Serial numbers are the unique identifiers of block storage devices in an operating system, including cloud disks, local disks, and elastic ephemeral disks, and can be used to identify and distinguish the block storage devices. You can use serial numbers of block storage devices to determine the IDs of the devices. This topic describes how to query the serial numbers of block storage devices and determine the IDs of block storage devices based on serial numbers in Linux and Windows operating systems.
Limits
When you query serial numbers, take note of the following limits:
Only block storage devices that are created on or after June 10, 2020 have serial numbers.
Serial number query is supported only for I/O optimized instances or non-I/O optimized instances that expired and are migrated. To check whether an I/O optimized instance is used, call the DescribeInstances operation to query the IoOptimized parameter in the response.
NoteSerial number query is not supported by the non-I/O optimized instances that are not migrated and the existing cloud disks that were created before June 10, 2020. For such non-I/O optimized instances or disks, call the DescribeDisks operation to query the device names based on the Device parameter in the response.
Windows instances require virtio driver version 58017 or later. For more information, see Update the virtio driver for a Windows instance.
Query the serial numbers of block storage devices
Linux
Connect to an ECS instance.
For information about the connection methods, see Connection method overview.
Run the sudo fdisk -lu command to query the names of the block storage devices that are attached to a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
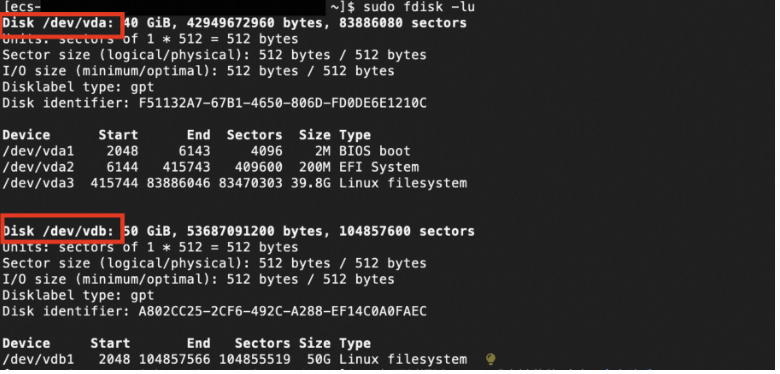
The preceding command output indicates that two block storage devices are attached to the ECS instance: the system disk whose device name is /dev/vda and the data disk whose device name is /dev/vdb.
Check whether the block storage devices are attached based on the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol.
The device names of block storage devices that are not attached based on the NVMe protocol follow the /dev/vd[a-z] format. Examples: /dev/vdb, /dev/vdc, and /dev/vdd.
The device names of block storage devices that are attached based on the NVMe protocol follow the /dev/nvme<X>n1 format. Examples: /dev/nvme0n1, /dev/nvme1n1, and /dev/nvme2n1. For information about cloud disks that support the NVMe protocol, see NVMe protocol.
Query the serial number of a block storage device.
For a block storage device that is not attached based on the NVMe protocol, run the following command to query the serial number of the device:
udevadm info --query=all --name=<Name of the block storage device> | grep ID_SERIALIn this example, the serial number of the block storage device whose name is /dev/vda is queried. The value of the ID_SERIAL parameter in the command output is the serial number of the block storage device, which is bp1d4foh3ef8bntl****.
[ecs-user@ecs ~]$ udevadm info --query=all --name=/dev/vda | grep ID_SERIAL E: ID_SERIAL=bp1d4foh3ef8bntl****For a block storage device that is attached based on the NVMe protocol, run the following commands to query the serial number of the block storage device.
Install the nvme-cli tool. The commands that you can run to install the tool vary based on the operating system of the instance.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2, Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, or CentOS 6 or later
NoteCentOS 6 reached end of life (EOL). In accordance with Linux community rules, all content was removed from the following CentOS 6 repository address: http://mirror.centos.org/centos-6/. If you continue to use the default CentOS 6 repository on Alibaba Cloud, an error is reported. To use specific installation packages of CentOS 6, change the CentOS 6 repository address. For more information, see How do I change CentOS 6 repository addresses?
sudo yum install nvme-cli -yDebian 9 or later, or Ubuntu 14 or later
ImportantDebain9 and Debain10 reached their EOL. If your instance runs Debain9 or Debain10, change the repository addresses of the operating system. For more information, see Change repository addresses after CentOS or Debian reached its EOL
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install nvme-cli -yQuery the serial number of a block storage device:
sudo nvme id-ctrl <Name of the block storage device> |grep "sn"In this example, the serial number of the block storage device whose name is /dev/nvme1n1 is queried. The value of the sn parameter in the command output is the serial number of the block storage device, which is bp1bmed6djhiibh*****.
