FAQ about upgrading or downgrading instances
Can I upgrade the instance type and configurations of a subscription ECS instance?
Can I upgrade the instance type and configurations of a pay-as-you-go ECS instance?
Does upgrading an ECS instance affect my cloud service configurations?
Can I cancel an upgrade order and restore the original configurations?
Query instance information
Start, stop, release, or change the properties of instances
ICP filing and compliance
Install databases on instances
Manage spot instances
Issues with changing spot instances
Issues with releasing spot instances
I have set a release time for my spot instance. Can I cancel or change it?
My payments are not overdue. Why was my spot instance released?
How is the release rate on the buy page calculated? Why is it mostly between 0% and 3%?
Will I be notified when my spot instance is released? How will I be notified?
Can data be automatically retained after a spot instance is released?
How can I retain the public IP address of a spot instance as long as possible?
Spot instances with no protection period
Troubleshoot instance downtime
Troubleshoot instance startup failures
Manage instance runtime environment configurations
Cloud Assistant issues
Are there permission limits for running commands on an ECS instance?
Can I run a Cloud Assistant command on multiple instances at the same time?
What are the default installation paths of Cloud Assistant Agent on different operating systems?
Why can a Shell script run on systems such as CentOS but not on Ubuntu?
Can I use Cloud Assistant on classic network-type instances?
The run log contains 'Failed to open gshell: Device or resource busy'. How do I resolve this issue?
Workloads within instances
Upload and download files
Instance security issues
File backup
Other issues
Appendix
Can I upgrade the instance type and configurations of a subscription ECS instance?
Yes, you can. For more information, see Change the instance type of a subscription instance.
Can I upgrade the instance type and configurations of a pay-as-you-go ECS instance?
Yes, you can, but you must stop the instance first. For more information, see Change the instance type of a pay-as-you-go instance or call the ModifyInstanceSpec API operation to upgrade the configurations of a pay-as-you-go instance.
How long does it take to upgrade an ECS instance?
Upgrading the instance type of a subscription instance does not require you to stop the instance. The upgrade takes about 15 minutes.
Upgrading the instance type of a pay-as-you-go instance requires you to stop the instance. The upgrade takes about 15 minutes.
Upgrading the bandwidth of an instance does not require you to stop the instance. The upgrade takes about 5 minutes.
How are the fees for upgrading an ECS instance calculated?
When you upgrade the instance type and configurations of an ECS instance, the fees are displayed on the page. You can also go to the Expenses and Costs page to view the fee details.
Does upgrading an ECS instance affect the configurations of my cloud services?
When you upgrade a pay-as-you-go instance, you must stop the instance first. When you upgrade a subscription instance, you must restart the instance for the new configurations to take effect. The upgrade operation causes a brief interruption to your services. We recommend that you perform upgrades during off-peak hours. After the upgrade, the instance seamlessly integrates with your services. You do not need to reconfigure the ECS environment.
How do I upgrade ECS resources?
For more information about how to upgrade ECS resources, see Overview of instance upgrade or downgrade.
Except for instances with local storage, ECS supports online upgrades of CPU, memory, and bandwidth. Downgrades are supported after an instance upgrade takes effect.
An ECS instance can have a maximum of 16 data disks attached. You can expand a single disk, but you cannot scale it in after the expansion takes effect.
The bandwidth of an ECS instance is measured in Mbit/s. The bandwidth range is 0 Mbit/s to 200 Mbit/s. You can modify the bandwidth or change the bandwidth billing method.
Why does the instance configuration upgrade not take effect?
After you upgrade the instance configurations, you must restart the instance in the console or by calling an API operation for the changes to take effect.
Can I cancel an upgrade order and restore the original configurations?
After an upgrade order takes effect, the new configurations are applied and the order cannot be canceled. To restore the original configurations, you can downgrade the instance. You will then be billed based on the downgraded configuration.
How do I view all subscription instances in all regions under the same account?
Go to the Renewal page to view all subscription instances in all regions.
Log on to the ECS console.
In the top menu bar, choose .
How do I export ECS resource usage information?
You can export information about your resources from the last month by downloading a resource usage report in Hybrid Cloud Monitoring. If you are using Hybrid Cloud Monitoring for the first time, you must enable it separately. Hybrid Cloud Monitoring uses a pay-as-you-go billing method. You are not charged for enabling Hybrid Cloud Monitoring. You are charged based on your actual usage. For more information about billing, see Resource usage report.
What do I do if an ECS instance is in the Starting state for a long time and the Aliyun Assist Service is disabled or deleted?
Problem description: After starting an ECS instance, it remains in the Starting state for a long time and then automatically shuts down. When you log on to the system to check the system services, you find that the Cloud Assistant service has been deleted or disabled.
Solution:
If the Cloud Assistant service is disabled:
Change the Cloud Assistant service startup type to Automatic.
Restart the ECS instance.
If the Cloud Assistant service is deleted:
Run the following command to re-add the service.
sc.exe create AliyunService type= "own" start= "auto" binPath= "C:\ProgramData\aliyun\assist\{Version}\aliyun_assist_service.exe -d" tag= "no" DisplayName= "AliyunService"NoteMake sure to keep the space after the
=sign.Open the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\AliyunService and change
C:\ProgramData\aliyun\assist\{Version}\aliyun_assist_service.exe -dto"C:\ProgramData\aliyun\assist\{Version}\aliyun_assist_service.exe" -d.Restart the ECS instance.
