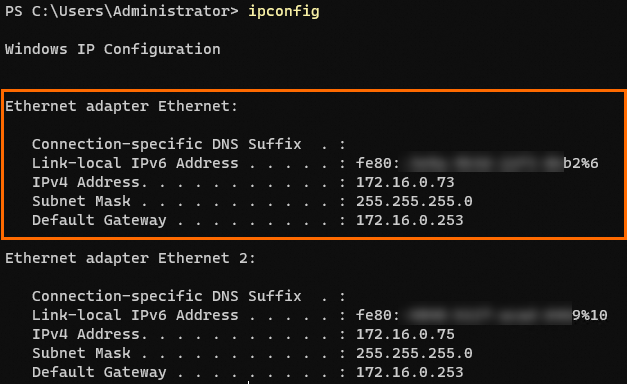
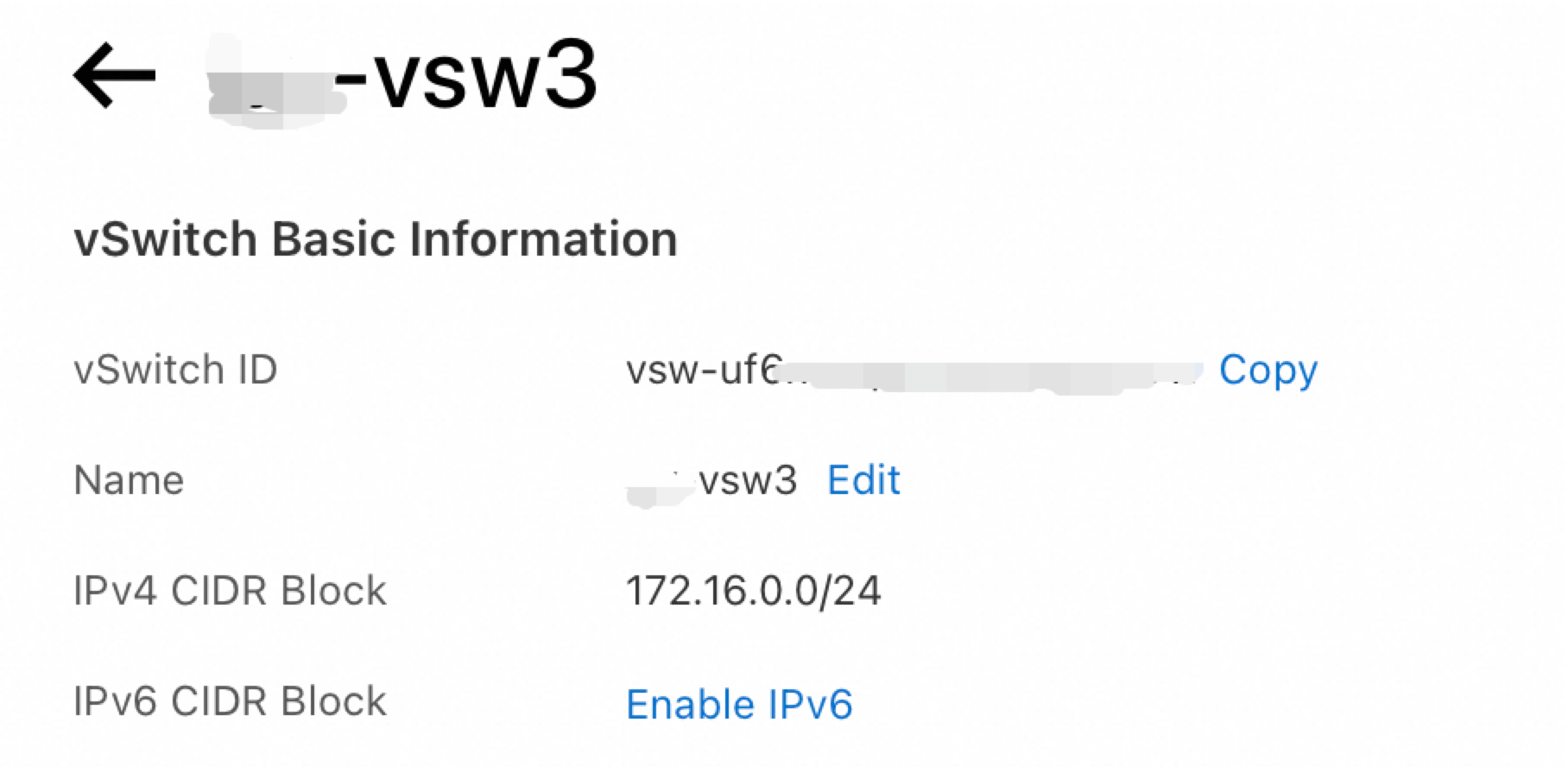
Check whether the default gateway address is correct. You can compare the default gateway address of the Windows instance against the IPv4 CIDR block of the vSwitch to which the instance is connected. If the default gateway address is the third-to-last address within the CIDR block of the vSwitch, the address is correct. In this example, the CIDR block of the vSwitch is 172.16.0.0/24, as shown in the preceding figure. The correct default gateway address is 172.16.0.253.
