DataWorks provides built-in checks, such as code review before node deployment and checks in Data Governance Center. DataWorks also supports custom checks. You can develop a custom check program based on your business requirements and connect the custom check program to DataWorks to manage the processes of nodes. This topic describes how to subscribe to status change events of an auto triggered node instance by using the OpenEvent module of DataWorks Open Platform. In this topic, the status changes of an auto triggered node instance are obtained from Operation Center.
Background information
For more information about the features and basic concepts of DataWorks Open Platform that are involved in this topic, see Overview.
Description of subscription configuration
When you configure the Pattern Content parameter for an event rule in EventBridge, set type to dataworks:InstanceStatusChanges:InstanceStatusChanges. This way, you can subscribe to status change events of an auto triggered node instance.
Prerequisites
EventBridge is activated. For more information, see Billing.
DataWorks is activated. For more information, see Purchase guide.
A workspace is created in DataWorks. For more information, see Create a workspace.
Procedure
Step 1: Configure a custom bus
This section describes the core configuration steps and precautions for configuring a custom bus. For more information about how to enable and configure event message subscription, see Enable event message subscription.
Log on to the EventBridge console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Buses.
In the upper-right corner of the Event Buses page, click Quickly Create to create a custom bus.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Buses. On the Event Buses page, find the custom bus that you created and click its name. The Overview page of the custom bus appears.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Rules. On the page that appears, click Create Rule to create an event rule.
In this example, the custom bus is configured to receive node committing event messages and node deployment event messages. The following content provides an example on how to configure a demo and the core parameters for the event rule:
Configure Basic Info: In this step, you must configure the Name parameter.
Configure Event Pattern:
Event Source Type: Set it to Custom Event Source.
Event Source: Leave this parameter empty.
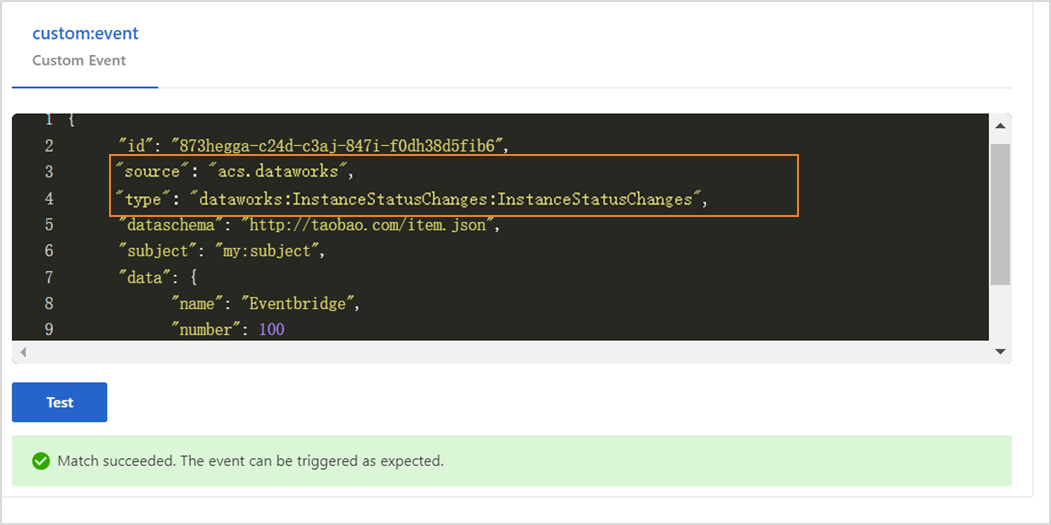
Pattern Content: Configure this parameter in the JSON format. Enter the following content.
{ "source": [ "acs.dataworks" ], "type": [ "dataworks:InstanceStatusChanges:InstanceStatusChanges" ] }source: the identifier of the service in which an event occurs. Set this parameter to acs.dataworks.
type: the type of the event that occurs in the service. Set this parameter to dataworks:InstanceStatusChanges:InstanceStatusChanges.
