After you configure a change tracking task, you can use the SDK demo that is provided by Data Transmission Service (DTS) to track and consume data. This topic describes how to use the SDK demo to consume the data tracked from distributed databases. The supported source databases are PolarDB for Xscale (PloarDB-X) 1.0 instances and Data Management (DMS) logical databases.
Prerequisites
- The Java Development Kit (JDK) V1.8 is installed.
- IntelliJ IDEA is installed.
Usage notes
If you want to track and consume data as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, the RAM user must have the AliyunDTSFullAccess permission and the permissions to access the source objects. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Use a system policy to authorize a RAM user to manage DTS instances and Grant permissions to the RAM user.
Procedure
This topic describes how to use the SDK demo to consume the data tracked from a PolarDB-X 1.0 instance. In this example, IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2020.1 for Windows is used.
- Create a change tracking task. For more information, see Track data changes from an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance .
- Create one or more consumer groups. For more information, see Create consumer groups.
- Download the SDK demo package and decompress the package.
- Open the file that you want to use as a project in IntelliJ IDEA.
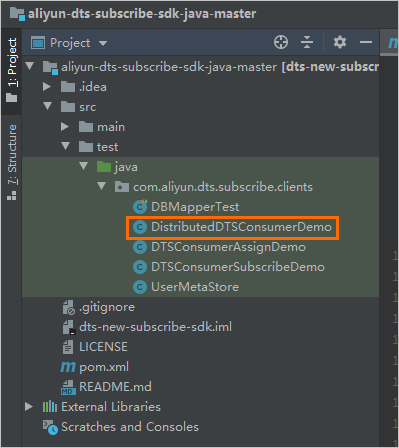
- In IntelliJ IDEA, expand the folders to find the Java files. Then, double-click a Java file based on the mode in which you use an SDK client.In this scenario, select DistributedDTSConsumerDemo.
- Set the required parameters in the code of the Java file.
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClientException { // Configure a change tracking task for a distributed database such as a PolarDB-X 1.0 instance. Set the parameters that are used to specify your AccessKey pair, instance ID, task ID, and consumer groups. String accessKeyId = "LTA***********99reZ"; String accessKeySecret = "****************"; String regionId = "cn-hangzhou"; String dtsInstanceId = "dtse5212sed162****"; String jobId = "l791216x16d****"; String sid = "dtsip412t13160****"; String userName = "xftest"; String password = "******"; String proxyUrl = "dts-cn-****.com:18001"; // initial checkpoint for first seek(a timestamp to set, eg 1566180200 if you want (Mon Aug 19 10:03:21 CST 2019)) String checkpoint = "1639620090"; // Convert physical database/table name to logical database/table name boolean mapping = true; // if force use config checkpoint when start. for checkpoint reset, only assign mode works boolean isForceUseInitCheckpoint = false; ConsumerContext.ConsumerSubscribeMode subscribeMode = ConsumerContext.ConsumerSubscribeMode.ASSIGN; DistributedDTSConsumerDemo demo = new DistributedDTSConsumerDemo(userName, password, regionId, jobId, sid, dtsInstanceId, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, subscribeMode, proxyUrl, checkpoint, isForceUseInitCheckpoint, mapping); demo.start(); }Parameter Description Method to obtain the parameter value accessKeyId The AccessKey ID. For more information about how to obtain the AccessKey pair, see Create and obtain an AccessKey pair. accessKeySecret The AccessKey secret. regionId The ID of the region in which the change tracking task resides. In the DTS console, find the change tracking instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID. On the Basic Information page, you can obtain the region in which the instance resides. For example, if the instance resides in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the parameter to cn-hangzhou. For more information, see Supported regions.dtsInstanceId The ID of the change tracking instance. In the DTS console, find the change tracking instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID. On the Basic Information page, you can view DTS Instance ID. jobId The ID of the change tracking task. You can call the DescribeDtsJobs operation to query the task ID. sid The ID of the consumer group. In the DTS console, find the change tracking instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID. In the left-side navigation pane, click Consume Data. You can view Consumer Group ID/Name of the instance and Account of the consumer group. Note The password of the consumer group account is specified when you create the consumer group.userName The account of the consumer group. password The password of the consumer group. proxyUrl The endpoint and port number of the change tracking instance. Note If you track data changes over internal networks, the network latency is minimal. This is applicable if the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance on which you deploy the SDK client resides on the classic network or in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the change tracking instance.In the DTS console, find the change tracking instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID. On the Basic Information page, you can view Network of the instance. checkpoint The consumer offset. It is the timestamp generated when the SDK client consumes the first data record. The value is a UNIX timestamp in seconds. Note The consumer offset can be used in the following scenarios:- If the consumption process is interrupted, you can specify the consumer offset to resume data consumption. This allows you to prevent data loss.
- When you start the change tracking client, you can specify the consumer offset to consume data based on your business requirements.
The consumer offset of consumed data must be within the data range of the change tracking instance. The consumer offset must be converted to a UNIX timestamp. Note- You can view the data range of the change tracking instance in the Data Range column on the Change Tracking Tasks page.
- You can use a search engine to obtain a UNIX timestamp converter.
- In the top menu bar of IntelliJ IDEA, choose to run the client. Note When you run IntelliJ IDEA for the first time, it takes a period of time to load and install relevant dependencies.
- The result shows that the SDK client can track data changes from the source instance.
- The SDK client calculates and displays information about the consumed data at regular intervals. The information includes the total number of data records that are sent and received, the total amount of data, and the number of requests per second (RPS).
Table 1. The following table describes the parameters in the information. Parameter Description outCountsThe total number of data records consumed by the SDK client. outBytesThe total amount of data consumed by the SDK client. Unit: bytes. outRpsThe RPS in which the SDK client consumes data. outBpsThe number of bits transmitted per second in which the SDK client consumes data. countNone. inBytesThe total amount of data that is sent by the DTS server. Unit: bytes. DStoreRecordQueueThe size of the current data cache queue when the DTS server sends data. inCountsThe total number of data records that are sent by the DTS server. inRpsThe RPS in which the DTS server sends data. inBpsThe number of bits transmitted per second when the DTS server sends data. __dtThe timestamp that is generated when the SDK client receives data. Unit: milliseconds. DefaultUserRecordQueueThe size of the current data cache queue after serialization.
- Optional:To modify the data type of the data to track, you can modify the code in the
buildRecordListener()method or use a custom class.public static Map<String, RecordListener> buildRecordListener() { // user can impl their own listener RecordListener mysqlRecordPrintListener = new RecordListener() { @Override public void consume(DefaultUserRecord record) { OperationType operationType = record.getOperationType(); if (operationType.equals(OperationType.INSERT) || operationType.equals(OperationType.UPDATE) || operationType.equals(OperationType.DELETE) || operationType.equals(OperationType.HEARTBEAT)) { // consume record RecordListener recordPrintListener = new DefaultRecordPrintListener(DbType.MySQL); recordPrintListener.consume(record); //commit method push the checkpoint update record.commit(""); } } }; return Collections.singletonMap("mysqlRecordPrinter", mysqlRecordPrintListener); }