Why does an ECS instance fail to load the kernel and start?
Problem description: During system startup, selecting any option from the GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) menu results in no response. After attaching a LiveCD image to the ECS instance and logging on to the system, the file system permissions and message log information appear normal.
Cause: The system is infected with ransomware.
Solution: Back up important data and re-initialize the system.
When can I force stop an instance? What are the consequences?
If you cannot stop an instance through the normal shutdown process, you can force stop it. Force stopping an instance is like cutting off the power. Data in the instance's operating system that has not been written to disks may be lost.
Why does a restart fail?
A restart may fail for the following reasons:
Your account has an overdue payment. Settle the bill and try again.
The system is busy. Try again later.
The resources are out of stock.
NoteYou can go to the ECS Instance Types Available for Each Region page to view the instance types available in each region.
When I use Auto Scaling, I enabled release protection for an ECS instance in a scaling group. Why was the instance still automatically released?
After Auto Scaling automatically creates an ECS instance, if you enable release protection for the instance on the instance list page in the ECS console or by calling the ModifyInstanceAttribute operation, it does not prevent Auto Scaling from automatically releasing the instance.
You can put the ECS instance in a scaling group into the Protected state in the Auto Scaling console to prevent it from being automatically released. For more information, see Put an instance into the Protected state.
How do I apply for an ICP filing for a domain name after purchasing an ECS instance?
The purchased ECS instance must meet the ICP filing requirements. For more information, see Prepare and check the instance and access information.
Does an ECS instance provide a database by default?
An ECS instance does not provide a database by default. You can:
Deploy a database yourself.
Separately purchase the Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB RDS service.
Use an Alibaba Cloud Marketplace image to configure the database environment.
Can I build a database on an ECS instance?
Yes, you can. You can install database software and configure the environment as needed. ECS does not impose any restrictions. You can also separately purchase the Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB RDS service.
Does an ECS instance support Oracle databases?
Yes. To confirm that an ECS instance can meet the read and write requirements of your Oracle database, we recommend performing a stress test on the instance before you install the database.
Can I change the region of an ECS instance after purchase?
No, you cannot. However, you can use CloudOps Orchestration Service's public template ACS-ECS-CloneInstancesAcrossRegion to copy an ECS instance to another region. The copied instance has identical disk data, but its IP address may change.
Can an ECS instance be used for load balancing?
Both Linux and Windows ECS instances can be used for load balancing. However, you must ensure that the web server configurations and website code are consistent. A single ECS instance under the same account can use load balancing, but for optimal performance, we recommend using two or more ECS instances for load balancing.
How do I migrate data between ECS instances?
Migration methods vary based on the region and account ownership of the source and destination ECS instances:
The source and destination instances are in the same region and belong to the same account
Migrate instance data using an image
Create a custom image from the source ECS instance.
Use the image to create a new ECS instance or replace the image of the existing destination ECS instance. For more information, see Create an instance from a custom image or shared image and Change the operating system (system disk).
Migrate instance data using a snapshot
Create a snapshot of the source instance's disk. For more information, see Create a snapshot.
Use the snapshot to create a new disk. For more information, see Create a data disk from a snapshot.
Attach the new disk to the destination instance. For more information, see Attach a data disk.
The source and destination instances are in different regions
Create a custom image from the source ECS instance.
Copy the custom image to the region of the destination instance. For more information, see Copy a custom image.
Use the image to create a new ECS instance or replace the image of the existing destination ECS instance. For more information, see Create an instance from a custom image or shared image and Change the operating system (system disk).
The source and destination instances are in the same region but belong to different accounts
Create a custom image from the source ECS instance.
Share the image with the account of the destination instance. For more information, see Share a custom image.
Use the image to create a new ECS instance or replace the image of the existing destination ECS instance. For more information, see Create an instance from a custom image or shared image and Change the operating system (system disk).
The source and destination instances are in different regions and belong to different accounts
Create a custom image from the source ECS instance.
Copy the image to the destination region. For more information, see Copy a custom image.
Share the image with the account of the destination instance. For more information, see Share a custom image.
Use the image to create a new ECS instance or replace the image of the existing destination ECS instance. For more information, see Create an instance from a custom image or shared image and Change the operating system (system disk).
For more information, see Copy an ECS instance across regions using a custom image.
Additionally, Server Migration Center (SMC) supports various features such as full migration, incremental migration, batch migration, and migration within a VPC. You can also complete migrations between ECS instances in the SMC console. For more information, see Migrate ECS instances between accounts or within the same account.
Can I transfer the remaining usage duration of one ECS instance to another?
No, you cannot. If you need a solution that is both flexible and cost-effective, we recommend that you purchase pay-as-you-go instances and use them with reserved instances. For more information, see Overview of reserved instances.
I purchased an ECS instance and want to add a sound card and a graphics card, but I found that I cannot add them. Why?
Alibaba Cloud ECS provides standard servers, not multimedia servers. By default, they do not include sound card or graphics card components. Therefore, you cannot add them in the system.