Event Pattern Debugging: You can change the values of the source and type parameters in this section and then click Test. If the test is successful, click Next Step.
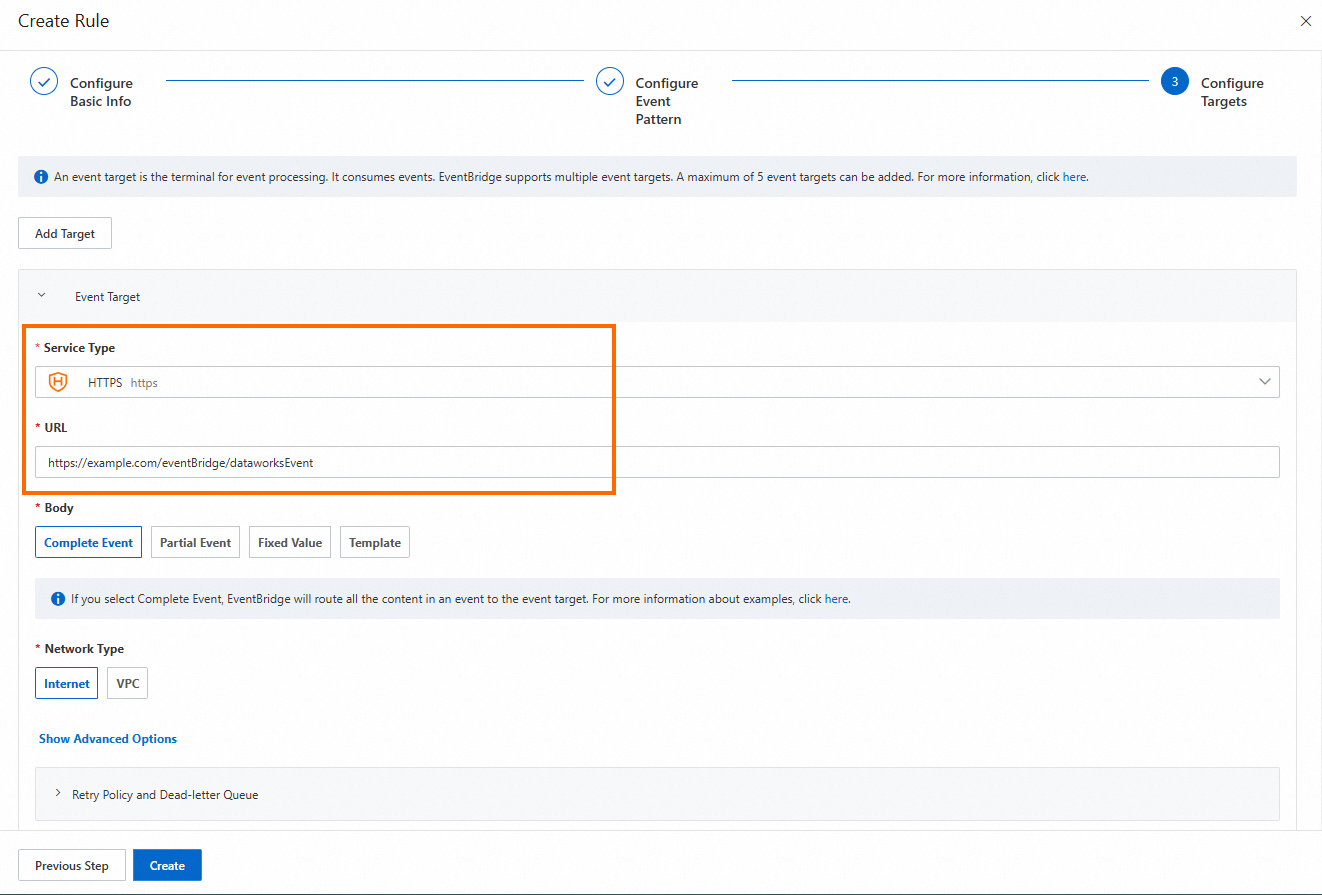
Configure Targets:
Service Type: Set it to HTTPS or HTTP. For more information about service types, see Manage event rules.
