You can test the performance of block storage devices to be familiar with the capabilities of your block storage devices and optimize and tune the block storage devices that you use to ensure optimal performance. Tests on raw disks help you obtain real block storage performance. This topic describes how to use the flexible I/O tester (fio) on a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to measure the key performance metrics of raw disks attached to the instance, including the IOPS, throughput (data transmission rate), and latency (response time).
fio is an open source, powerful I/O performance benchmarking tool that can test the performance metrics of block storage devices, such as random read and write operations and sequential read and write operations.
Procedure
Tests on raw disks help you obtain real block storage performance. If a block storage device contains partitions, file systems, and data, direct use of the fio tool may cause exceptions on the file systems and result in data loss. To prevent the preceding issues, we recommend that you create snapshots for the block storage devices that you want to test to back up disk data before you use the fio tool to test the devices. For more information, see Create a snapshot manually.
To prevent data loss, we strongly recommend against using the system disk or any data disk that contains data for storage performance tests. Instead, we recommend performing the test on a newly created, uninitialized, and empty data disk.
Performance test results are obtained in a test environment and are only for reference. In a production environment, the performance of cloud disks may vary due to factors such as the network environment and concurrency access.
After testing the new disk, proceed as follows:
This item is reserved and cannot be used directly. For more information, see Re-initialize a data disk.
If you do not want to keep the disk, detach a data disk and then release a disk.
In the examples in the following section, an Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bit public image is used. The operations may vary based on the image of your instance.
Connect to an ECS instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Query the names of block storage devices.
sudo fdisk -lu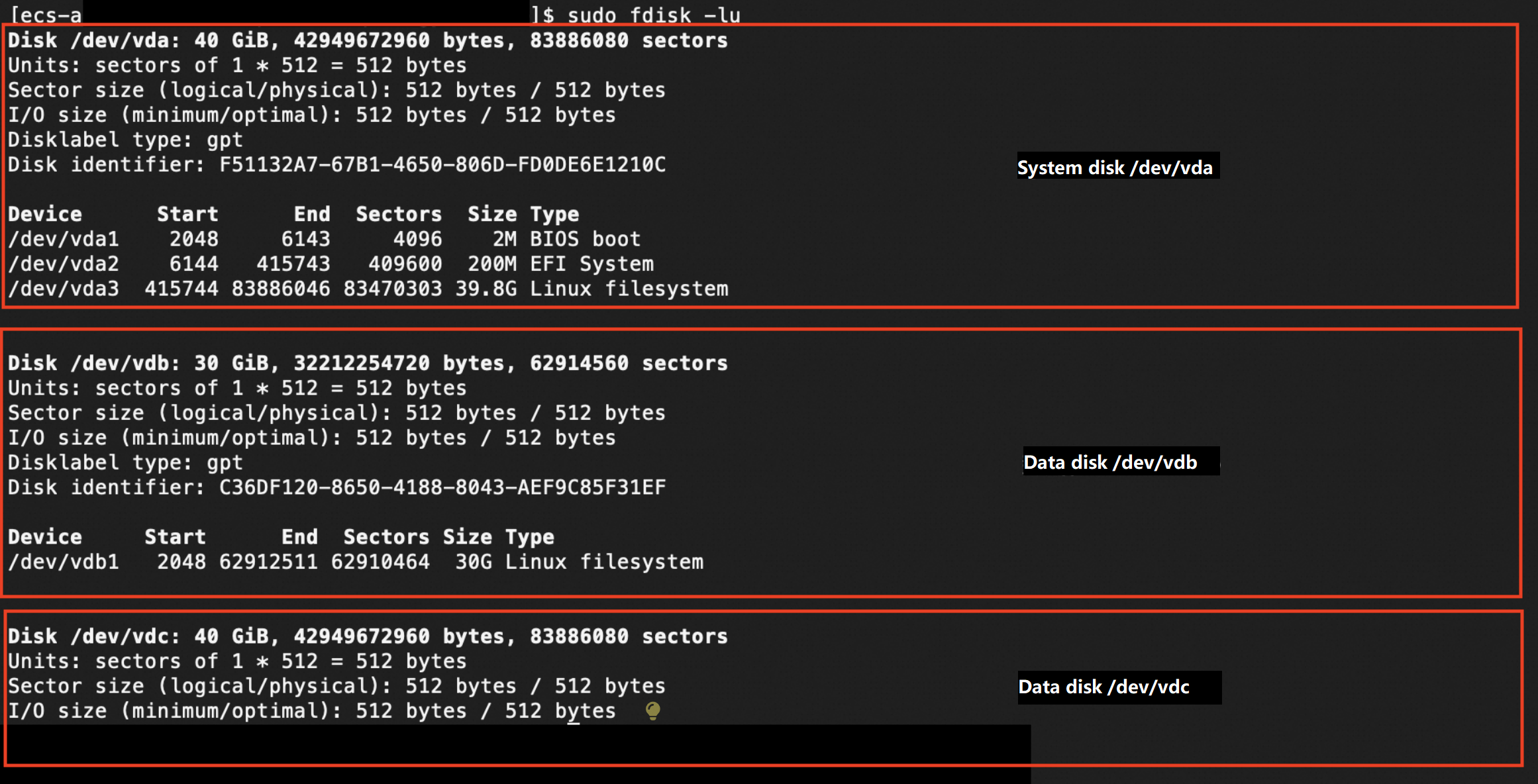 The preceding figure shows that the instance has three block storage devices: the system disk named /dev/vda and two data disks named /dev/vdb and /dev/vdc.