How do I change the owner and group of a directory or file on a Linux instance?
If the permissions of a file or directory on a web server are incorrect, it can lead to a 403 error when you access the website. Therefore, before you adjust file and directory permissions, confirm the running identity of the process.
You can use the ps and grep commands to query the running identity of the process for a file or directory.
You can use the ls -l command to query the owner and group of a file or directory.
You can use the chown command to modify permissions. For example, chown -R www.www /alidata/www/phpwind/ changes the owner and group of all files and directories under the /alidata/www/phpwind directory to the www account.
Can a spot instance be converted to a subscription instance?
No, it cannot.
Can I change the instance type of a spot instance?
Not supported.
The configurations of my spot instance are insufficient. How can I switch to a higher configuration at a low cost?
Because you cannot change the instance type of a spot instance, we recommend that you create a custom image from the system disk of the spot instance. You can then use the custom image to create a spot instance with a larger instance type. For more information, see Create a custom image from a snapshot and Create an instance from a custom image or shared image.
If I select Automatic Bidding when purchasing a spot instance, can the instance still be released due to insufficient inventory?
Automatic bidding sets the upper limit to the price of a pay-as-you-go instance, which prevents the instance from being released due to a bid lower than the market price during market price fluctuations. However, the instance can still be released if the inventory for the corresponding instance type is insufficient.
If I set the maximum price to the highest possible bid, which is the price of a pay-as-you-go instance, when I purchase a spot instance, can the instance still be released?
Setting the price to that of a pay-as-you-go instance prevents the instance from being released due to a bid lower than the market price during market price fluctuations. However, the instance can still be released if the inventory for the corresponding instance type is insufficient.
I have set a release time for my spot instance. Can I cancel or change it?
Yes, you can. You can cancel or change the release time at any point before the spot instance is released.
My payments are not overdue. Why was my spot instance released?
After the protection period of a spot instance ends, if the market price at a certain moment is higher than your bid, or if the supply and demand for ECS resources change, the spot instance will be reclaimed.
How is the release rate on the buy page calculated? Why is it mostly between 0% and 3%?
The release rate is calculated based on the zone and instance type. The daily release rate is calculated as: Total releases in a day / Total retained instances in a day. A release rate mostly between 0% and 3% is expected. Alibaba Cloud is continuously optimizing to lower the release rate so that you can hold spot instances more stably.
Will I be notified when my spot instance is released? How will I be notified?
You will receive a notification when a spot instance is scheduled for release due to market price changes or supply adjustments. The instance then enters a pending revocation state and is automatically released approximately 5 minutes later.
To subscribe to notifications, you can subscribe to spot instance interruption notifications in CloudMonitor. For more information, see Set event notifications.
To confirm the pending-release state, you can check the instance status through instance metadata or the OperationLocks information returned by the DescribeInstances API operation. For more information, see Instance metadata and DescribeInstances.
Can data be automatically retained after a spot instance is released?
No, it cannot. If you do not need to use the spot instance temporarily, we recommend that you first create a snapshot to back up data and the environment, release the instance, and then purchase a new one when needed. For more information, see Create a snapshot.
I enabled economical mode when I stopped a spot instance. What do I do if the instance fails to start again?
After you enable economical mode, the instance may fail to start if the resource inventory is insufficient. To save the business data in the instance, follow these steps:
Create a snapshot of the disk for the instance (let's call it A). For more information, see Create a snapshot.
When the snapshot creation progress reaches 100%, the snapshot is created.
Use the created snapshot to create a custom image. For more information, see Create a custom image from a snapshot.
When the image status is Available, the custom image is created.
Use the created custom image to create an instance (let's call it B).
For more information, see Create an instance from a custom image or shared image.
Check if there are any issues with the business data in instance B.
If there are no issues with the business data, you can release instance A. For more information, see Release an instance.
If there are issues with the business data, you can detach the disk from instance A (do not select Release with instance when detaching the disk), attach it to instance B, and then release instance A. For more information, see Detach a data disk and Release an instance.
After the protection period of a spot instance ends, if the market price is greater than my bid, the instance enters a pending-release state. During the 5-minute notification period before the instance is released, if the market price drops below my bid, will the instance be retained?
The spot instance will not be retained. Once an instance receives a pending-release notification, it is marked for release. This mark is irreversible, and the instance will be released on schedule.
How can I retain the public IP address of a spot instance as long as possible?
When a spot instance is released, its public IP address is also reclaimed. To use a specific public IP address, we recommend that you use the Elastic IP Address feature.
You can convert an existing public IP address to an Elastic IP Address. For more information, see Convert a static public IP address to an EIP and Convert a static public IP address of a classic network-type ECS instance to an EIP.
In terms of price, which is more cost-effective: a spot instance with no protection period or one with a protection period?
A spot instance with no protection period is always more cost-effective than one with a protection period and offers a price that is approximately 10% lower.
Is the release rate of a spot instance with no protection period higher than that of a spot instance with a protection period?
