This document describes how to verify the DNS configuration for your email domain. It covers query methods for ownership verification, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), and MX records. Three query methods are described: the Alibaba Cloud DNS check tool, Windows commands, and macOS commands. The examples use the root domain example.com.
Example using the email domain sub.example.com in the China (Hangzhou) region
The domain sub.example.com is a subdomain of example.com, and its prefix is sub.
Before you use the following query methods, configure the required DNS records in the console of your domain name service provider (SP). You can find the record values in the Direct Mail console on the Email Domains > Configure page. After the configuration is complete, use these methods to verify that the settings have taken effect.
When you run queries, replace the example domain name with your own domain name.
1. Query using the Alibaba Cloud DNS check tool
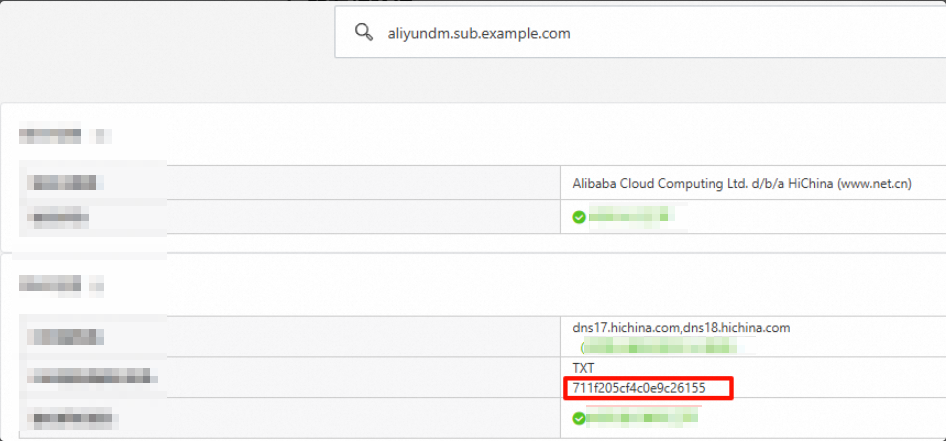
1. Ownership verification
Purpose: To prove that you own or control the domain name. This verification typically requires you to add a specific TXT record provided by the SP.
Domain to query:
aliyundm.sub.example.comRecord type: TXT
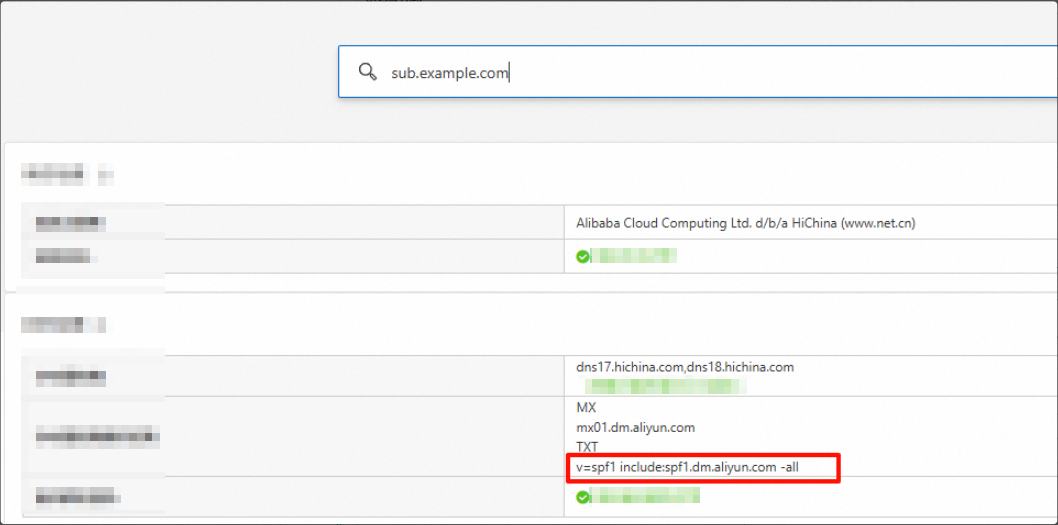
2. SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
Purpose: To prevent sender spoofing by specifying a list of servers that are authorized to send email for your domain.
