Data Management (DMS) allows you to manage security rules for relational and non-relational databases on the SQL Console tab. The definition and classification of security rules on this tab vary for relational and non-relational databases. This topic describes how to configure security rules for MongoDB databases on the SQL Console tab.
Checkpoints on the SQL Console tab
| Checkpoint | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Configuration Item | Allows you to specify basic configurations of the rule set, such as the maximum number that can be returned per query and whether the result set can be edited. |
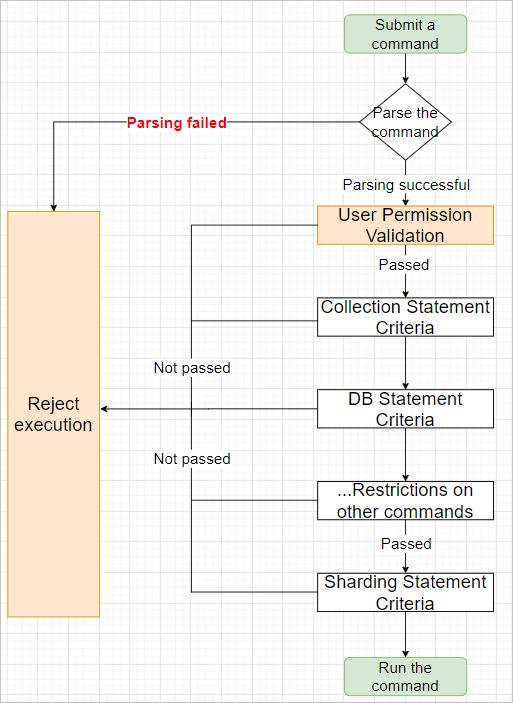
| User Permission Validation | Allows you to specify whether to check the permissions of specific users when they submit commands. For example, you can configure this checkpoint so that DMS checks the permissions of regular users when they submit commands. |
| Collection Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on collection commands. |
| DB Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on database commands. |
| Cache Query Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on commands related to the query plan cache. |
| User Management Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on user management commands. |
| Role Management Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on role management commands. |
| Replication Set Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on replica set commands. |
| Sharding Statement Criteria | Allows you to set constraints on sharding commands. |
Note You can use the default rules provided by DMS, or set custom rules as required. For more information, see Configure security rules.
The following flowchart shows how checkpoints work.
Factors and actions
- Factor: A factor is a system built-in variable that is used to obtain the context to be validated by security rules, such as the subcategories of commands and the number of rows in which data is affected.
- A factor name consists of the prefix
@fac.and the display name of the factor. - Each tab on the Details page of a security rule set displays different factors for different checkpoints.
Table 1. Factors provided on the SQL Console tab Factor Description @fac.sql_sub_type The subcategory of the command. For more information about the valid values, see Supported MongoDB commands. @fac.env_type The type of the environment. The value is the display name of the environment type, such as DEVorPRODUCT. For more information, see Change the environment type of an instance.@fac.current_sql The current command. @fac.user_is_admin Indicates whether the current user is a DMS administrator. Valid values: - true
- false
@fac.user_is_dba Indicates whether the current user is a database administrator (DBA). Valid values: - true
- false
@fac.user_is_inst_dba Indicates whether the current user is a DBA of the current database instance. Valid values: - true
- false
@fac.user_is_sec_admin Indicates whether the current user is a security administrator. Valid values: - true
- false
- A factor name consists of the prefix
- Action: An action is an operation that the system performs if the conditions specified in the
IFstatement are met. The action that you specify for a security rule shows the purpose of the security rule. For example, you can forbid the submission of a ticket, select an approval process, allow the execution of SQL statements, or reject the execution of SQL statements.- An action name consists of the prefix
@act.and the display name of the action. - Each tab on the Details page of a security rule set displays different actions for different checkpoints.
Table 2. Actions provided on the SQL Console tab Action Description @act.reject_execute Rejects the request to run the current command. @act.allow_execute Allows the current command to be run. @act.reject_sql_type_execute Rejects the request to run a specific subcategory of commands. You must specify a subcategory after the action name. Example: @act.reject_sql_type_execute 'UPDATE'.@act.allow_sql_type_execute Allows a specific subcategory of commands to be run. You must specify a subcategory after the action name. - An action name consists of the prefix
Supported MongoDB commands
For more information about the MongoDB commands supported by DMS, see Supported MongoDB commands.