You can view the release rate for a specific instance type on the buy page. This rate applies to both instances with and without a protection period. The release rate is mainly determined by the supply and demand of the instance type and the bidding policy.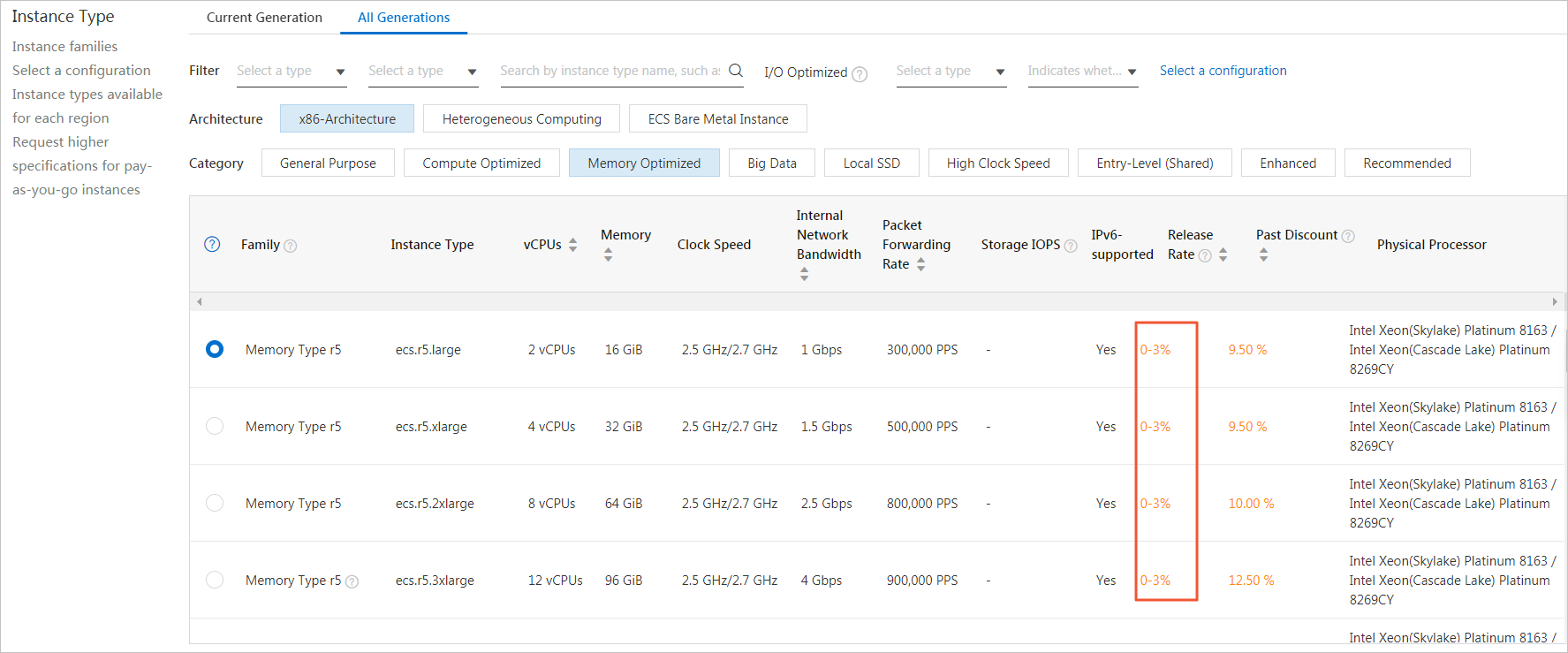
Are spot instances with no protection period released with a higher priority?
No, it does not.
After I create a spot instance with no protection period, will all new spot instances I create have no protection period?
No. To ensure a consistent user experience, a spot instance with no protection period is created only when you manually select that option. Otherwise, newly created spot instances will still have a default 1-hour protection period.
You can only set the protection period when you create a spot instance.
Will I still receive a notification 5 minutes before a spot instance with no protection period is released?
Yes, you will. You will be notified, which gives you the same amount of processing time as for a spot instance with a protection period.
In terms of resource quantity, are there fewer resources for spot instances with no protection period than for those with a protection period?
There is no significant difference in the quantity of resources between the two.
Can I switch between a protection period and no protection period?
No, you cannot. A spot instance has a default 1-hour protection period. You can only set the protection period when you create the spot instance. You cannot change the protection period setting after the instance is created.
After installing MySQL on an ECS instance, I can log on locally but fail to connect to the MySQL database remotely. The error message "1045 - Access denied for user 'root'@'****'(using password:YES)" is reported. What do I do?
Symptom
After you install MySQL on an ECS instance, you can log on locally, but when you try to connect to the MySQL database remotely with the same username and password, it fails with the error message "1045 - Access denied for user 'root'@'****'(using password:YES)" (you have confirmed that the correct username and password were entered).
Cause
After you install MySQL on an ECS instance, by default, it only allows local logon. The MySQL database has not been authorized for remote logon from other IP addresses.
Solution
Follow these steps to grant permission to other IP addresses.
Remotely connect to the ECS instance.
For more information, see Connection methods.
Log on to the database and run the following SQL commands to grant remote logon permission to the MySQL database.