URL: Enter the URL for receiving messages pushed by the custom bus, such as
https://Server address:Port number/event/consumer.Body: Set it to Complete Event.
Network Type: Set it to Internet.
Step 2: Configure an event distribution channel
Go to the Open Platform page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . The Developer Backend tab appears.
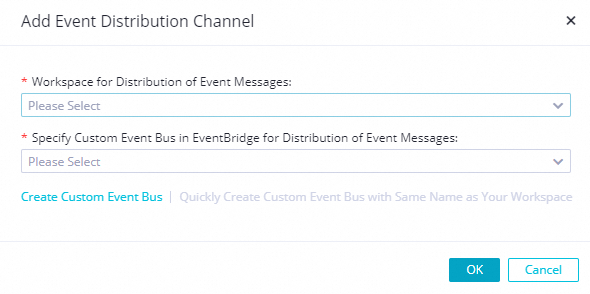
In the left-side navigation pane of the Developer Backend page, click OpenEvent. On the page that appears, click Add Event Distribution Channel. In the Add Event Distribution Channel dialog box, configure the parameters.
Workspace for Distribution of Event Messages: Select a workspace.
Specify Custom Event Bus in EventBridge for Distribution of Event Messages: Select the event bus that you created in Step 1.
After you save the event distribution channel, find the event distribution channel on the OpenEvent page and click Enable in the Actions column.
Develop a service program
Sample code
Modify the code to obtain the messages that EventBridge pushes to the service and generate the messages.
package com.aliyun.dataworks.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.aliyun.dataworks.config.Constants;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author dataworks demo
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/event")
public class ExtensionsController {
/**
* Receive event messages that are sent from EventBridge.
* @param jsonParam
*/
@PostMapping("/consumer")
public void consumerEventBridge(@RequestBody String jsonParam){
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(jsonParam);
String eventCode = jsonObj.getString(Constants.EVENT_CODE_FILED);
if(Constants.INSTANCE_STATUS_EVENT_CODE.equals(eventCode)){
JSONObject dataParam = JSON.parseObject(jsonObj.getString("data"));
// The time when the auto triggered node instance started to wait for the scheduling time.
System.out.println("beginWaitTimeTime: "+ dataParam.getString("beginWaitTimeTime"));
//DagId
System.out.println("dagId: "+ dataParam.getString("dagId"));
// The type of the directed acyclic graph (DAG). Valid values:
// 0: for auto triggered nodes
// 1: for manually triggered nodes
// 2: for smoke testing
// 3: for nodes for which you backfill data
// 4: for manually triggered workflows
// 5: for temporary workflows
System.out.println("dagType: "+dataParam.getString("dagType"));
// The type of the node. Valid values:
// NORMAL(0): The node is an auto triggered node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node.
// MANUAL(1): The node is a manually triggered node. The scheduling system does not regularly run the node.
// PAUSE(2): The node is a frozen node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Failed when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP(3): The node is a dry-run node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP_UNCHOOSE(4): The node is an unselected node in a temporary workflow. This type of node exists only in temporary workflows. The scheduling system sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP_CYCLE(5): The node is scheduled by week or month, and is waiting for the scheduling time to arrive. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// CONDITION_UNCHOOSE(6): The node is not selected by its ancestor branch node and is run as a dry-run node.
// REALTIME_DEPRECATED(7): The node has instances that are generated in real time but are deprecated. The scheduling system sets the node status to Succeeded.
System.out.println("taskType: "+dataParam.getString("taskType"));
// The time when the node instance was modified.
System.out.println("modifyTime: "+dataParam.getString("modifyTime"));
// The time when the node instance was created.
System.out.println("createTime: "+dataParam.getString("createTime"));
// The ID of the workspace. You can call the ListProjects operation to query the ID.