The preceding figure shows that the instance has three block storage devices: the system disk named /dev/vda and two data disks named /dev/vdb and /dev/vdc. Query whether partitions and file systems exist on the block storage devices.
sudo blkid The preceding figure shows that the block storage devices named /dev/vda and /dev/vdb have partitions and file systems. The command output does not contain information about the block storage device named /dev/vdc, which indicates that the block storage device does not have partitions or file systems.
Warning
The preceding figure shows that the block storage devices named /dev/vda and /dev/vdb have partitions and file systems. The command output does not contain information about the block storage device named /dev/vdc, which indicates that the block storage device does not have partitions or file systems.
WarningIf the test object contains partitions, file systems, and data, direct use of the fio tool may cause exceptions on the file systems and result in data loss. If your data disk has partitions and file systems, we recommend creating an empty data disk and test the new disk.
You can create a pay-as-you-go disk that has the same specifications as your data disk and attach the new disk to your instance for testing. For more information, see Create an empty data disk.
After the test is completed, you can release the pay-as-you-go disk. For more information, see Release a disk.
Before you test the performance of the block storage devices, make sure that you back up the data that is stored on the devices to prevent data loss. For more information, see Create a snapshot manually.
NoteYou are charged for snapshots. For information about the billing of snapshots, see Snapshot billing.
Run one of the following commands to install the libaio library and the fio tool based on your operating system.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2/3, or CentOS 6 or later
NoteCentOS 6 reached end of life (EOL). In accordance with Linux community rules, all content was removed from the following CentOS 6 repository address: http://mirror.centos.org/centos-6/. If you continue to use the default CentOS 6 repository on Alibaba Cloud, an error is reported. To use specific installation packages of CentOS 6, change the CentOS 6 repository address. For more information, see How do I change CentOS 6 repository addresses?
sudo yum install libaio libaio-devel fio -yDebian 9 or later, or Ubuntu 14 or later
ImportantDebian 9 and Debian 10 reached their EOL. If your instance runs Debian 9 or Debian 10, change the repository addresses of the operating system. For more information, see Change repository addresses after CentOS or Debian reached its EOL
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install libaio* fio -yChange the path:
cd /tmpRun the test commands.
For information about the commands used to test the performance of cloud disks, see the Commands used to test the performance of cloud disks section of this topic.
For information about the commands used to test the performance of local disks, see the Commands used to test the performance of local disks section of this topic.
View the test results. The metric values vary based on the cloud disk category. The metric values shown in the following figures are only for reference.
