After you encrypt sensitive data columns in a table of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, PolarDB for MySQL, or PolarDB for PostgreSQL database, you can use the EncJDBC driver to connect to the database from a Java application and access the plaintext data in these encrypted columns. This topic describes how to use EncJDBC to connect to a database and access plaintext data in encrypted columns.
Prerequisites
Column encryption is configured for the target database, and the target database account is granted the Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption) permission. For more information about how to configure column encryption for a database and for a detailed description of account permissions, see Configure column encryption for databases.
You have obtained the connection information for the encrypted database, including the endpoint, port, database name, database account, and password.
Background information
The column encryption feature lets you encrypt specific columns in a database to improve data security. Encrypted data is stored as ciphertext in the database. However, an authorized client can transparently decrypt the ciphertext and access the plaintext data.
Alibaba Cloud provides the always-encrypted client driver EncJDBC for the Java programming language. You can use the driver on the client to connect to the database and specify the Master Encryption Key (MEK) in the database connection URL to access the encrypted database. The driver automatically decrypts the ciphertext and returns plaintext data.
Generate an MEK
The client transmits the MEK to the database server over a secure asymmetric key encryption protocol. This process ensures that both the server and client share the same key, which enables secure data transmission using symmetric encryption.
Value range: A 16-byte hexadecimal string, which is 32 characters long.
The MEK is the root credential that authorizes a client to access encrypted data. For security reasons, the encrypted database does not hold or manage your MEK. It also does not provide services to generate or back up the MEK. You must generate the MEK yourself. Storing and managing the MEK is critical to database security. We recommend that you back up your MEK securely.
Depending on the Encryption Method selected in the column encryption configuration, you can obtain a KMS Key or generate a Local Key to use as the MEK for decrypting the database.
KMS key
When you use a KMS key, ensure that Key Management Service (KMS) is available. Otherwise, the always-encrypted client driver EncJDBC will not function.
You need to obtain the endpoint of the KMS instance that contains the selected KMS key from the column encryption configuration. You also need the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the corresponding Alibaba Cloud account or Resource Access Management (RAM) user. This account or user must have KMS decryption permissions to allow the client to read the KMS key. Perform the following steps:
Log on to the console using an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user.
Local key
When the Encryption Method in the column encryption configuration is set to Local Key, you need to generate an MEK. For example, 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff.
Common generation methods include using a password generation tool or a random function in a programming language.
For example:
On Linux, you can use the built-in OpenSSL tool and run the
openssl rand -hex 16command to generate a key.On Windows, you can install the OpenSSL software package.
Client access instructions
Use Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8 or later.
On the client, you can change the database connection driver to EncJDBC, update the database connection URL, and specify the MEK to access the plaintext data in encrypted columns.
1. Install dependencies
Add the following dependency to the pom.xml file of your Maven project.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-cls-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.0.10-1</version>
</dependency>2. Configure the MEK to connect to the database
You can use the following methods to configure the MEK: JDBC properties configuration, file configuration, and URL configuration. If you configure your Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) using more than one method, the following priority applies: JDBC properties configuration > File configuration > URL configuration.
In the URL configuration method, you can concatenate multiple parameters with an ampersand (
&).With the following configuration and connection methods, the
MEKis processed locally on the client and sent to the server securely using envelope encryption. This ensures that theMEKis not leaked.
Based on the Encryption Method in the column encryption configuration, connect to the database using either a local key or a KMS key.
Connect to the database using a KMS key
If you use a temporary access credential from the Security Token Service (STS) to obtain the KMS-managed MEK, you can use an STS software development kit (SDK) to obtain a temporary STS token. For STS SDK examples, see STS SDK overview.
Do not hard-code the AccessKey pair (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret) in your business code. This example uses system environment variables to manage the AccessKey pair. For more information, see Configure environment variables on Linux, macOS, and Windows.
JDBC properties configuration
When you connect using standard JDBC, you can set custom user properties through Properties. The following example shows how to configure and run JDBC in this way:
// Prepare the connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password.
// ...
String hostname = "your-hostname";
String port = "your-port";
String dbname = "your-database-name";
String username = "your-username";
String password = "your-password";
// Get the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret from system environment variables.
String accessKeyId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String accessKeySecret = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// If you use an STS temporary access credential to read the KMS key, you also need to provide the obtained Security Token Service (STS) token.
// String stsToken= "yourSecurityToken";
// The endpoint of the KMS instance. Use the public endpoint for Internet access. Use the instance VPC endpoint for VPC access.
String kmsEndpoint = "kms.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("user", username);
props.setProperty("password", password);
props.setProperty("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID", accessKeyId);
props.setProperty("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", accessKeySecret);
props.setProperty("ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_ENDPOINT", kmsEndpoint);
// props.setProperty("ALIBABA_CLOUD_STS_TOKEN","stsToken");
// The following is the connection URL format for an RDS for MySQL database: "jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s".
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s", hostname, port, dbname);
// The following loads the EncJDBC driver for an RDS for MySQL database.
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, props);
// ... Initiate a query ...URL configuration
You can embed the parameters for obtaining the KMS key in the URL, as shown in the following example:
// Prepare the connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password.
// ...
String hostname = "your-hostname";
String port = "your-port";
String dbname = "your-database-name";
String username = "your-username";
String password = "your-password";
// Get the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret from system environment variables.
String accessKeyId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String accessKeySecret = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// If you use an STS temporary access credential to read the KMS key, you also need to provide the obtained STS token.