System.out.println("appId: "+dataParam.getString("appId"));
// The ID of the tenant that manages the workspace to which the auto triggered node instance belongs.
System.out.println("tenantId: "+dataParam.getString("tenantId"));
// The operation code of the auto triggered node instance. You can ignore the field value.
System.out.println("opCode: "+dataParam.getString("opCode"));
// The ID of the workflow. For an auto triggered node instance, the field value is 1. For a manually triggered workflow or an auto triggered node instance of the internal workflow type, the field value is the actual workflow ID.
System.out.println("flowId: "+dataParam.getString("flowId"));
// The ID of the node for which the auto triggered node instance was generated.
System.out.println("nodeId:"+dataParam.getString("nodeId"));
// The time when the auto triggered node instance started to wait for resources.
System.out.println("beginWaitResTime: "+dataParam.getString("beginWaitResTime"));
// The ID of the auto triggered node instance.
System.out.println("taskId: "+dataParam.getString("taskId"));
// The status of the node. Valid values:
// 0: The node is not running.
// 2: The node is waiting for the scheduling time to arrive. The scheduling time is specified by the dueTime or cycleTime parameter.
// 3: The node is waiting for resources.
// 4: The node is running.
// 7: The tables that are specified in the node are issued to Data Quality and data in the tables is checked based on monitoring rules in Data Quality.
// 8: Branch conditions are being checked.
// 5: The node failed to be run.
// 6: The node is successfully run.
System.out.println("status: "+dataParam.getString("status"));
}else{
System.out.println("Failed to filter out other types of events. Check the parameter configurations.");
}
}
}
Sample project deployment
Prepare the environment and the project.
Environment requirement: Java 8 or later and Maven. Maven is a build automation tool for Java.
Download link for the project file: event-demo-instance-status.zip.
After you download the project file, enter the root directory of the project and run the following command:
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true spring-boot:repackageAfter you obtain the JAR package that can be directly installed, run the following command:
java -jar target/event-demo-instance-status-1.0.jarThe following figure shows the successfully started project.
Enter
http://localhost:8080/indexin the address bar of a browser and press Enter. If"hello world!"is returned, the extension is successfully deployed. You can subscribe to event messages after network connections are established between DataWorks and your extension and between EventBridge and your extension.
Enable and configure event message subscription (OpenEvent)
Enable event message subscription
In the EventBridge console, create a custom bus. You do not need to configure the parameters in the Event Source, Event Rule, and Event Target steps.
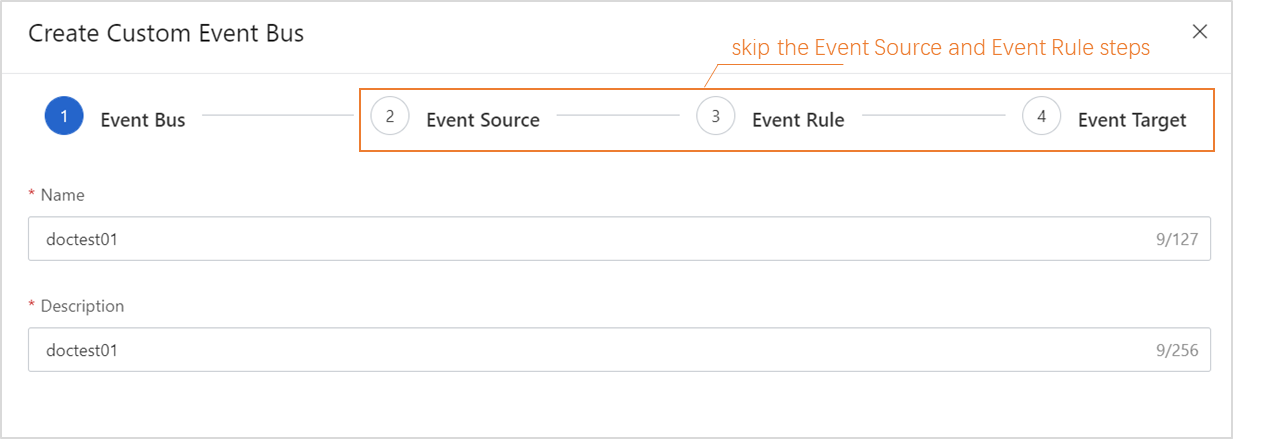
In the EventBridge console, create an event rule for the custom bus.
In this example, the custom bus is configured to receive messages for status change events of an auto triggered node instance. The following content provides an example on how to configure a demo and the core parameters for the event rule:
Configure the parameters in the Configure Event Pattern step.
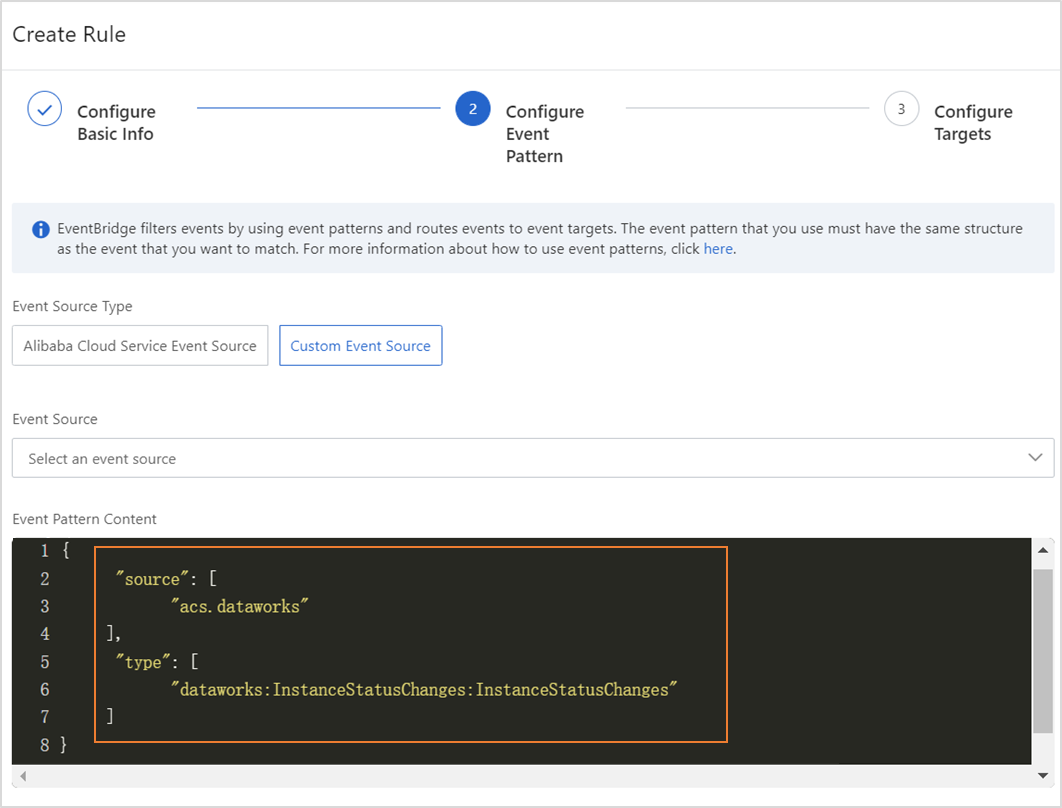
{ "source": [ "acs.dataworks" ], "type": [ "dataworks:InstanceStatusChanges:InstanceStatusChanges" ] }source: the identifier of the service in which an event occurs. Set this parameter to acs.dataworks.
type: the type of the event that occurs in the service. Set this parameter to dataworks:InstanceStatusChanges:InstanceStatusChanges. You can change the values of the source and type parameters in the Event Pattern Debugging section and then click Test. If the test is successful, click Next Step.

