You can configure custom logic for an extension to manage operations performed in DataWorks, such as blocking specific operations. Extensions return processing results on specific events to implement process control in DataWorks. This topic describes how to develop and deploy an extension based on Function Compute.
Background information
Function Compute is an event-driven, fully-managed computing service. You can deploy an extension in Function Compute to allow DataWorks to push the messages of extension point events to the ExtensionRequest class. In the code of an extension, you can construct an ExtensionRequest object to receive the messages and context of extension point events by implementing the handleRequest method of the PojoRequestHandler interface. Then, you can write the processing logic for the extension and use the ExtensionResponse class to return the processing results of extension point events to DataWorks. This way, DataWorks automatically obtains the processing results of extension point events from the ExtensionResponse class and determines whether to block a process.
Limits
Only users of DataWorks Enterprise Edition can use the Extensions module.
The Extensions module is available in the following regions: China (Beijing), China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Shenzhen), China (Chengdu), US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia), Germany (Frankfurt), Japan (Tokyo), China (Hong Kong), and Singapore.
Precautions
Only the Open Platform administrator, tenant administrator, Alibaba Cloud accounts, and RAM users to which the AliyunDataWorksFullAccess policy is attached have read and write permissions on the developer backend. For more information about permission management, see Manage permissions on global-level services and Manage permissions on the DataWorks services and the entities in the DataWorks console by using RAM policies.
If DataWorks Enterprise Edition expires, extensions become invalid and cannot be triggered to check extension point events. If an extension is triggered to check an event and does not complete the check before DataWorks Enterprise Edition expires, the check is terminated and the result Check Passed is returned.
If a combined node, such as a Platform for AI node, do-while node, or for-each node, triggers an extension check, you must wait until all inner nodes of the combined node pass the check before you can perform subsequent operations.
You can associate multiple extensions with the same extension point event. This way, the associated extensions are triggered when the event occurs.
Extensions that are deployed based on Function Compute can process only the following events: pre-events for data download, pre-events for asset publishing and unpublishing, and pre-events for data upload.
Process
The following figure shows how an extension that is developed and deployed based on Function Compute processes extension point events.

After an extension is triggered by an extension point event, the event process enters the Checking state. After the extension sends the processing result to DataWorks by calling an API operation, DataWorks determines whether to block the process.
User
Before you deploy an extension based on Function Compute, you must develop the extension on your on-premises machine. You can use the fc-java-core library to run a handler and download fc_dataworks_demo01-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar to obtain the sample code. For more information, see Event handlers.
Step 1: Configure dependencies for an extension
When you develop an extension, you must add the following dependencies to the pom.xml file.
DataWorks dependency library
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>dataworks_public20200518</artifactId>
<version>5.6.0</version>
</dependency>Function Compute dependency library
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun.fc.runtime/fc-java-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.fc.runtime</groupId>
<artifactId>fc-java-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun.fc.runtime/fc-java-event -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.fc.runtime</groupId>
<artifactId>fc-java-event</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>Dependency packaging
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.RSA</exclude>
</excludes>
</filter>
</filters>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>You can use Apache Maven Shade or Apache Maven Assembly to package dependency libraries. In the preceding sample code, Apache Maven Shade is used.
Step 2: Develop an extension
To develop an extension based on Function Compute, you must use the PojoRequestHandler interface to implement the handleRequest method to receive the requests specified by the ExtensionRequest class and the context. Then, you can write the processing logic for the extension and use the ExtensionResponse class to return the processing results of extension point events to DataWorks.
Develop the code of an extension.
Parse event messages
For information about the formats of event messages sent by DataWorks, see Development reference: Event lists and event message formats. In an event message, the
messageBodyfield specifies the message content. During actual development, you can use themessageBody.eventCodefield to confirm the message type and themessageIdfield to obtain the message details.Write the processing logic
Write the processing logic for event messages that are pushed by DataWorks based on your business requirements. When you develop the code of an extension, you can use the following methods to improve the development efficiency and application effect.
Use extension parameters. For example, you can configure the
extension.project.disabledparameter to prevent the extension from taking effect for the specified workspace. For more information, see Advanced feature: Configure extension parameters.Configure the
MessageIdparameter in the GetIDEEventDetail operation for extension point events in DataStudio to obtain snapshots of extension point events.
