This topic describes how to access a database instance over HTTPS after the secure access proxy feature is enabled for the database instance.
Prerequisites
The secure access proxy feature is enabled for the database instance.
NoteTo check whether the secure access proxy feature is enabled for a database instance, perform the following steps: Log on to the Data Management (DMS) console. In the top navigation bar, choose . On the Created tab of the Proxy List page, the instances for which the secure access proxy feature is enabled are displayed. For more information about how to enable this feature for a database instance, see Enable the secure access proxy feature.
You are authorized to access the database instance by using proxy endpoints.
NoteOn the Details page of a database instance, check whether you are an authorized user of the database instance. If you are not an authorized user, apply for the permissions to use proxy endpoints to access the database instance. For more information, see Apply for the permissions to access a database instance by using proxy endpoints.
Usage notes
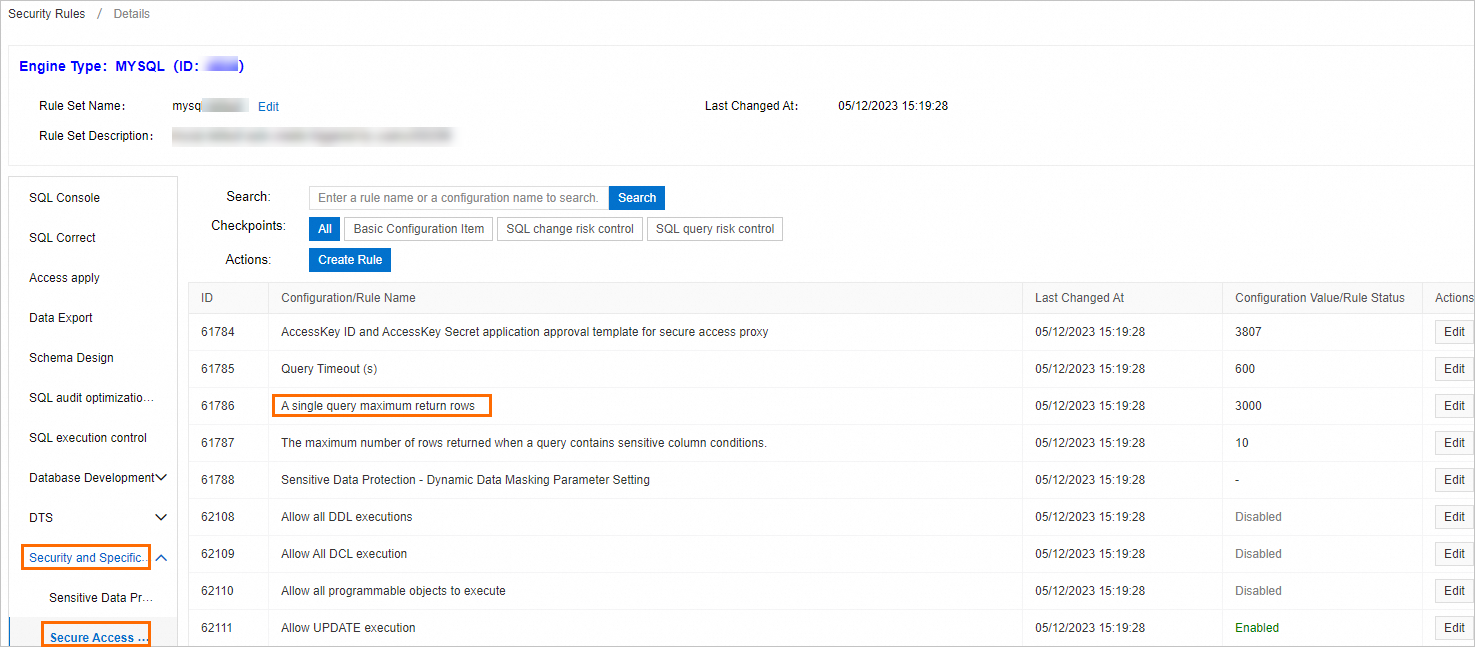
If your database instance is managed in Security Collaboration mode, it is affected by security rules. A maximum of 100,000 rows can be returned for each query.