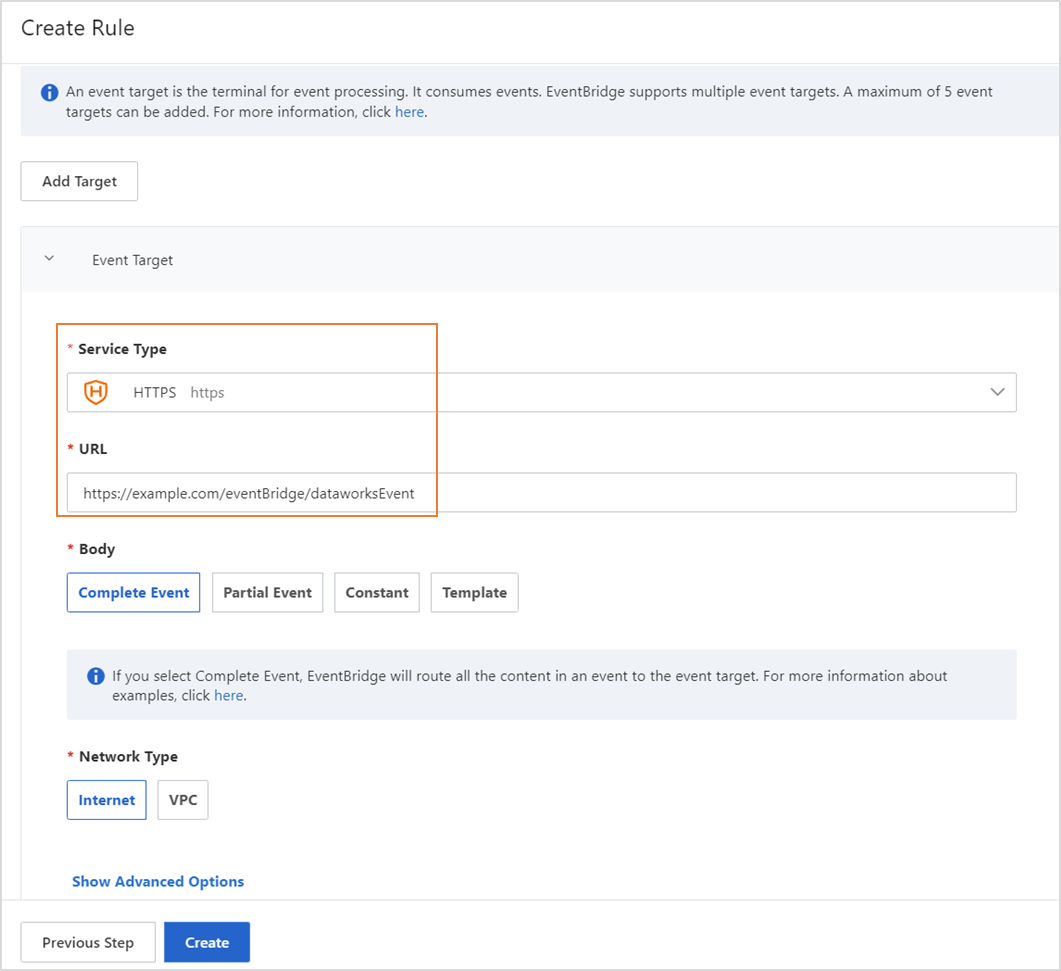
In the Configure Targets step, set Service Type to HTTPS and enter a valid URL. Use the default settings for other parameters.