// String stsToken= "yourSecurityToken";
// The endpoint of the KMS instance. Use the public endpoint for Internet access. Use the instance VPC endpoint for VPC access.
String kmsEndpoint = "kms.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// The following is the connection URL format for an RDS for MySQL database.
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s?ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID=%s&ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=%s&ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_ENDPOINT=%s", hostname, port, dbname, accessKeyId,accessKeySecret,kmsEndpoint);
// Use an STS token.
// String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s?ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID=%s&ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=%s&ALIBABA_CLOUD_KMS_ENDPOINT=%s&ALIBABA_CLOUD_STS_TOKEN=%s", hostname, port, dbname, accessKeyId,accessKeySecret,kmsEndpoint,stsToken);
// The following loads the EncJDBC driver for an RDS for MySQL database.
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, username, password);
// ... Initiate a query ...Connect to the database using a local key
JDBC properties configuration
When you connect using standard JDBC, you can set custom user properties through Properties. The following example shows how to configure and run JDBC in this way:
// Prepare the connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password.
// ...
String hostname = "your-hostname";
String port = "your-port";
String dbname = "your-database-name";
String username = "your-username";
String password = "your-password";
// Customer master key.
String mek = "00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("user", username);
props.setProperty("password", password);
props.setProperty("MEK", mek);
// The following is the connection URL format for an RDS for MySQL database: "jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s". For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the format with "jdbc:postgresql:encdb://%s:%s/%s".
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s", hostname, port, dbname);
// The following loads the EncJDBC driver for an RDS for MySQL database. For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the driver with "com.aliyun.encdb.postgresql.jdbc.EncDriver".
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, props);
// ... Initiate a query ...File configuration
You can import parameters, such as the required MEK, from a configuration file.
The file configuration method is applicable only to configuring a local key MEK.
In your project, you can set a property named encJdbcConfigFile and set its value to the path of the configuration file. If you do not set this property, the encjdbc.conf file is used by default. The content of the configuration file is as follows:
MEK=00112233445566778899aabbccddeeffYou can place the configuration file in one of the following two locations:
Place the file in the resources folder of your project, as shown in the following figure:

Place the file in the project root directory, which is the runtime directory of the program.
After you configure the file, you do not need to make additional configurations in your program, as shown in the following example:
// Prepare the connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password.
// ...
String hostname = "your-hostname";
String port = "your-port";
String dbname = "your-database-name";
String username = "your-username";
String password = "your-password";
// The following is the connection URL format for an RDS for MySQL database: "jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s". For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the format with "jdbc:postgresql:encdb://%s:%s/%s".
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s", hostname, port, dbname);
// The following loads the EncJDBC driver for an RDS for MySQL database. For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the driver with "com.aliyun.encdb.postgresql.jdbc.EncDriver".
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, username, password);
// ... Initiate a query ...URL configuration
You can embed parameters, such as the MEK, in the URL, as shown in the following example:
// Prepare the connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password.
// ...
String hostname = "your-hostname";
String port = "your-port";
String dbname = "your-database-name";
String username = "your-username";
String password = "your-password";
// Customer master key.
String mek = "00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff";
// The following is the connection URL format for an RDS for MySQL database: "jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s?MEK=%s". For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the format with "jdbc:postgresql:encdb://%s:%s/%s?MEK=%s".
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s?MEK=%s", hostname, port, dbname, mek);
// The following loads the EncJDBC driver for an RDS for MySQL database. For an RDS for PostgreSQL database, replace the driver with "com.aliyun.encdb.postgresql.jdbc.EncDriver".
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, username, password);
// ... Initiate a query ...3. Query the plaintext data of encrypted columns
After you successfully connect to the database, you can perform database operations as you would with a normal JDBC query. EncJDBC automatically decrypts the encrypted columns and returns plaintext data.
Sample code:
// Initiate a query.
// Create a query statement.
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM your_table_name");
// Traverse the result set.
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < resultSet.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getString(i + 1));
System.out.print("\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}Complete code example
This section provides an example of using the JDBC properties configuration to set a local key MEK. It shows how to use a database account with the Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption) permission to query the plaintext data in encrypted columns in an RDS for MySQL database.
For information about the database configuration in the following example, see the RDS MySQL database column encryption example in Verify column encryption results.
This example uses Maven 3.9.9 and the development tool IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2024.1.2.
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class EncryptedColumnAccess {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// Replace the following connection information, such as the endpoint (hostname), port, database instance name (dbname), username, and password, with your instance information.
String hostname = "rm-******.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com";
String port = "3306";
String dbname = "sddp_em_db";
String username = "sddp_em03";
String password = "******";
// This is only an example. We recommend that you use a more complex key.
String mek="00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("user", username);
props.setProperty("password", password);
props.setProperty("MEK", mek);
String dbUrl = String.format("jdbc:mysql:encdb://%s:%s/%s", hostname, port, dbname);
// Load the EncJDBC driver.
Class.forName("com.aliyun.encdb.mysql.jdbc.EncDriver");
// Get the database connection.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, props);
// Initiate a query.
try {
// Create a query statement.
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM users");
// Traverse the result set.
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("username");
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
// Process other fields based on your table schema.
System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name + ", Phone: " + phone);
}
// Close the resources.
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
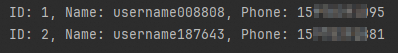
}Sample output: