Security-enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel feature that provides a security policy-based protection mechanism for access control. In general, we recommend that you enable SELinux to limit the permissions of processes, thereby guarding against threats from malicious programs. However, SELinux's strict access control mechanism may prevent some trusted applications or services from starting as expected. In development or debugging scenarios, you may temporarily disable SELinux.
For more information about SELinux, see What is SELinux?
Considerations
This topic uses the following images to describe how to enable and disable SELinux:
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bit
CentOS 7.6 64-bit
If you use other Linux distributions, such as Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9, Debian, or Ubuntu, perform the operations described in the corresponding official documentation or community guide. The methods and tools that you can use to enable and disable SELinux vary based on your Linux distribution. For information about how to configure SELinux on a specific version of a Linux distribution, visit the official website of the Linux distribution or consult the community forums.
Enable SELinux
Connect to a Linux Elastic Computer Service (ECS) instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Run the following command to check the status of SELinux:
sestatusIf
disabledis returned for theSELinux statusparameter, SELinux is disabled on the instance.
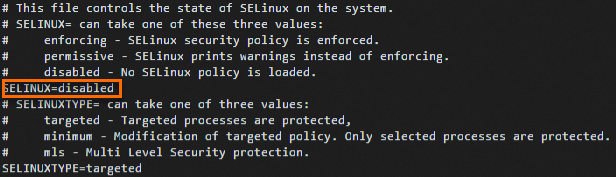
Run the following command on the instance to open the
configfile of SELinux:sudo vi /etc/selinux/configFind the line that contains
SELINUX=disabledand press theIkey to enter Insert mode.The following table describes the modes in which you can enable SELinux. You can select a mode based on your business requirements.
Mode
Value
Description
Enforcing
SELINUX=
enforcingAll requests that violate the security policy of SELinux are denied.
Permissive
SELINUX=
permissiveRequests that violate the security policy of SELinux are not denied, but are recorded in logs.
Press the
Esckey to exit Insert mode, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the file.ImportantAfter you modify the
configfile, you must restart the instance for the changes to take effect. However, if you restart the instance immediately after the modification, the system may fail to start. To prevent this issue, you must create an.autorelabelfile before you restart the instance.Run the following command to create the
.autorelabelfile in the root directory:sudo touch /.autorelabelRestart the ECS instance. For more information, see Restart an instance.
NoteWhen the ECS instance is restarting, SELinux automatically relabels all system files. The relabel operation is a comprehensive scanning process. The amount of time required to relabel all system files varies based on the number and size of system files. We recommend that you do not perform any operations on the instance after the instance begins to restart until the relabel operation is completed. This ensures the correctness of file security settings.
Disable SELinux
Disabling SELinux renders your system more vulnerable against attacks. Therefore, we recommend that you carefully evaluate the potential risks and make sure that there are other effective security measures protecting your system.
Connect to a Linux ECS instance.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Run the following command to check the status of SELinux:
sestatusIf
enabledis returned for theSELinux statusparameter, SELinux is enabled on the instance.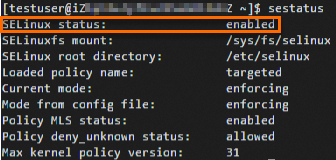
Temporarily or permanently disable SELinux.
NoteTemporarily disabling SELinux affects only the current session. After the instance is restarted, the original status of SELinux is restored. You can modify the configuration file to permanently disable SELinux. This way, SELinux remains disabled after an instance restart.
Temporarily disable SELinux
Run the following command to temporarily change the mode of SELinux from
enforcingtopermissive:sudo setenforce 0Permanently disable SELinux
Run the following command to open the
configfile of SELinux:sudo vi /etc/selinux/configFind the line that contains
SELINUX=enforcingorSELINUX=permissive, press theIkey to enter Insert mode, and then change the line toSELINUX=disabled.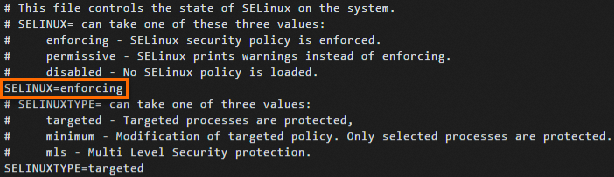
Press the
Esckey to exit Insert mode, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the file.Restart the ECS instance.
For more information, see Restart an instance.
Run the following command to check the status of SELinux:
sestatusIf
disabledis returned for theSELinux statusparameter, SELinux is permanently disabled.
References
In permissive mode, you can review logs to find events that violate the security policy of SELinux and modify SELinux policy rules to prevent requests that are accidentally blocked after the SELinux mode is changed to enforcing. For more information, see View system logs and screenshots.