[ecs-user@ecs ~]$ sudo nvme id-ctrl /dev/nvme1n1 |grep "sn" sn : bp1bmed6djhiibh*****
Windows
Query the serial number of a block storage device in Windows Server 2012 or later.
Connect to an ECS instance.
For information about the connection methods, see Connection method overview.
Open Windows PowerShell.
Enter PowerShell in the search box next to the Start icon and then click Windows PowerShell.
Query the block storage devices corresponding to logical volumes (LVs):
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition |select Antecedent, Dependent |flView the Disk # values corresponding to LVs. The following command output indicates that the Disk # value corresponding to Disk C is 0 and the Disk # value corresponding to Disk D is 1.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition |select Antecedent, Dependent |fl Antecedent : Win32_DiskPartition (DeviceID = "Disk #0, Partition #0") Dependent : Win32_LogicalDisk (DeviceID = "C:") Antecedent : Win32_DiskPartition (DeviceID = "Disk #1, Partition #0") Dependent : Win32_LogicalDisk (DeviceID = "D:")Check whether block storage devices are attached based on the NVMe protocol and query the serial numbers of the devices:
Get-Disk |select Number, SerialNumber, BusTypeIf a block storage device is not attached based on the NVMe protocol, the value of the BusType parameter is not NVMe. In this example, the serial number of the block storage device whose Disk # value is 1 is queried. In the following sample command output, find a value of 1 in the Number column and view the value bp14dzwwr539hzqi**** in the SerialNumber column, which is the serial number of the Disk #1 block storage device.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-Disk |select Number, SerialNumber, BusType Number SerialNumber BusType ------ ------------ ------- 1 bp14dzwwr539hzqi**** SCSI 0 bp16htuqeqnvlee8**** SCSIIf a block storage device is attached based on the NVMe protocol, the value of the BusType parameter is NVMe. In this example, the serial number of the block storage device whose Disk # value is 1 is queried. In the following sample command output, find a value of 1 in the Number column and view the value in the SerialNumber column. The bp1heipctzsr7bhh**** part of the value in the SerialNumber column is the serial number of the Disk #1 block storage device.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-Disk |select Number, SerialNumber Number SerialNumber BusType ------ ------------ ------- 1 bp1heipctzsr7bhh****_00000001. NVMe 0 bp16q98m9p2tssdt****_00000001. NVMeNoteThe SerialNumber value queried for each block storage device that is attached based on the NVMe protocol consists of the serial number of the device and a namespace ID of 00000001.
Query the serial number of a block storage device in a version earlier than Windows Server 2012.
Connect to an ECS instance.
For information about the connection methods, see Connection method overview.
Open Windows PowerShell.
Enter PowerShell in the search box next to the Start icon and then click Windows PowerShell.
Query the block storage devices corresponding to LVs:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition |select Antecedent, Dependent |flView the Disk # values corresponding to LVs. The following command output indicates that the Disk # value corresponding to Disk C is 0 and the Disk # value corresponding to Disk D is 1.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition |select Antecedent, Dependent |fl Antecedent : \\ecs\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #0, Partition #0" Dependent : \\ecs\root\cimv2:Win32_LogicalDisk.DeviceID="C:" Antecedent : \\ecs\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #1, Partition #0" Dependent : \\ecs\root\cimv2:Win32_LogicalDisk.DeviceID="D:"Query the serial numbers of block storage devices:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_PhysicalMedia |select Tag, SerialnumberIn this example, the serial number of the block storage device whose Disk # value is 0 is queried. The following command output indicates that the serial number of the Disk #0 block storage device is bp1bet4g35opq6vq****.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_PhysicalMedia |select Tag, Serialnumber DeviceID Serialnumber -------- ------------ \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE0 bp1bet4g35opq6vq****
Determine the ID of a block storage device based on the serial number
An ID in the d-<Serial number> format is allocated to each block storage device. After you obtain the serial number of a block storage device, you can determine the ID of the device based on the serial number and find the device in the ECS console based on the device ID.
For example, if the serial number of a block storage device is bp1gks8z0fh3m1z9****, the ID of the device that is displayed in the ECS console is d-bp1gks8z0fh3m1z9****.