Replace
<user_name>and<password>with the username and password that failed to log on remotely.CREATE USER '<user_name>'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO '<user_name>'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;NoteAfter you run this SQL command, the user can log on to the database from any IP address and perform operations on any object in any database. Note: This command sequence is for MySQL 8.0 and later. MySQL 5.7 and earlier may support the original single GRANT command. For security reasons, do not allow access from any IP address (%) in a production environment. We recommend that you: 1) Restrict access to specific IP addresses (such as 'root'@'192.168.1.100'). 2) Create a dedicated account for remote access. 3) Set a strong password. 4) Avoid granting ALL PRIVILEGES.
The following table describes the parameters in the SQL command.
Parameter
Description
*.*
The first asterisk (*) is the database placeholder. The value
*represents all databases. The second asterisk (*) is the table placeholder. The value*represents all tables in the database.'root'@'%'
root is the database account for logon authorization, and the percent sign (%) is an IP address placeholder. To allow logon from only the IP address
1.1.1.1, change%to1.1.1.1. If you specify%, logon is allowed from any IP address.Run the following SQL statement to refresh the permissions.
flush privileges;Try to remotely connect to the MySQL database again. If the error message no longer appears, the issue is resolved.
I failed to remotely connect to MySQL on a Linux ECS instance. The error message "ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '39.106.**.**' (110)" is reported. What do I do?
Symptom
A user fails to remotely connect to MySQL on a Linux ECS instance, and the error message "ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '39.106.**.**' (110)" is reported.
Cause
This may be because the IP address 39.106.**.** does not have permission to access MySQL (meaning port 3306 is not listening on this IP address), which prevents a remote connection to MySQL.
Solution
Remotely log on to the Linux instance where MySQL is installed.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using a password or key.
Run the following command to back up the
my.cnffile.cp my.cnf my.cnf.bakModify the
my.cnfconfiguration file.Run the following command to open the
my.cnffile.vim /etc/my.cnfPress the
ikey to enter edit mode, and add the following content to themy.cnffile.bind-address = 0.0.0.0The following figure shows the location to add the content.
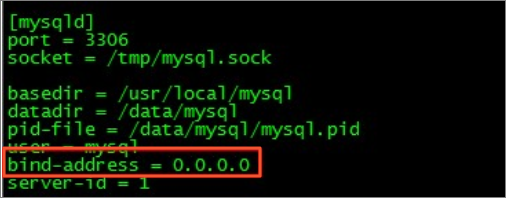
After you add the content, press the
Esckey to exit edit mode, enter:wq, and press theEnterkey to save and exit the file.
Run the following command to restart the MySQL service and confirm that MySQL port 3306 is listening normally.
service mysqld restart
What are the daily O&M recommendations for hosting a small website on an ECS instance?
When you maintain a website application, you can refer to the following operational recommendations.
Perform daily backups of disk data. For more information, see Create a snapshot or Create an automatic snapshot policy for a disk.
We recommend that you use an SSL Certificate service to implement website identity verification and encrypted data transmission. For more information, see What is Certificate Management Service?.
Install a malware scanning plugin, an anti-DDoS attack service, or enable the Security Center service. ECS provides free security services. For more information, see Basic security services or Anti-DDoS Basic.
Monitor the inbound and outbound traffic of your website to identify unusual traffic intervals. Add security group rules to deny access and temporarily manage single-point abnormal requests. For more information, see View instance monitoring information and Add a security group rule.
Monitor the performance of your ECS instance and disks, and mark peak traffic periods. Familiarize yourself with upgrading or downgrading instances, elastic scaling, or expanding disks to handle sudden surges in requests. For more information, see Overview of instance upgrade or downgrade, What is Auto Scaling?, or Overview of disk expansion.
In scenarios where you log on to an ECS instance using root/administrator username and password credentials, you need to regularly update the administrator password. For more information, see Reset the logon password of an instance.
Regularly update software patches. Alibaba Cloud public images are updated with security patches on a regular basis. We recommend that you periodically create custom images from public images. For more information, see Update a custom image.
How do I upload files to a Linux instance?
You can use an FTP service to upload files to a Linux instance.
How do I use an FTP tool to upload files on macOS?
Method 1: Upload through the macOS built-in terminal
You can upload files through the macOS terminal or iTerm2 (Download iTerm2). Make sure to select the correct path for uploading files.
Connect to the FTP service.
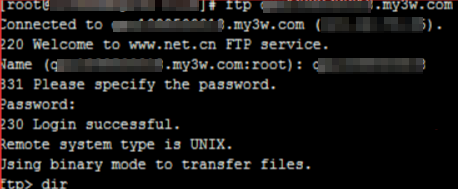
Go to the correct directory. No switch is needed for Windows systems. For Linux systems, switch to htdocs.
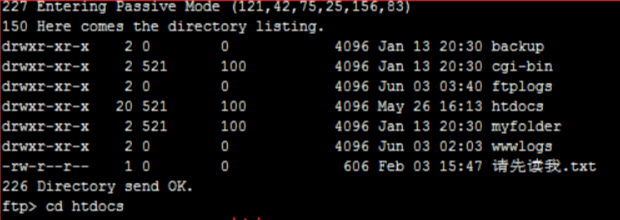
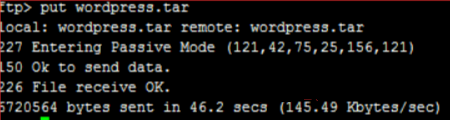
Run the put command to upload.