If you do not want your database instance to be affected by security rules, access your database instance by using the connection address that is provided by the database console, or contact DMS technical support to evaluate specific scenarios.
If your database instance is not managed in Security Collaboration mode, you cannot customize the maximum number of returned rows per query. By default, the maximum number of rows that can be returned for each query is 3000.
Request parameters
Parameter | Description | Required | Assignment method |
accessId | AccessID | Yes | You can pass the value of this parameter by using one of the following methods:
|
accessSecret | AccessSecret | Yes | You can pass the value of this parameter by using one of the following methods:
|
schema | Database name | No | You can pass the value of this parameter by using one of the following methods:
|
sql | SQL statements | Yes | You can pass the value of this parameter by using one of the following methods:
|
Response parameters
If you access the instance over HTTPS, data is returned in the JSON format.
The following table describes the response parameters in the JSON format.
Parameter | Type | Description |
columnMetas | Array | The metadata of columns. |
columnName | String | The name of the column. |
columnLabel | String | The label for the column, which is specified in the AS clause in the SQL statement. If the AS clause is not specified, the value of this parameter is the same as that of the columnName parameter. |
columnTypeName | String | The data type of the column, such as VARCHAR and BIGINT. |
precision | Integer | The precision for the values of the column. This parameter can be specified for columns of some data types such as VARCHAR. For example, VARCHAR(32) indicates that the precision for the values is 32. |
scale | Integer | The scale for the values of the column. This parameter can be specified for columns of floating-point data types to indicate the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in a value. For example, DECIMAL(10,2) indicates that the number of digits to the right of the decimal point is two. |
nullable | Boolean | Indicates whether the column can be left empty. A value of true indicates that the column can be left empty. A value of false indicates that you must specify a value for the column. |
autoIncrement | Boolean | Indicates whether the value of the column automatically increments for each new row. A value of true indicates that the column is an auto-increment column. A value of false indicates that the column is not an auto-increment column. |
tableName | String | The name of the table to which the column belongs. |
msg | String | The error message returned if the execution failed. |
updateCount | Integer | The number of entries affected by the DML statement. |
requestId | String | The request ID. This parameter can help troubleshoot issues. |
rowCount | Integer | The number of entries returned when you perform a query. |
rows | Array | The entries returned when you perform a query. Each element in the array indicates a row of data. The data structure of the Array data type is the same as that of the List or Map data type. |
success | Boolean | Indicates whether the request was successful. A value of true indicates that the request was successful. A value of false indicates that the request failed. |
Sample responses:
Successful data query
{ "columnMetas": [ { "columnName":"column1", "columnLabel":"column1", "columnTypeName":"varchar", "precision":10, "scale":2, "nullable":true, "autoIncrement":true, "tableName":"table1" }, { "columnName":"column2", "columnLabel":"column2", "columnTypeName":"varchar", "precision":10, "scale":2, "nullable":true, "autoIncrement":true, "tableName":"table1" } ], "updateCount": 0, "requestId": "xhqej0xgcytbhc8scjopgqsywcaibi", "rowCount": 1, "rows": [ { "col1": 1, "col2": "xxxx" } ], "success": true }Successful data update
{ "updateCount": 0, "requestId": "xhqej0xgcytbhc8scjopgqsywcaibi", "success": true }Access failure
{ "message": 'AccessID is required.', "requestId": "xhqej0xgcytbhc8scjopgqsywcaibi", "success": false }
Examples of accessing a database instance for which the secure access proxy feature is enabled
You can use commands, an SQL client, or program code to access a database instance for which the secure access proxy feature is enabled.