The value of the
IOPSmetric shown in the following figure indicates the IOPS test result.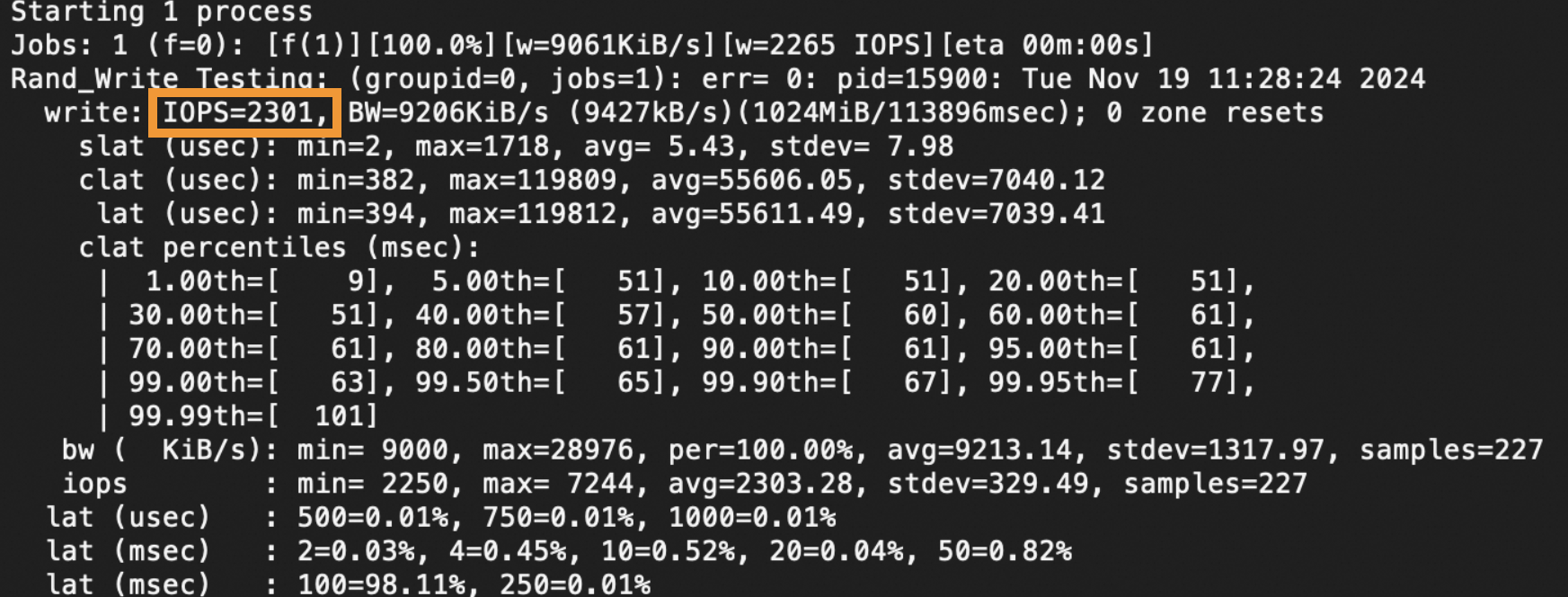
The value of the
BWmetric shown in the following figure indicates the throughput test result.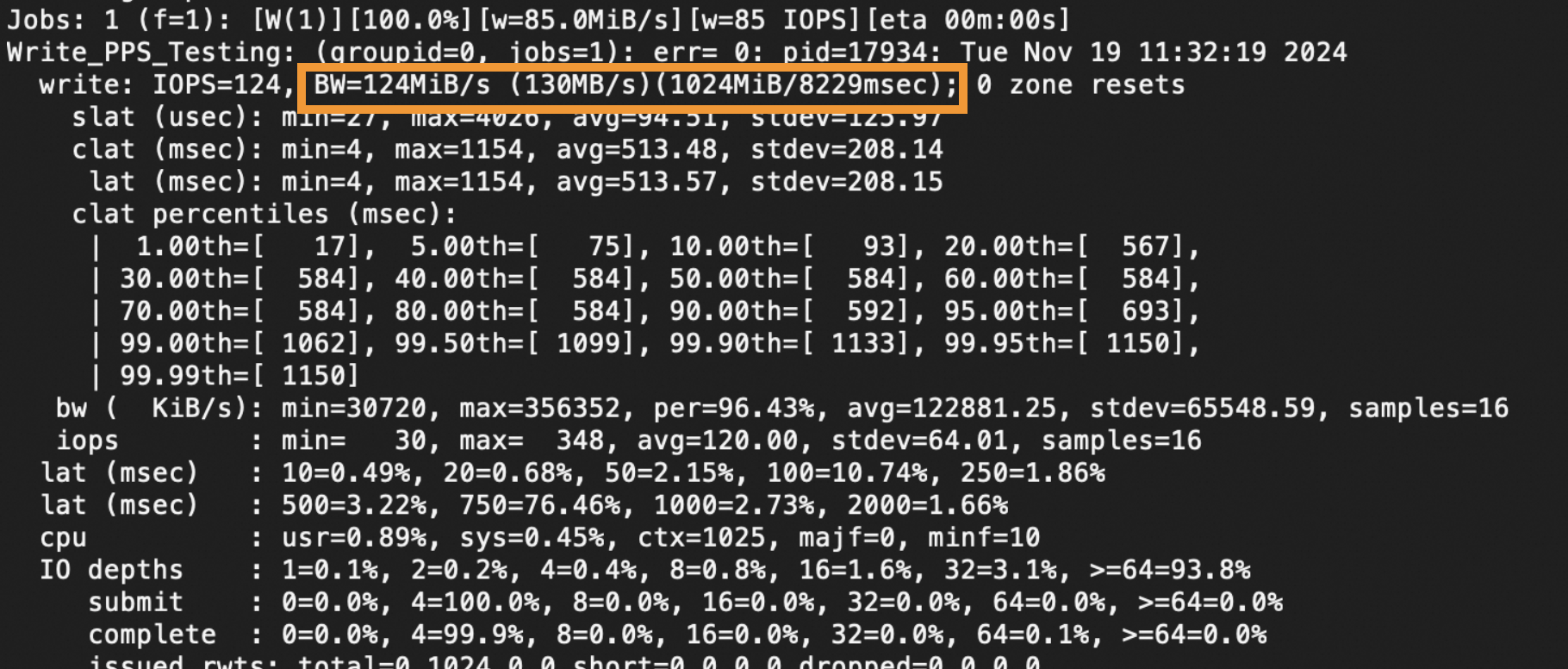
The value of the lat (usec) metric shown in the following figure indicates the latency test result.