NoteThe
MessageIdparameter corresponds to the id field in an event message. For more information, see the Appendix: Message formats section of the "Development reference: Event messages and formats of event messages" topic.Return the processing result of the extension to DataWorks
When you encapsulate the
ExtensionResponseclass, you must configure theCheckResultparameter. DataWorks automatically reads the processing results from theCheckResultparameter to determine whether to fail a process.OK: An extension point event passes the check of an extension.FAIL: An extension point event fails the check of an extension. You must check and handle the reported error at the earliest opportunity to ensure that your service runs as expected.WARN: An extension point event passes the check of an extension, but a warning is reported for the event.
You can download fc_dataworks_demo01-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar and upload it to Function Compute for verification and test. The content in the following tabs describes the code details.
Package the extension code into an executable
.jarpackage or.zipfile for subsequent use in Function Compute.Open the CLI of the code editor, switch to the root directory, and then run the
mvn clean packagecommand to package the extension code.If the message shows that compilation failed, modify the code based on the error message.
If the compilation is successful, the compiled JAR file is located in the target directory in the project folder and is named java-example-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar based on the artifactId and version fields in pom.xml.
NoteFor macOS and Linux OSs, make sure that you have the read and execute permissions on the related code file before you package the file.
Function Compute
Step 1: Deploy the extension
Log on to the Function Compute console 2.0. In the left-side navigation pane, click Tasks.
Click Create Function to create a Function Compute service and the required function, and deploy the extension. The extension you developed directly sends specific event messages to the created service. For more information, see Create a service and Create a function. The following figure shows how to configure a function.
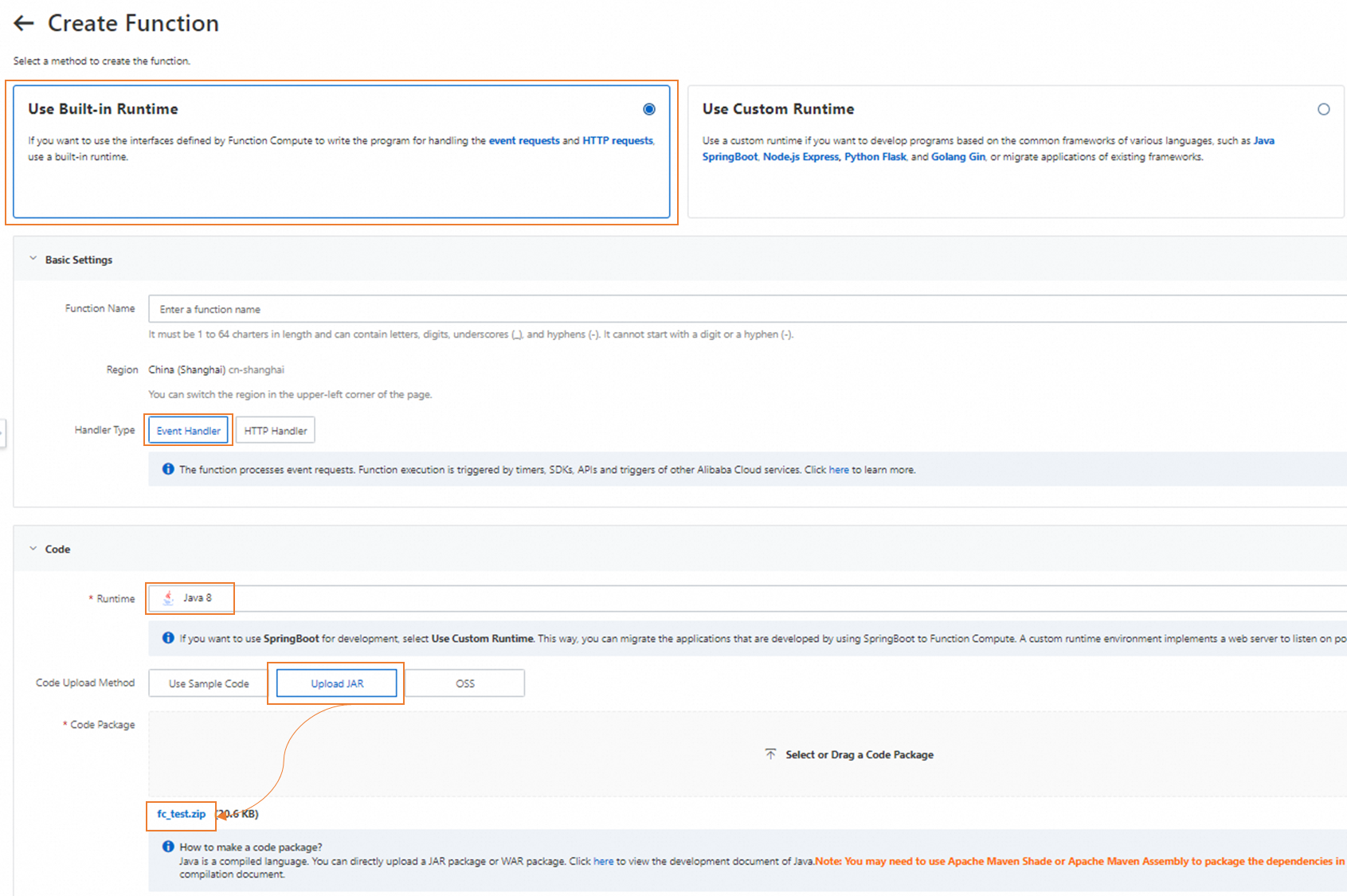
Select a runtime environment based on your code. If you use the sample package
fc_dataworks_demo01-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jarprovided in Step 1, set the Runtime parameter to Java 8. You must download thefc_dataworks_demo01-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jarpackage to your on-premises machine and upload it as the code package. You can configure the parameters based on your business requirements.For more information about the operations that you can perform on a function, see Manage functions.
Configure the handler of the function.
You can configure a handler for the function in the Function Compute console. For functions that use the Java language, you can configure a handler in the
[Package name].[Class name]::[Method name]format. Example:Package name:
exampleClass name:
HelloFCMethod name:
handleRequest
The handler is
example.HelloFC::handleRequest.NoteThe default handler is