Method 2: Upload through a third-party tool
Download Yummy FTP.
Install Yummy FTP on macOS.
Enter the FTP server's IP address, username, and password. Set Protocol to Standard (FTP) and Port to the default 21 (or the port you are using). Do not select SSH key.
Click Connect.
On the right, select the directory to upload to (no directory selection needed for Windows, select the htdocs directory for Linux hosts). In the left window, select the file to upload and click Upload.
If the system prompts "Your security preferences allow installation of only apps from the Mac App Store and identified developers" during Yummy FTP installation, follow these steps to configure your computer.
Go to .
Click the lock icon in the lower-left corner and enter the administrator password to unlock.
In the Allow Apps Downloaded From menu, select Anywhere.
After these settings are configured, you can install the software normally.
I failed to upload a file to a Linux ECS instance using vsftp. The error message "553 Could not create file" is reported. What do I do?
Cause
This may be due to the following reasons:
The disk space on the Linux instance is full.
The FTP
homedirectory does not havewritepermission.
Solution
Follow these steps to check the disk space of the Linux instance and the permissions of the FTP
homedirectory.Remotely connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using a password or key.
Run the following command to check if the disk space on the Linux instance is full, which would cause the file upload to fail with this error.
df -hNoteIf the disk partition usage reaches 100%, the disk space is full.
The system displays information similar to the following. For example, the usage of the
/dev/xvda1partition is 59%.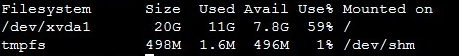
Run the following command to check if the FTP
homedirectory haswritepermission.NoteBefore you run the following command, replace the
/home/userdirectory with your actual FTPhomedirectory name.ls -l /home/userIf there is no
win the permissions shown in the red box in the following figure, it means you do not havewritepermission.
Run the following command to add
writepermission and save.chmod +w /home/userRun the following command. If the command output contains
w, it means thewritepermission has been successfully added.ls -l /home/user
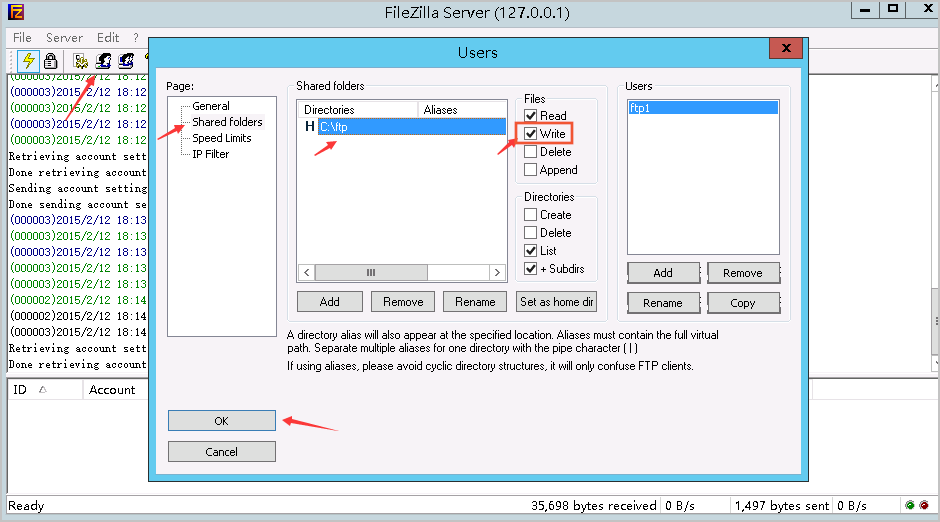
I failed to upload a file to FileZilla Server using FTP on a Windows ECS instance. The error message "550 Permission denied" is reported. What do I do?
Failed to install Cloud Assistant Agent on a Linux ECS instance with the "No such file or directory" error.
How do I view the run logs of Cloud Assistant?
What are the default installation paths of Cloud Assistant Agent on different operating systems?
How do I check the status of the Cloud Assistant service?
After you remotely connect to the ECS instance, use the following methods:
Check the status of the Cloud Assistant service to confirm if it is enabled and running normally:
Linux systems:
Method 1
sudo systemctl status aliyunMethod 2
ps aux | grep aliyunWindows Server systems:
Go to Computer Management > Services and Applications > Services, and find Aliyun Service.
Find the log file in the corresponding directory. For example:
tail -n 100 /usr/local/share/aliyun-assist/$(/usr/sbin/aliyun-service -v)/log/aliyun_assist_main.logFind the heartbeat or update log file in the corresponding directory. For example:
tail -n 100 /usr/local/share/aliyun-assist/$(/usr/sbin/aliyun-service -v)/log/aliyun_assist_update.log
Why can a Shell script run on systems such as CentOS but not on Ubuntu?
This is because the default Shell environment for higher versions of Ubuntu is dash, not bash. The Shell syntax of dash is not fully compatible with bash. You can switch the default Shell environment to resolve this issue.
Run the following command to confirm if the Shell environment is dash.
ls /bin/shRun the following command to switch to the default Shell environment.
dpkg-reconfigure dash
Follow the on-screen prompts and choose not to set dash as the default Shell environment.
Can I use Cloud Assistant on classic network-type instances?