Domain to query:
sub.example.comRecord type: TXT
1. You can have only one SPF record. If you have multiple outbound IP addresses, merge them into a single record.
Example of value parsing syntax:
Domain + Domain: v=spf1 include the following:spf.qiye.aliyun.com include the following:spf1.dm.aliyun.com -all
Domain name and IP address: v=spf1 include the following:spf.qiye.aliyun.com ip4:x.x.x.x -all
Domain + IP range (use with caution): v=spf1 include the following:spf.qiye.aliyun.com ip4:x.x.x.x/24 -all
Note: Use ip4, not ipv4.
2. Do not use a domain name for Direct Mail if it is also used for a corporate mailbox. This may affect email delivery for the corporate mailbox. We recommend that you use a subdomain for Direct Mail.
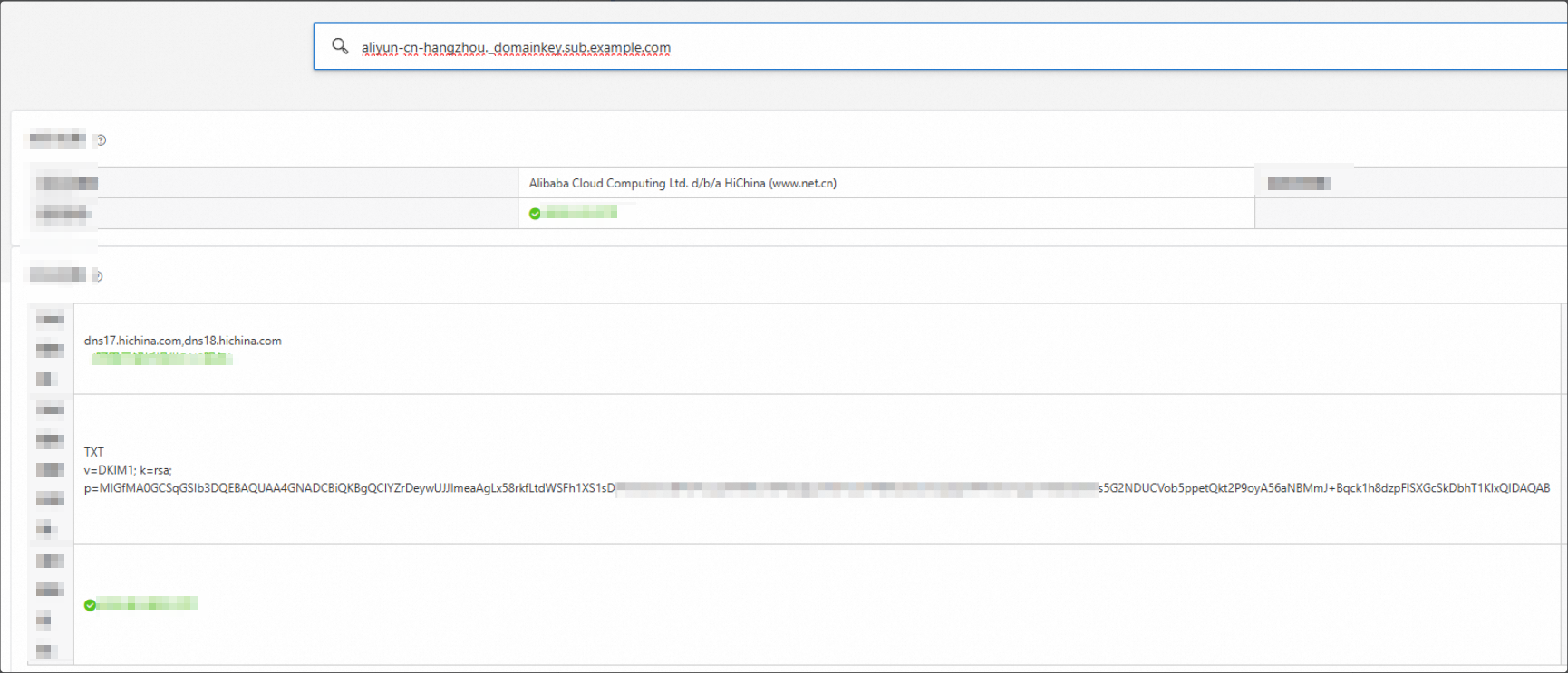
3. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
Purpose: To use a digital signature to verify email integrity and prevent tampering during transit.
