Data Management (DMS) integrates the SQL review optimization feature into security rules. After you submit SQL statements for data change or on the SQLConsole tab, DMS reviews the submitted SQL statements based on the specifications in security rules and offers optimization suggestions. This can help you review SQL statements and prevent invalid SQL statements before you perform a data change. This can also prevent the business from being affected.
Prerequisites
You are a database administrator (DBA) or a DMS administrator. For more information, see Manage users.
A security rule is created. For more information how to create a security rule, see Manage security rules.
One of the following database engines is used:
MySQL: ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, ApsaraDB for MariaDB, PolarDB for Xscale, AnalyticDB for MySQL, and third-party MySQL databases
Oracle
PolarDB for PostgreSQL(Compatible with Oracle)
OceanBase
Behavioral actions
DMS predefines three behavioral actions:
Must Improve: DMS stops the process and returns a message if you do not optimize the SQL statement. Default SQL review rules in DMS do not contain Must Improve.
NoteFor more information about the check items of SQL review rules, see Check items.
For example, you have set the behavioral action of the
The table must have a primary keyrule to Must Improve, and a developer submits an SQL statement to create a table but does not specify a primary key for the table, DMS stops the execution of the SQL statement and returns a message to request the developer to specify a primary key. After the modified SQL statement passes verification, DMS can execute it.Potential Issue: DMS reminds you that the SQL statement has potential issues, but does not stop the process.
Suggest Improve: DMS suggests that you optimize the SQL statement, but does not stop the process.
Supported features in different control modes
DMS provides three control modes. For more information, see Control modes.
Operation | Security Collaboration | Stable Change | Flexible Management |
Enable or disable a rule. | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Set a behavioral action for a rule. | Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
Modify the parameters of a rule. You can set parameters for specific rules, such as the number of indexes in a table and the number of fields in a table. | Supported | Supported | Not supported |
Enter the description of a behavioral action. You can enter the background of a behavioral action for a rule. | Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
Procedure
Security rules contain default SQL review rules. This example shows you how to customize a security rule and set the behavioral action of the The table must have a primary key rule to Must Improve.
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
Move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose . Note
icon in the upper-left corner and choose . NoteIf you use the DMS console in normal mode, choose in the top navigation bar.
Find the security rule set that you want to modify and click Edit in the Actions column.
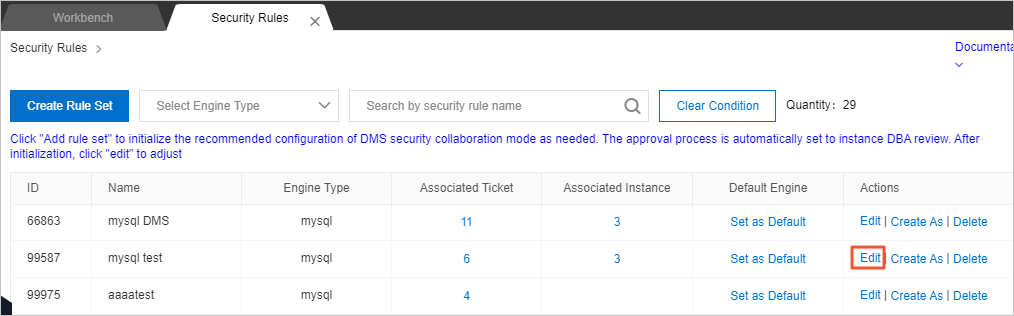 Note
NoteIf you want to configure the Flexible Management or Stable Change security rule set, find the security rule set that you want to configure and click SQL audit optimization recommendations in the Actions column.
In the left-side pane of the Details page, click the SQL audit optimization recommendations tab.