Yes, you can. For classic network-type instances, we recommend that you install the latest version of Cloud Assistant Agent. For more information, see the section on installing the client via a download link in Install Cloud Assistant Agent. If you are using an older version of the client, you must create a file named region-id in the Cloud Assistant installation path and enter the ID of the region where the ECS instance is located. For a list of values, see Regions and zones. For example, for a CentOS ECS instance in the China (Hangzhou) region:
Enter the region ID.
echo 'cn-hangzhou' > /usr/local/share/aliyun-assist/region-idRestart the Cloud Assistant service.
When I run a command in the ECS console, why am I prompted that the Cloud Assistant service is not installed on the instance?
This is because Cloud Assistant has not received the corresponding heartbeat information. Use the following methods to resolve this issue.
If the Cloud Assistant service process was shut down, you can restart it. For Windows Server systems, see How do I check the status of the Cloud Assistant service?. For Linux systems, follow these steps:
Run the following command to restart the Cloud Assistant service.
sudo systemctl restart aliyunRun the following command to confirm if the Cloud Assistant service starts automatically on boot.
sudo systemctl status aliyunIf the status is disable, run the following command to set it to start automatically on boot.
sudo systemctl enable aliyun
For classic network-type instances with an older version of Cloud Assistant Agent installed, you need to manually add a configuration file to specify the region information of the ECS instance. For more information, see Can I use Cloud Assistant on classic network-type instances?.
The run log contains "Failed to open gshell: Device or resource busy". How do I resolve this issue?
Symptom: The log contains the following information.
2019-11-06 03:10:15,993 INFO [default] /dev/virtio-ports/org.qemu.guest_agent.0:-1 2019-11-06 03:10:15,993 ERROR [default] Failed to open gshell: Device or resource busyTroubleshooting:
Method 1
Check if multiple processes of Cloud Assistant Agent are running. If there are multiple, stop all of them and then restart Cloud Assistant Agent.
ps aux | grep aliyunMethod 2
See which processes are using the org.qemu.guest_agent.0 file. Cloud Assistant processes all have the format aliyun-**. Stop all non-Cloud Assistant processes.
lsof /dev/virtio-ports/org.qemu.guest_agent.0
Why can some scripts be run on my local machine but report "command not found" when run using Cloud Assistant?
First, check the environment variables of the Cloud Assistant session to see if they include the corresponding command from the script.
Troubleshooting for Linux instances
Run the following command to view the environment variables.
exportRun the following command to set the environment variables (use the actual environment variables on the instance).
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
Troubleshooting for Windows instances
Run the following command to view the environment variables.
setRun the following command to set the environment variables (use the actual environment variables on the instance).
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\;C:\Users\Administrator\A
Why is the task status Failed after I run a task?
Check the following to troubleshoot the issue:
If you are using a Windows instance, check if PowerShell is working correctly on the instance.
Confirm if the failure was caused by a task timeout.
Confirm if the Cloud Assistant service status is normal. You can query this using DescribeCloudAssistantStatus.
View the Cloud Assistant log information. The default log paths are as follows:
Linux instances: /usr/local/share/aliyun-assist/Cloud-Assistant-version-number/log/
Windows instances: C:\ProgramData\aliyun\assist\Cloud-Assistant-version-number\log
Why is the task status Abort after I run a task?
A task status of "Abort" means the task was not sent to the instance within one minute. We recommend that you resend the task.
If it consistently fails, check the Cloud Assistant log information.
A Cloud Assistant script contains Chinese characters. Why are garbled characters displayed in the returned result?
Standard system command encoding: Linux instances use UTF-8 encoding by default. Windows instances use GBK encoding by default.
If a Cloud Assistant script contains Chinese characters, it will use the encoding provided in the input. Make sure to use the corresponding method to decode it.
What do I do if the WeChat Official Accounts Platform token verification fails for a deployment on an ECS instance?
Symptom
The WeChat Official Accounts Platform token verification for a deployment on an ECS instance fails.
Cause
Common possible causes are as follows:
Improper file editing, such as using Notepad or online editors, which adds a UTF-8 BOM signature to the file.
If the ECS instance has Security Dog or Security Center installed, it may block requests from Tencent servers.
Using a temporary domain name for verification on a virtual host, which is blocked by the system. This applies to HiChina virtual hosts.
The PHP file contains a line break or other characters after the closing tag.
Other debugging and verification methods were used.
The program has a Gzip encoding exception.
Solution
The recommended solutions for the common causes are as follows:
Improper file editing, such as using Notepad or online editors
We recommend that you use a multi-functional editor to remove the BOM.
The ECS instance has Security Dog or Security Center installed
We recommend uninstalling Safedog or configuring a whitelist in Security Center.
Using a temporary domain name for verification on a virtual host
We recommend that you use a formal domain name that has completed ICP filing with Alibaba Cloud for the verification.
The PHP file contains a line break or other characters after the closing tag
We recommend that you remove the extra characters.
Other debugging and verification methods were used
Run the
curl http://xxx/index.php/api/xxcommand to debug and verify, simulating a WeChat API request for analysis.The program has a Gzip encoding exception
We recommend that you temporarily disable the program's Gzip feature for testing and troubleshooting.
What do I do if Chinese characters are displayed as garbled text on a Linux ECS instance?