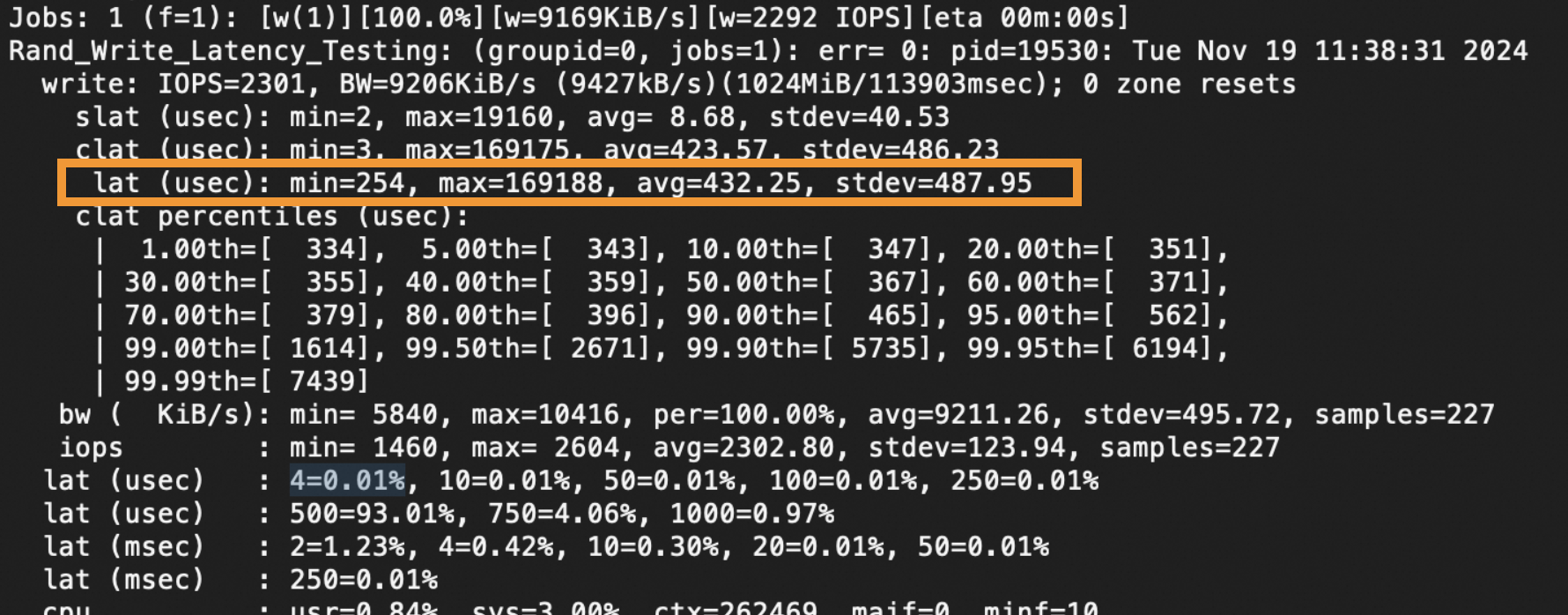
Commands used to test the performance of cloud disks
Running a stress test with fio directly on a disk that contains partitions, a file system, or other data can cause file system errors and data loss. If your data disk has partitions and a file system, create a new, empty data disk for testing:
You can create a pay-as-you-go disk with the same configuration and attach it to the instance for testing. For more information, see Create an empty data disk.