Find the rule named
The table must have a primary keyand click Edit in the Actions column.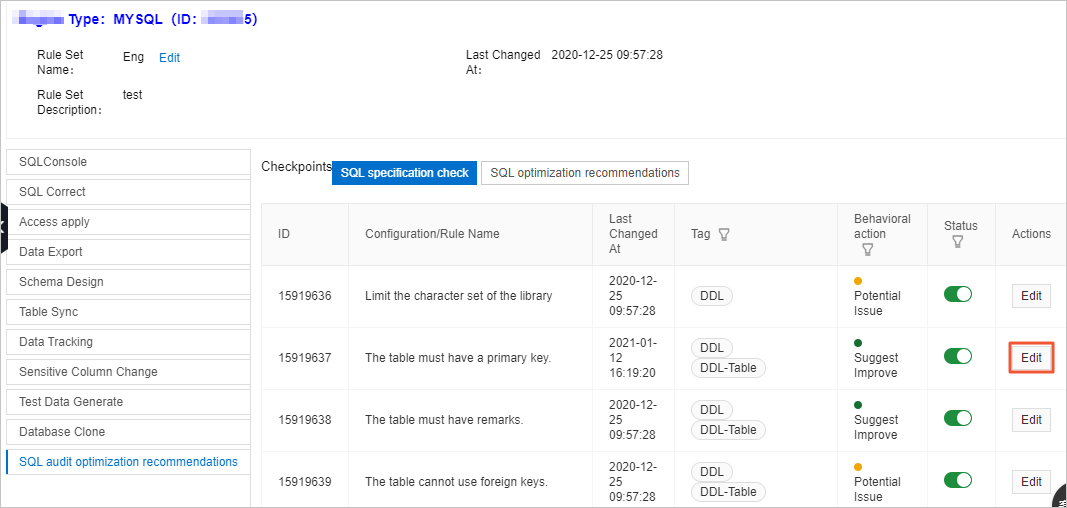 Note
NoteYou can click the
 icon to the right of Tag, Behavioral action, or Status to filter rules. The Tag parameter specifies the scope within which a rule is effective. A rule can apply to DDL statements and DML statements. The Status parameter specifies whether a rule is enabled or disabled.
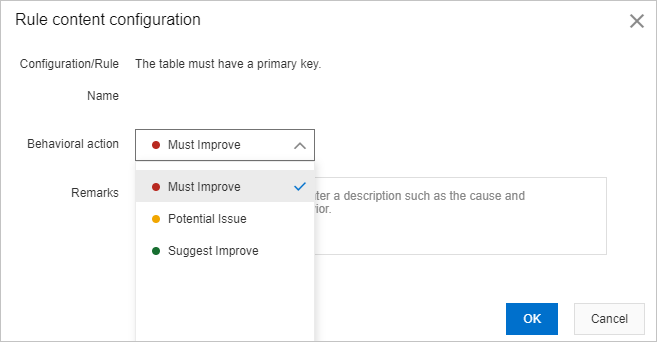
icon to the right of Tag, Behavioral action, or Status to filter rules. The Tag parameter specifies the scope within which a rule is effective. A rule can apply to DDL statements and DML statements. The Status parameter specifies whether a rule is enabled or disabled. In the Rule content configuration dialog box, set the parameters that are described in following table.
Parameter
Description
Behavioral action
In this example, set the Behavioral action parameter to Must Improve.
NoteDefault SQL review rules in DMS do not contain Must Improve.
Remarks
Enter the description of the behavioral action for this rule, such as the background information.
Click OK.
If you use the features such as data development, data change, and SQL review, the SQL review optimization feature verifies SQL statements based on the configured security rules.
In this example, if an SQL statement does not comply with the
The table must have a primary keyrule, DMS stops the process.
Check items
The following table describes the check items that are supported by the SQL review feature.
Schema design
Check item
Applicable SQL statement
Checkpoint
Database properties
CREATE DATABASERule name: The character set used to create the database must be restricted. Rule identifier: CREATE_DATABASE_LIMIT_CHARSET.
Table properties
CREATE TABLEALTER TABLE
Rule name: The table must have a primary key. Rule identifier: TABLE_MUST_HAVE_PRIMARY_KEY.
Rule name: The table must contain remarks. Rule identifier: TABLE_MUST_HAVE_COMMENTS.
Rule name: The table cannot contain foreign keys. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_FOREIGN_KEY.
Rule name: The case sensitivity of the table name must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_NAME_LIMIT_CHAR_CASE.
Rule name: The table storage engine must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_LIMIT_STORE_ENGINE.
Rule name: The table cannot be partitioned. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_PARTITION.
Rule name: The table must contain specific columns. Rule identifier: TABLE_MUST_HAVE_SOME_COLUMN.