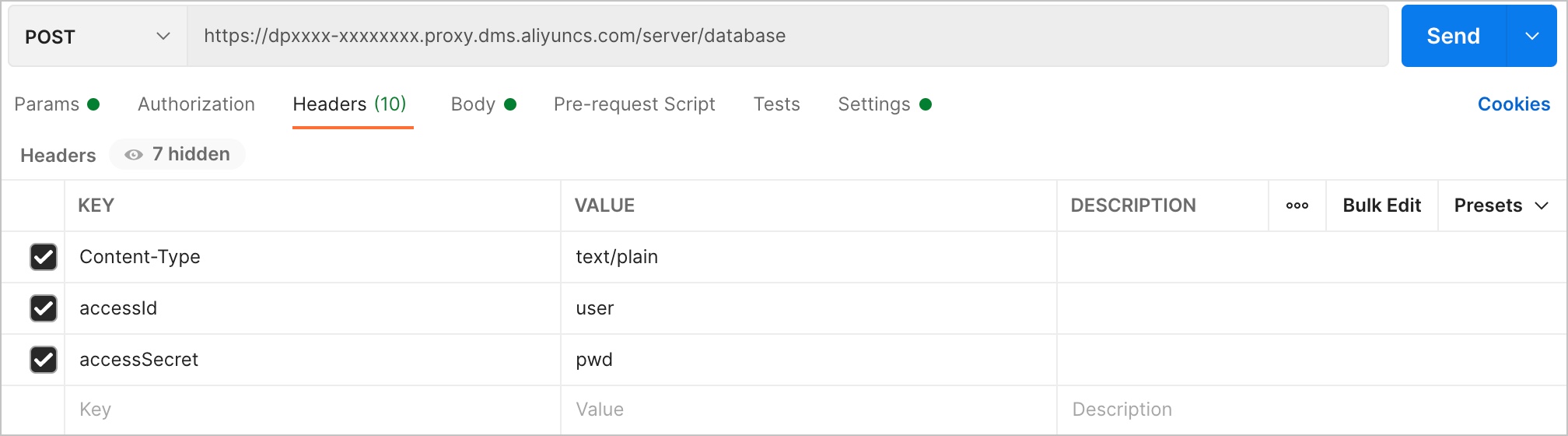
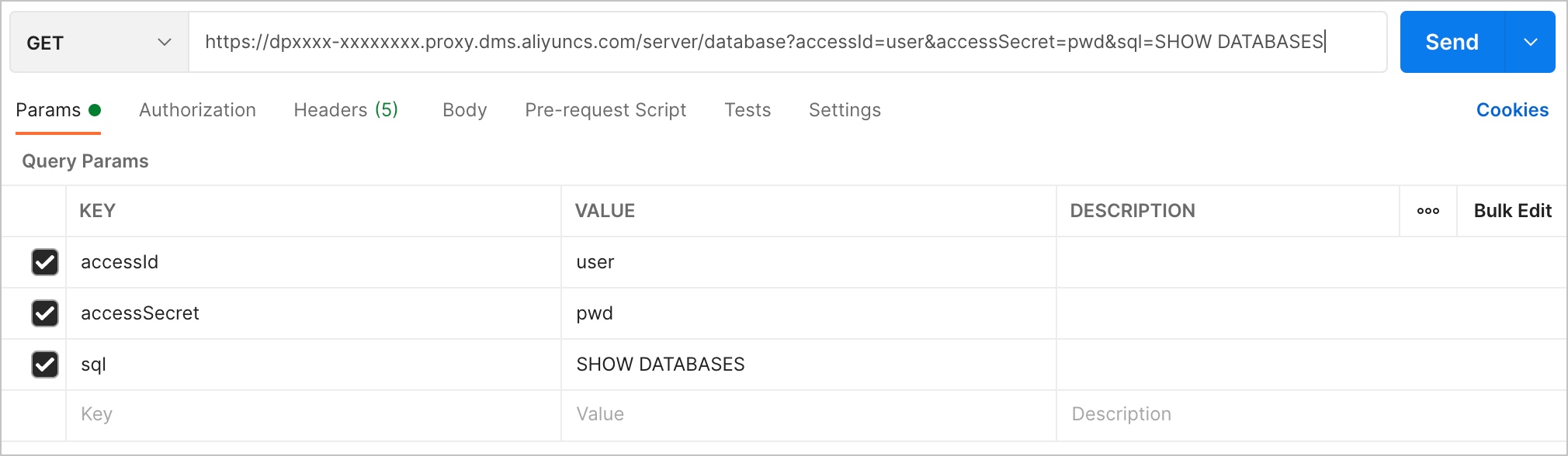
For example, the domain name of the instance is dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com, the name of the database to be accessed is database, the AccessKey ID is user, the AccessKey secret is pwd, and the SQL statement to be executed is SHOW DATABASES.