Domain to query:
aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com. This is constructed by combining the host record with the root domain.Record type: TXT
The selector value, such as aliyun-cn-hangzhou, varies depending on the region that you select in the console.
Host records for domains that were created earlier may not include the 1024 or 2048 key length identifier. Always use the exact host record displayed on the Email Domains > Configure page.
Original:
China (Hangzhou): aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com
Singapore: aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com
US: aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com or aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com (for some older domains)
Germany: aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com
1024-bit:
China (Hangzhou): aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
Singapore: aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
US: aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
Germany: aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
2048-bit:
China (Hangzhou): aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
Singapore: aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
US: aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
Germany: aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
4. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
Purpose: To define a policy for handling emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks and to receive reports on email authentication results.
The query requests the
TXTrecord of_dmarc.sub.example.com.Record type: TXT
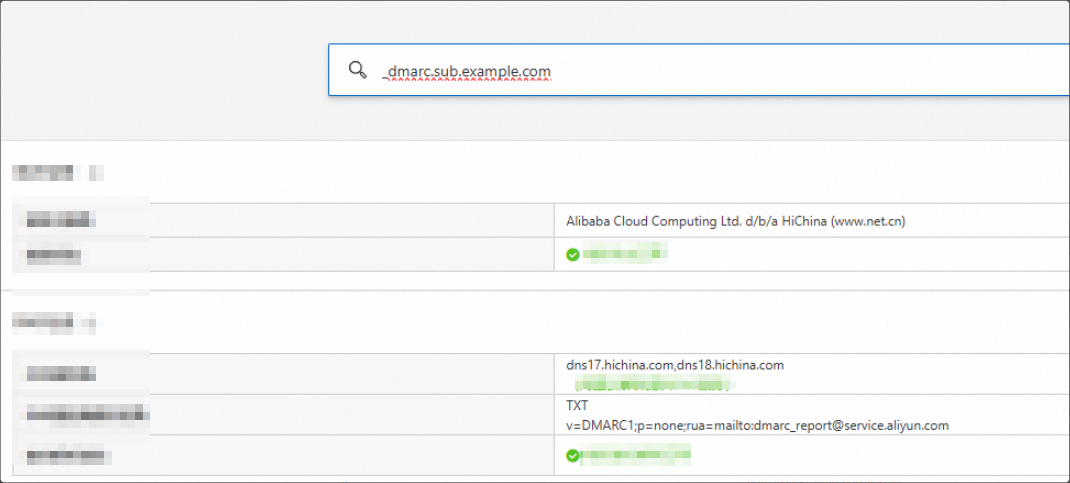
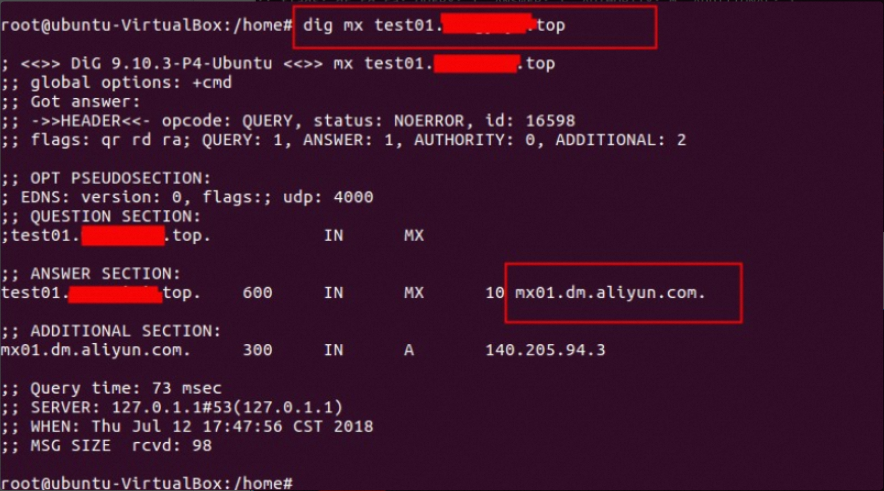
5. MX (Mail Exchange) record
Purpose: To specify the mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain name.