Rule name: The character set of the table must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_MUST_USE_SOME_CHARSET.
Rule name: The validation rules of the table must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_MUST_USE_SOME_COLLATION.
Rule name: The table name cannot be a keyword. Rule identifier: TABLE_NAME_FORBID_KEYWORD.
Rule name: The number of indexes in the table must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_LIMIT_INDEX_COUNT.
Rule name: The number of fields in the table must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_LIMIT_COLUMN_COUNT.
Rule name: The initial value of an auto-increment column in the table must be restricted. Rule identifier: TABLE_LIMIT_INIT_AUTO_INCREMENT.
Rule name: The table must contain an auto-increment primary key column. Rule identifier: LIMIT_PRIMARY_COLUMN_AUTO_INCREMENT.
Rule name: The use of views must be restricted for the table. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_VIEW.
Rule name: The use of triggers must be restricted for the table. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_TRIGGER.
Rule name: The use of events must be restricted for the table. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_EVENT.
Rule name: The use of stored procedures must be restricted for the table. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_STORED_PROCEDURE.
Rule name: The use of user-defined functions (UDFs) must be restricted for the table. Rule identifier: TABLE_FORBID_USE_CUSTOM_FUNCTION.
Rule name: We recommend that you use the
ALTER TABLE CONVERTsyntax to change the character set of the table. Rule identifier: MODIFY_CHARSET_USE_ALTER_TABLE_CONVERT.
Column properties
CREATE TABLEALTER TABLE
Rule name: The field name cannot be a keyword. Rule identifier: COLUMN_NAME_FORBID_KEYWORD.
Rule name: The case sensitivity of the field name must be restricted. Rule identifier: COLUMN_NAME_LIMIT_CHAR_CASE.
Rule name: The character set of a column cannot be specified. Rule identifier: COLUMN_FORBID_SET_CHARSET.
Rule name: Specific data types cannot be used in a column. Rule identifier: COLUMN_FORBID_DATA_TYPES.
Rule name: A column must contain comments. Rule identifier: COLUMN_MUST_HAVE_COMMENTS.
Rule name: The length of a field whose data type is
CHARmust be restricted. Rule identifier: COLUMN_LIMIT_CHAR_LENGTH.Rule name: The length of a field whose data type is
VARCHARmust be restricted. Rule identifier: COLUMN_LIMIT_VARCHAR_LENGTH.Rule name: Each column must use the
NOT NULLclause. Rule identifier: COLUMN_MUST_SET_NOT_NULL.Rule name: The recommended name for an auto-increment column is
ID. Rule identifier: COLUMN_AUTO_INCREMENT_NAME_ID.Rule name: An auto-increment column must contain the UNSIGNED attribute. Rule identifier: COLUMN_AUTO_INCREMENT_UNSIGNED.
Rule name: The
FLOATandDOUBLEdata types cannot be used. We recommend that you replace them with theDECIMALdata type. Rule identifier: COLUMN_FORBID_FLOAT_DOUBLE_TYPE.Rule name: Each column must have a default value. Rule identifier: EACH_COLUMN_NEED_DEFAULT_VALUE.
Rule name: The validation set of a column cannot be specified. Rule identifier: COLUMN_FORBID_SET_COLLATE.
Rule name: The columns cannot be renamed when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_FORBID_RENAME_COLUMN.
Rule name: The columns cannot be deleted when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_FORBID_DROP_COLUMN.
Rule name: The data type cannot be changed when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_FORBID_MODIFY_DATA_TYPE.
Rule name: All fields that are added when you modify a table can be empty. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_ADD_COLUMN_NULLABLE.
Rule name: The default value must be specified for a non-empty field that is added when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_ADD_NOT_NULL_COLUMN_NEED_DEFAULT.
Rule name: The default value must be specified when a field that can be left empty is modified as a non-empty field. Rule identifier: COLUMN_NULLABLE_TO_NOT_NEED_DEFAULT.
Rule name: The
ENUMdata type cannot be used. We recommend that you replace it with theTINYINTorCHARdata type. Rule identifier: COLUMN_FORBID_USE_ENUM_TYPE.Rule name: A field cannot contain the
ZEROFILLattribute. Rule identifier: COLUMN_DATA_TYPE_FORBID_ZEROFILL.