If the default gateway information is not displayed in the instance or the default gateway address is incorrect, perform the following steps to reconfigure the default gateway.
Step 2: Check the default route
Run the route print command to check whether a default route exists.
The route whose network destination and network mask are 0.0.0.0 is the default route, as shown in the following figure. The Windows instance uses the default route to communicate with the Internet.
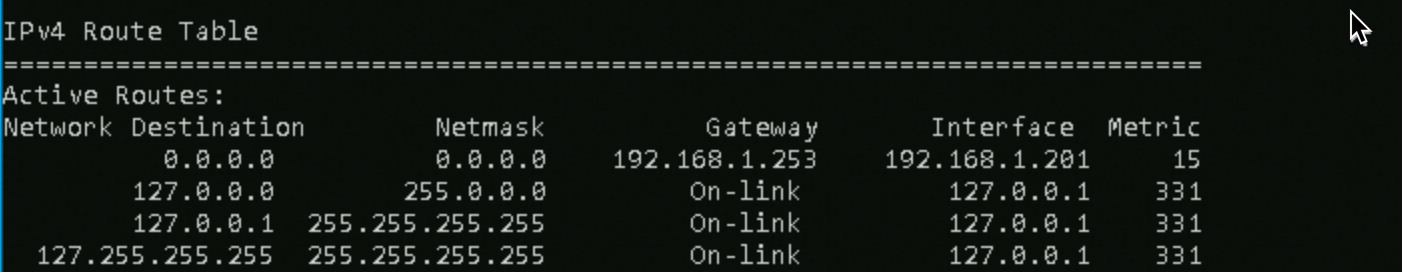
If no default route is available, run the following command to add a default route and replace <Default gateway address> with the actual default gateway address:
route -p add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 <Default gateway address>Sample command:
route -p add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.253Troubleshoot other causes
The following factors may also cause the preceding issue:
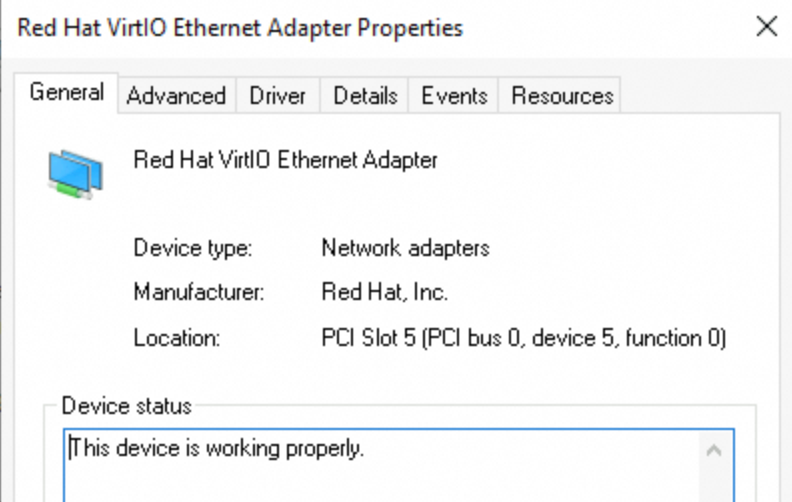
A network adapter is disabled or does not work as expected.
The network protocol stack is damaged due to viruses or malware.
You enabled specific built-in network tools, which are disabled by default, but you incorrectly configured the tools. In this case, you can configure rules to restrict network traffic and temporarily disable the network tools for troubleshooting.