This topic describes how to specify x86-based Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance types to create an elastic container instance.
Description of the ECS instance families
x86-based ECS instance families can be divided into enterprise-level instance families and shared instance families based on whether the instance families are suitable for enterprise scenarios:
Some of the preceding ECS instance families such as i2 and d1ne use local disks. If you want to specify ECS instance types that use local disks to create an elastic container instance and attach a local disk to the elastic container instance, specify the volume-related parameters. For more information, see Specify ECS instance types that use local disks to create an elastic container instance.
For more information about ECS instance families, see the following topics:
Configuration description
API mode
When you call the CreateContainerGroup operation to create an elastic container instance, you can use the InstanceType parameter to specify ECS instance types. The following table describes the parameter. For more information, see CreateContainerGroup.
Parameter | Type | Example | Description |
InstanceType | String | ecs.c6.xlarge,ecs.g6.xlarge | The ECS instance types. You can specify up to five ECS instance types at a time. Separate multiple instance types with commas (,). |
Console mode
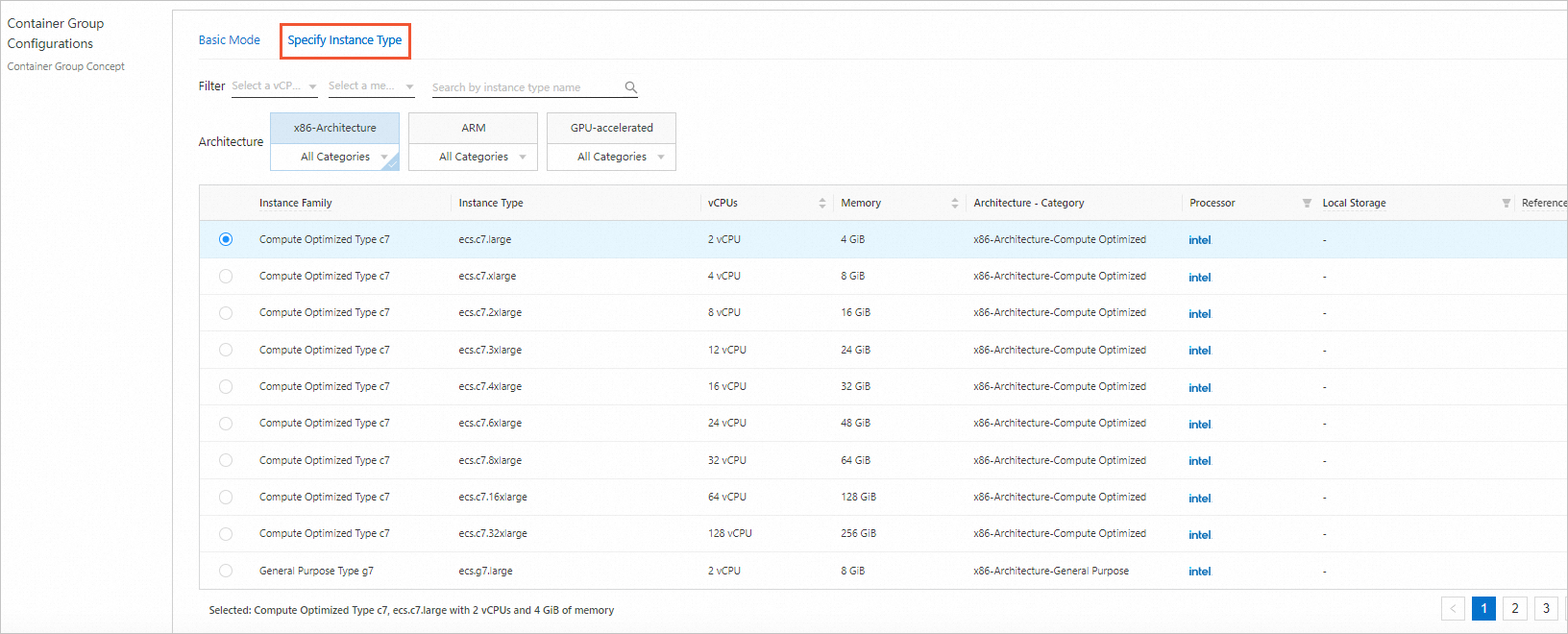
When you create an elastic container instance in the Elastic Container Instance console, you can click the Specify Instance Type tab in the Container Group Configurations section and select x86-based ECS instance types based on your business requirements.
You can select the number of vCPUs and a memory size or select a specific ECS instance type to filter ECS instance types. You can also filter ECS instance types by selecting a process in the Processor column.
If you want to use an x86-based ECS instance type that uses a local disk to create an elastic container instance, we recommend that you use the API mode because the console mode does not support in attaching local disks.