Symptom
When you remotely connect to an Alibaba Cloud Linux ECS instance using a third-party Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) client, Chinese fonts are displayed as garbled text.
Cause
This issue may be caused by the following reasons:
The Linux system does not have Chinese fonts installed: The default language of the Linux system does not support Chinese display. You need to install a Chinese language pack to enable Chinese display. See Method 1: Install the Chinese language pack on the Linux ECS instance to fix this.
Character set settings issue in the third-party SSH client tool. See Method 2: Modify the character set settings of the third-party SSH client tool to fix this.
Solution
Choose the appropriate method based on your situation.
Method 1: Install the Chinese language pack on the Linux ECS instance
The following operations use CentOS 7.8 as an example. For other versions of CentOS or other distributions (such as Red Hat, Debian, or Ubuntu), refer to the corresponding official documentation for configurations and commands.
Remotely connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance using a password or key.
Query the current system language.
echo $LANGNoteIf it is English, proceed to step 3.
If it is Chinese, it means the Linux ECS instance already has the Chinese language pack installed. This rules out the cause of garbled text due to missing Chinese fonts. Proceed to Method 2: Modify the character set settings of the third-party SSH client tool.
Check if the Chinese language pack is installed on the current system.
locale -a | grep "zh_CN"The system displays something similar to the following, where zh represents Chinese, CN represents China, and gb18030, gb2312, gbk, and utf8 are character sets.
zh_CN zh_CN.gb18030 zh_CN.gb2312 zh_CN.gbk zh_CN.utf8If the Chinese language pack is not installed, run the following command to install it.
sudo yum groupinstall "fonts"Run the following command to edit the
/etc/locale.confconfiguration file.vim /etc/locale.confPress the
ikey to enter edit mode, and then changeLANG=en_US.UTF-8toLANG=zh_CN.UTF-8to set the system language to Chinese.Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press Enter to save the changes and close the configuration file.
Run the following command for the configuration to take effect.
source /etc/locale.confRestart the server.
reboot(Optional) If the system language is still English after you restart the server, run the following command to edit the
/etc/profile.d/lang.shconfiguration file.vim /etc/profile.d/lang.shPress the
ikey to switch to edit mode, changezh*) LANG=en_US.UTF-8tozh*) LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8. The modified content is shown in the following figure.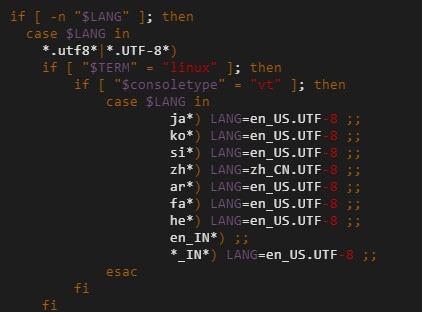
After you make the changes, press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and press Enter to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command to restart the server.
reboot
Method 2: Modify the character set settings of the third-party SSH client tool
The following operations use the XShell client as an example to show how to modify the character set settings of the XShell client tool.
Open the XShell client.
On the XShell client page, set Default Language to Unicode (UTF-8).
Log on to the instance again. If the error no longer occurs, the issue is resolved.
What is the AliVulfix process in an ECS instance?
The AliVulfix process is a program used by Security Center for vulnerability detection, which scans the ECS instance for vulnerabilities.
Can an ECS instance defend against network attacks?
Alibaba Cloud ECS instances are equipped with the Security Center service, which can defend against DDoS flood attacks. When a network attack occurs, the Alibaba Cloud monitoring system automatically detects and scrubs the unusual traffic. If the attack volume is very large, Alibaba Cloud performs blackhole routing to protect your ECS instance. For security reasons, we recommend that you install your own protection software to enhance the defense effect and close unused ports.
What security services does Alibaba Cloud offer?
Alibaba Cloud Security Center, combined with the powerful data analytics capabilities of the Alibaba Cloud platform, provides you with one-stop security services, such as security vulnerability detection, web trojan detection, host intrusion detection for ECS users, and defense against DDoS flood attacks.
For more security services, see the Security Products page.
For more security services, see the Security Products page.
How do I detect if a server is being used for mining?
Based on the features of mining programs, you can use the following methods to detect if your server is being used for mining.
Check if the CPU usage of the corresponding server is normal.
NoteIf your server's CPU usage is significantly high, for example, reaching 80% or more, and there are unknown processes continuously sending network packets, you can determine that there is a mining threat on your server.
Log on to the Security Alerts page of the Security Center console and check if there are any attack alerts being processed.
For more information, see Best practices for defending against mining programs and Best practices for handling mining programs.
How do I handle mining programs or request to unblock my server?
Handle mining programs
You can investigate mining programs in Security Center and mining worms in Cloud Firewall. For more information, see Best practices for defending against mining programs and Best practices for handling mining programs.
Request to unblock an ECS instance
A server may be locked due to reasons such as mining viruses or being attacked. You can request to have it unblocked. For the unblocking entry point, see Penalty List.
Note the following about unblocking:
You can only request self-service unblocking once.
After a successful unblocking request, an automatic check is performed within 3 days. If mining behavior is detected again, the server is blocked again and cannot be unblocked.
After unblocking, back up your data promptly.