Domain to query:
sub.example.comRecord type: MX
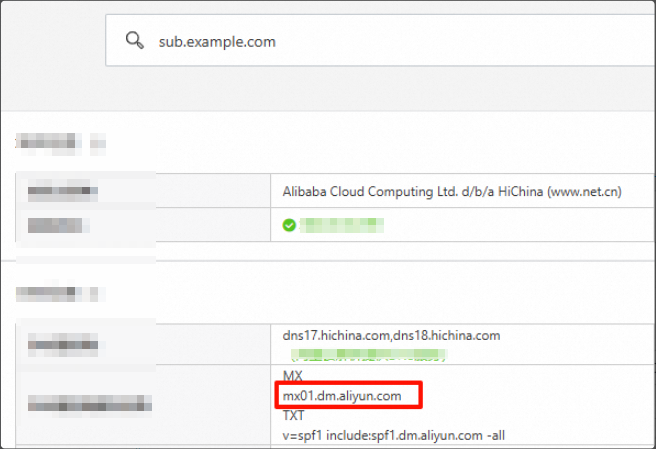
2. Other query methods
1. Using the nslookup command in Windows
Ownership verification, SPF, DMARC, and MX records:
nslookup -type=TXT aliyundm.sub.example.com # Ownership record nslookup -type=TXT sub.example.com # SPF record nslookup -type=TXT _dmarc.sub.example.com # DMARC record nslookup -type=MX sub.example.com # MX recordDKIM example:
# Query using the corresponding region. # Original: # China (Hangzhou): nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com # 1024-bit: # China (Hangzhou): nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # 2048-bit: # China (Hangzhou): nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
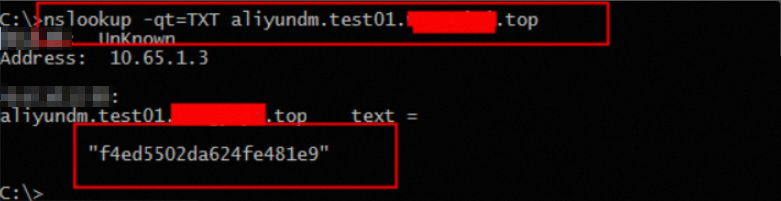
Query the ownership record: nslookup -qt=TXT aliyundm.your-configured-domain
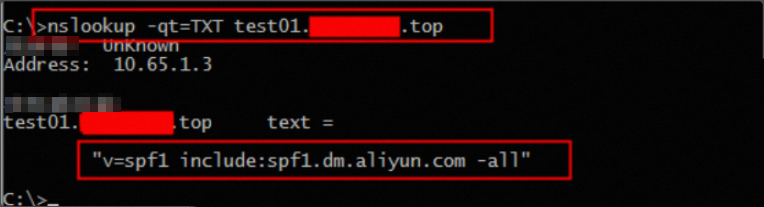
Query the SPF record: nslookup -qt=TXT your-configured-domain
Query the MX record: nslookup -qt=MX your-configured-domain
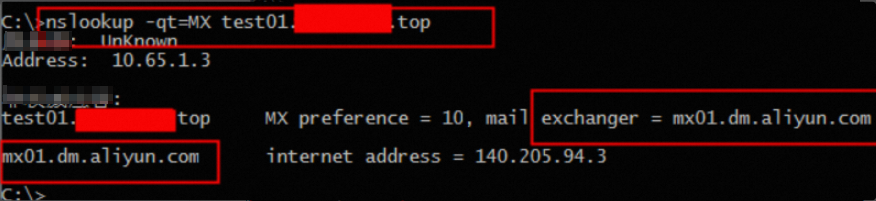