Index properties
CREATE TABLEALTER TABLE
Rule name: An index must have a name. Rule identifier: INDEX_MUST_HAVE_CLEARLY_NAME.
Rule name: The naming format of a unique index must be restricted. Rule identifier: UNIQUE_INDEX_NAME_PATTERN.
Rule name: The naming format of a regular index must be restricted. Rule identifier: COMMON_INDEX_NAME_PATTERN.
Rule name: The number of index columns must be restricted. Rule identifier: INDEX_LIMIT_CONTAINS_COLUMNS.
Rule name: The number of primary key columns must be restricted. Rule identifier: PRIMARY_LIMIT_CONTAINS_COLUMNS.
Rule name: The data type of a primary key column must be restricted. Rule identifier: PRIMARY_LIMIT_COLUMN_DATA_TYPE.
Rule name: The primary key cannot be deleted when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_FORBID_DROP_PRIMARY.
Rule name: The indexes cannot be deleted when you modify a table. Rule identifier: ALTER_TABLE_FORBID_DROP_INDEX.
Data query
Check item
Applicable SQL statement
Checkpoint
SELECTstatementSELECTINSERT SELECTSubquery clauses that are nested in the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement
Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you use theWHEREclause. Rule identifier: SELECT_SUGGEST_ASSIGN_WHERE.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not use theORDER BY RAND()function. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_USE_ORDER_BY_RAND.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not perform theGROUP BYoperation on constants. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_GROUP_BY_CONST.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not perform theORDER BYoperation on constants. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_ORDER_BY_CONST.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not perform theGROUP BYorORDER BYoperation on different tables. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_GROUP_ORDER_BY_DISTINCT_TABLE.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not perform theORDER BYoperation to sort multiple fields in different ordering directions. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_ORDER_BY_MULTI_COLUMN_RANK.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not use theGROUP BYorORDER BYclause in an expression or a function. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_GROUP_ORDER_BY_EXPR_OR_FUNCTION.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not use theUNIONoperator. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_USE_UNION.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, the number of tables to be joined is restricted. Rule identifier: SELECT_LIMIT_TABLE_JOIN_COUNT.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, the offset value of theLIMITclause is restricted. Rule identifier: SELECT_CONFINE_LIMIT_MAX_OFFSET.Rule name: In the
SELECTstatement, we recommend that you do not use theHAVINGclause. Rule identifier: SELECT_FORBID_USE_HAVING.
WHEREclauseThe
SELECT,UPDATE,DELETE, orINSERT SELECTstatement that contains theWHEREclauseRule name: In the
WHEREclause, fields to be indexed cannot contain mathematical operators or functions. Rule identifier: WHERE_FORBID_INDEX_COLUMN_HAS_MATH.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, we recommend that you do not use wildcards to search for fields. Rule identifier: WHERE_FORBID_BEFORE_WILDCARD_SEARCH.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, DMS checks whether theLIKEclause contains wildcards. Rule identifier: WHERE_CHECK_LIKE_HAS_NOT_WILDCARD.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, we recommend that you do not use reverse queries such asNOT INandNOT LIKE. Rule identifier: WHERE_FORBID_USE_REVERSE_SEARCH.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, the number of elements in theINclause is restricted. Rule identifier: WHERE_LIMIT_IN_ITEM_MAX_COUNT.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, DMS checks whether the data types of fields are implicitly converted. Rule identifier: WHERE_CHECK_COLUMN_IMPLICIT_TYPE_CONVERSION.Rule name: In the
WHEREclause, DMS checks whether filter conditions are connected by using theORoperator. Rule identifier: WHERE_CHECK_OR_LINK_CONDITION.