example.App::handleRequest. You can modify the handler based on your business requirements. For more information, see Handler.
Step 2: Test the function
After you create the function, you can perform the following operations to test the function: Find the created function and click the name of the function. On the page that appears, click the Code tab. Then, click Test Function. After the function passes the test, you can register the extension in the DataWorks console.
DataWorks
Step 1: Register the extension
After you deploy the extension in Function Compute, you must register the extension in DataWorks. To register the extension in DataWorks, perform the following steps:
Go to the Developer Backend tab.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Go to Open Platform. The Developer Backend tab appears.
Register the extension.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Extensions.
Click Register Extension in the List of Extensions section. In the Select Deployment Method step of the Register Extension wizard, set the Select a deployment method for your extension parameter to Deploy Based on Function Compute (Highly Recommended) and configure the parameters in the Register Extension step.
The following table describes the parameters for registering an extension. You can configure the parameters based on your business requirements.
Click OK.
After you register the extension, you can view the extension in the List of Extensions section of the Extensions page.
Step 2: Publish the extension
After you develop, deploy, and register the extension in DataWorks, you must test the extension, submit the extension for review, and then publish the extension. Then, administrators, besides the owner of the extension, can enable the extension in Management Center. For more information, see Use an extension.
Appendix: Formats of event messages sent to Function Compute
The following sample code shows the general format for the types of event messages that are pushed to Function Compute. The messageBody parameter specifies the details of a DataWorks event message. The content of an event message varies based on the event type.
{
"blockBusiness": true,
"eventCategoryType": "resources-download",// The event category.
"eventType": "upload-data-to-table",// The event type.
"extensionBizId": "job_6603643923728775070",
"messageBody": {
// The content of an event message varies based on the event type. The following fields are the fixed fields in an event message.
"tenantId": 28378****10656,// The ID of the tenant. Each Alibaba Cloud account in DataWorks corresponds to a tenant. Each tenant has its own tenant ID. To view the tenant ID, click the username in the upper-right corner of the DataStudio page and then click User Info in the Menu section.
"eventCode": "xxxx"//
},
"messageId": "52d44ee7-b51f-4d4d-afeb-*******"// The event ID. The ID is the unique identifier of an event.
}The content of the messageBody field varies based on the event type. For more information about event messages, see Development reference: Event lists and event message formats.
References
For more information about Function Compute, see What is Function Compute?
You can also deploy an extension based on a self-managed service. For more information, see Develop and deploy an extension based on a self-managed service.