Use the curl command
# GET request syntax curl 'https://[Instance domain name]/server/[Database name]?accessId=[AccessKey ID]&accessSecret=[AccessKey secret]&sql=[SQL statement]'# Sample GET request curl 'https://dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com/server/database?accessId=user&accessSecret=pwd&sql=SHOW%20DATABASES'# POST request syntax curl 'https://[Instance domain name]/server/[Database name]' -H 'accessId:[AccessKey ID]' -H 'accessSecret:[AccessKey secret] -H 'Content-Type:text/plain' -d '[SQL statement]'# Sample POST request curl 'https://dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com/server/database' -H 'accessId:user' -H 'accessSecret:pwd -H 'Content-Type:text/plain' -d 'SHOW DATABASES'Use a Python 2 program
NoteIn this example, a Python 2 program is used to access the database instance.
GET request syntax
import requests url = "https://[Instance domain name]/server/[Database name]?accessId=[AccessKey ID]&accessSecret=[AccessKey secret]&sql=[SQL statement]" print requests.get(url).textSample GET request
import requests url = "https://dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com/server/database?accessId=user&accessSecret=pwd&sql=SHOW DATABASES" print requests.get(url).textPOST request syntax
import requests url = "https://[Instance domain name]/server/[Database name]" headers = { "Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8", "accessId": "[AccessKey ID]", "accessSecret": "[AccessKey secret]" } print requests.post(url, headers=headers, data='[SQL statement]').textSample POST request
import requests url = "https://dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com/server/database" headers = { "Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8", "accessId": "user", "accessSecret": "pwd" } print requests.post(url, headers=headers, data='SHOW DATABASES').textUse a Node.js program
GET request syntax
const https = require("https"); https.get("https://[Instance domain name]/server/[database name]?accessId=[AccessKey ID]&accessSecret=[AccessKey secret]&sql=SHOW DATABASES", resp => { resp.on("data", data => { console.log(JSON.parse(data)); }); });Sample GET request
const https = require("https"); https.get("https://dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com/server/database?accessId=user&accessSecret=pwd&sql=SHOW DATABASES", resp => { resp.on("data", data => { console.log(JSON.parse(data)); }); });POST request syntax
const https = require("https"); var req = https.request({ hostname: '[Instance domain name]', port: 443, path: '/server/[Database name]', method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=UTF-8', accessId: '[AccessKey ID]', accessSecret: '[AccessKey secret]' } }, resp => { resp.on("data", data => { console.log(JSON.parse(data)); }); }); req.write("[SQL statement]"); req.end();Sample POST request
const https = require("https"); var req = https.request({ hostname: 'dpxxxx-xxxxxxxx.proxy.dms.aliyuncs.com', port: 443, path: '/server/database', method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=UTF-8', accessId: 'user', accessSecret: 'pwd' } }, resp => { resp.on("data", data => { console.log(JSON.parse(data)); }); }); req.write("SHOW DATABASES"); req.end();Use the Postman client
GET request syntax
POST request syntax