After the test is complete:
If you want to keep the disk: Re-initialize a data disk.
If you no longer need the disk: detach and then release it.
The parameter values in the following sample commands are only for reference. Replace /dev/your_device with the name of the block storage device that you want to test. To obtain the name of a block storage device, perform Step 2 in the "Procedure" section of this topic. For example, if the device name of the cloud disk that you want to test is /dev/vdb, replace /dev/your_device with /dev/vdb in the following sample commands. For more information about fio parameters, see the fio parameters section of this topic.
Test the random write IOPS of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Write_TestingTest the random read IOPS of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Read_TestingTest the sequential write throughput of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=64 -rw=write -ioengine=libaio -bs=1024k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Write_PPS_TestingTest the sequential read throughput of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=64 -rw=read -ioengine=libaio -bs=1024k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Read_PPS_TestingTest the random write latency of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Write_Latency_TestingTest the random read latency of a cloud disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -size=1G -numjobs=1 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=Rand_Read_Latency_Testing
For more information, see Test the IOPS performance of an ESSD.
Commands used to test the performance of local disks
Running fio stress tests directly on a disk that contains partitions, file systems, or other data will cause file system errors and data loss. If your data disk has partitions and a file system, create a new instance with local disks for testing:
Local disks can be created only when you create an instance. Therefore, create a new instance with the same configuration for testing. For more information, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
After the test is complete:
To keep the instance, see Re-initialize a data disk.
To discard the instance, uninstall and then release the disk.
The following sample commands are applicable to local Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) SSDs and local Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) HDDs. The parameter values in the following sample commands are only for reference. Replace /dev/your_device with the name of the block storage device that you want to test. To obtain the name of a block storage device, perform Step 2 in the "Procedure" section of this topic. For example, if the device name of the local disk that you want to test is /dev/vdb, replace /dev/your_device with /dev/vdb in the following sample commands. For more information about fio parameters, see the fio parameters section of this topic.
Test the random write IOPS of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=32 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=4 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the random read IOPS of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=32 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=4 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the sequential write throughput of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=write -ioengine=libaio -bs=128k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the sequential read throughput of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=128 -rw=read -ioengine=libaio -bs=128k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the random write latency of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randwrite -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the random read latency of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=randread -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the sequential write latency of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=write -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=testTest the sequential read latency of a local disk.
sudo fio -direct=1 -iodepth=1 -rw=read -ioengine=libaio -bs=4k -numjobs=1 -time_based=1 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -filename=/dev/your_device -name=test
fio parameters
The following table describes the parameters in the preceding fio commands that are used to test disk performance.
Parameter | Description |
direct | Specifies whether to use direct I/O. Default value: 1. Valid values:
|
iodepth | The I/O queue depth during the test. For example, if you set the |
rw | The read/write policy that is used during the test. Valid values:
|
ioengine | The I/O engine that the fio tool uses to test disk performance. In most cases, libaio is used. For information about other available I/O engines, see the fio documentation. |
bs | The block size of I/O units. Default value: 4k, which indicates 4 KiB. Values for reads and writes can be specified in the <Value for reads>,<Value for writes> format. If you do not specify a value, the default value is used. |
size | The size of the test files. The fio tool ends the test only after the specified size of the files is read or written, unless limited by specific factors such as runtime. If you do not specify this parameter, the fio tool uses the size of all given files or devices. The valid values can also be a percentage that ranges from 1 to 100. For example, if the size parameter is set to 20%, the fio tool uses 20% of the size of all given files or devices. |
numjobs | The number of concurrent threads that are used during the test. Default value: 1. |
runtime | The duration of the test, which indicates the period of time for which the fio tool runs. If you do not specify this parameter, the test does not end until the files whose size is specified by the size parameter are read or written in the block size specified by the bs parameter. |
group_reporting | The display mode of the test results. If you specify this parameter, per-process statistics are displayed instead of per-task statistics. |
filename | The path of the object that you want to test. The path can be the device name of the disk or a file address. In this topic, the test object of the fio tool is an entire disk that does not have file systems (a raw disk). To prevent data of other disks from being damaged, replace /dev/your_device in the preceding commands with the actual path. |
name | The name of the test. You can specify this parameter based on your business requirements. In the preceding examples, Rand_Write_Testing is used. |
For more information about the parameters, see fio(1) - Linux man page.