2. Using the dig command on Linux
Ownership verification, SPF, DMARC, and MX records:
dig TXT aliyundm.sub.example.com # Ownership record dig TXT sub.example.com # SPF record dig TXT _dmarc.sub.example.com # DMARC record dig MX sub.example.com # MX recordDKIM example:
# Query using the corresponding region. # Original: # China (Hangzhou): dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com # 1024-bit: # China (Hangzhou): dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com # 2048-bit: # China (Hangzhou): dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # Singapore: dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # US: dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com # Germany: dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
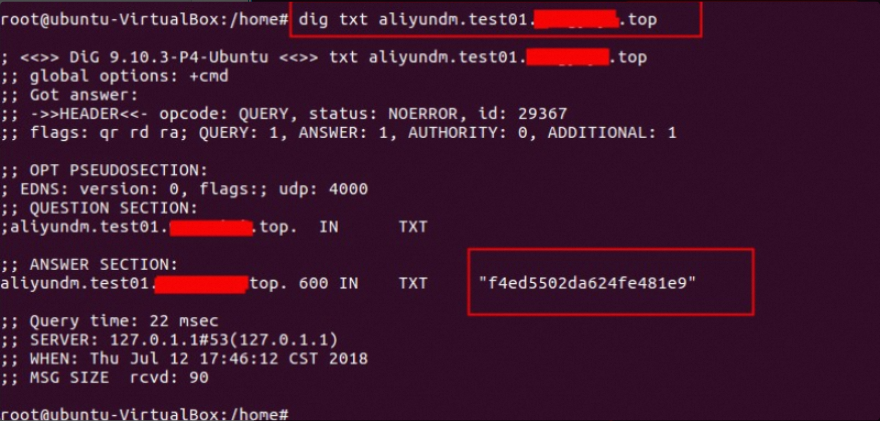
Query the ownership record: dig txt aliyundm.your-configured-domain
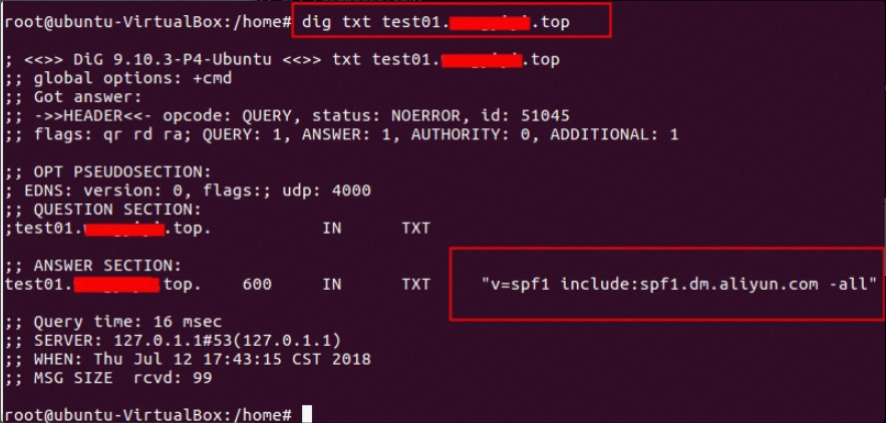
Query the SPF record: dig txt your-configured-domain
Query the MX record: dig mx your-configured-domain