Data change
Check item
Applicable SQL statement
Checkpoint
Data insertion
INSERT SELECTINSERT [IGNORE]REPLACE
Rule name: In the
INSERTstatement, we recommend that you specify the list of fields where you want to insert data. Rule identifier: ASSIGN_INSERT_COLUMN_NAME_LIST.Rule name: In the
INSERTstatement, the names of fields where you want to insert data cannot be duplicated. Rule identifier: INSERT_COLUMN_NAME_FORBID_DUPLICATE.Rule name: In the INSERT statement, a
NULLvalue cannot be inserted into aNOT NULLcolumn. Rule identifier: NOT_NULL_COLUMN_FORBID_INSERT_NULL.Rule name: In the
INSERTstatement, the list of fields into which you want to insert data must match the list of values that you want to insert. Rule identifier: INSERT_COLUMN_MUST_MATCH_VALUES.Rule name: In the INSERT statement, the total number of rows in an
INSERT VALUESclause is restricted. Rule identifier: LIMIT_INSERT_VALUES_TOTAL_ROWS.Rule name: In the
INSERTstatement, DMS checks whether the table or field into which you want to insert data exists. Rule identifier: INSERT_CHECK_TABLE_COLUMN_EXISTS.Rule name: In the INSERT statement, we recommend that you do not use the
SYSDATA()function. Rule identifier: INSERT_FORBID_USE_SYSDATE_FUNCTION.
Data update and deletion
UPDATEDELETE
Rule name: In the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement, the number of tables to be joined is restricted. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_LIMIT_TABLE_JOIN_COUNT.Rule name: In the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement, we recommend that you use theWHEREclause. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_ASSIGN_WHERE_CONDITION.Rule name: In the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement, DMS checks whether theWHEREclause contains subqueries. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_CHECK_WHERE_EXIST_SUB_QUERY.Rule name: In the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement, the data size that is specified by theLIMITclause is restricted. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_CHECK_LIMIT_AFFECTED_ROWS.Rule name: In the
UPDATEorDELETEstatement, DMS checks whether the syntax that is used to join multiple tables is complete. For example, DMS checks whether theONclause is omitted for theJOINclause. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_CHECK_TABLE_JOIN_LOSS_ON.Rule name: The
UPDATEorDELETEstatement cannot contain theORDER BYclause. Rule identifier: UPDELETE_FORBID_ORDER_BY.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, DMS checks whether the delimiters such asANDamong multiple columns in theSETclause are valid. Rule identifier: UPDATE_CHECK_SET_ITEM_DELIMITER.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, DMS checks whether the table prefix is specified for the columns of multiple tables in theSETclause. Rule identifier: UPDATE_MULTI_TABLE_CHECK_SET_COLUMN_PREFIX.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, DMS checks whether the tables or fields that you want to update exist. Rule identifier: UPDATE_CHECK_TABLE_COLUMN_EXIST.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, DMS checks whether the primary key is updated. Rule identifier: UPDATE_CHECK_PRIMARY_KEY_CHANGE.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, DMS checks whether the unique key is updated. Rule identifier: UPDATE_CHECK_UNIQUE_KEY_CHANGE.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, we recommend that you also update the Modify Time column in tables. Rule identifier: UPDATE_ALSO_TO_UPDATE_MODIFY_TIME_COLUMN.Rule name: In the
UPDATEstatement, we recommend that you do not update the Creation Time column in tables. Rule identifier: UPDATE_FORBID_MODIFY_CREATE_TIME_COLUMN.
The following table describes the check items that are supported by the SQL review optimization feature.
Scenario
Checkpoint
N/A
Rule name: The table whose primary key uses the
INTdata type needs to be optimized. Rule identifier: OPTIMIZE_PRIMARY_IS_INT_TABLE.Rule name: The auto-increment primary key column needs sufficient space. Rule identifier: SNIFFING_AUTO_PRIMARY_REMAIN_SPACE.
Rule name: The value of the unique index cannot be empty. Rule identifier: SNIFFING_UNIQUE_EXIST_NULL_RISK.
Rule name: The DDL statement needs to be optimized due to the risk of a data change failure or a table lock. Rule identifier: ALTER_LOCK_FAIL_SNIFFING_OPTIMIZE.
Rule name: SQL injection risks need to be detected. Rule identifier: CHECK_SQL_INJECTION_RISK.
Rule name:
Force indexrisks need to be detected. Rule identifier: CHECK_SQL_ASSIGN_FORCE_INDEX.Rule name: Indexes need to be checked in SQL execution plans. Rule identifier: SQL_EXPLAIN_INDEX_CHECK.
Rule name: DMS needs to analyze indexes and provide suggestions. Rule identifier: DMS_INDEX_ANALYZE_AND_SUGGEST.