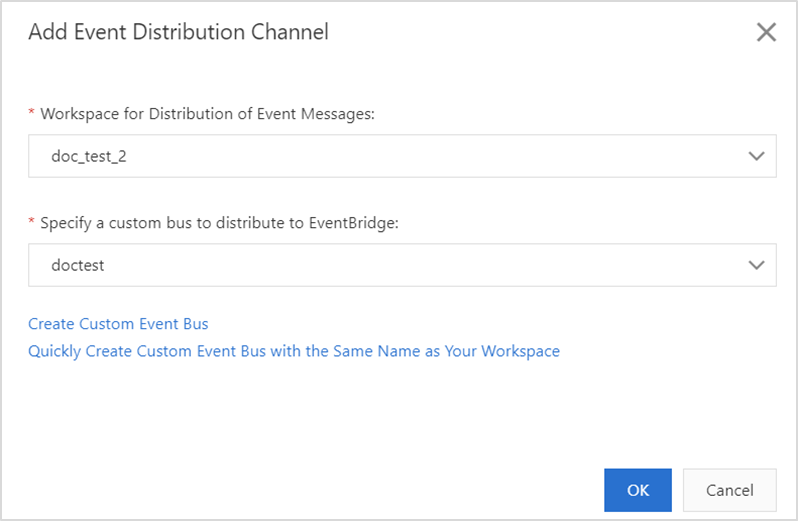
Go to the Open Platform page in the DataWorks console. In the left-side navigation tree, click OpenEvent. On the page that appears, add an event distribution channel.
Write code
package com.aliyun.dataworks.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.aliyun.dataworks.config.Constants;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author dataworks demo
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/event")
public class ExtensionsController {
/**
* Receive event messages that are sent from EventBridge.
* @param jsonParam
*/
@PostMapping("/consumer")
public void consumerEventBridge(@RequestBody String jsonParam){
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(jsonParam);
String eventCode = jsonObj.getString(Constants.EVENT_CODE_FILED);
if(Constants.INSTANCE_STATUS_EVENT_CODE.equals(eventCode)){
JSONObject dataParam = JSON.parseObject(jsonObj.getString("data"));
// The time when the auto triggered node instance started to wait for the scheduling time.
System.out.println("beginWaitTimeTime: "+ dataParam.getString("beginWaitTimeTime"));
//DagId
System.out.println("dagId: "+ dataParam.getString("dagId"));
// The type of the directed acyclic graph (DAG). Valid values:
// 0: for auto triggered nodes
// 1: for manually triggered nodes
// 2: for smoke testing
// 3: for nodes for which you backfill data
// 4: for manually triggered workflows
// 5: for temporary workflows
System.out.println("dagType: "+dataParam.getString("dagType"));
// The type of the node. Valid values:
// NORMAL(0): The node is an auto triggered node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node.
// MANUAL(1): The node is a manually triggered node. The scheduling system does not regularly run the node.
// PAUSE(2): The node is a frozen node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Failed when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP(3): The node is a dry-run node. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP_UNCHOOSE(4): The node is an unselected node in a temporary workflow. This type of node exists only in temporary workflows. The scheduling system sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// SKIP_CYCLE(5): The node is scheduled by week or month, and is waiting for the scheduling time to arrive. The scheduling system regularly runs the node but sets the node status to Succeeded when the scheduling system starts to run the node.
// CONDITION_UNCHOOSE(6): The node is not selected by its ancestor branch node and is run as a dry-run node.
// REALTIME_DEPRECATED(7): The node has instances that are generated in real time but are deprecated. The scheduling system sets the node status to Succeeded.
System.out.println("taskType: "+dataParam.getString("taskType"));
// The time when the node instance was modified.
System.out.println("modifyTime: "+dataParam.getString("modifyTime"));
// The time when the node instance was created.
System.out.println("createTime: "+dataParam.getString("createTime"));
// The ID of the workspace. You can call the ListProjects operation to query the ID.
System.out.println("appId: "+dataParam.getString("appId"));
// The ID of the tenant that manages the workspace to which the auto triggered node instance belongs.
System.out.println("tenantId: "+dataParam.getString("tenantId"));
// The operation code of the auto triggered node instance. You can ignore the field value.
System.out.println("opCode: "+dataParam.getString("opCode"));
// The ID of the workflow. For an auto triggered node instance, the field value is 1. For a manually triggered workflow or an auto triggered node instance of the internal workflow type, the field value is the actual workflow ID.
System.out.println("flowId: "+dataParam.getString("flowId"));
// The ID of the node for which the auto triggered node instance was generated.
System.out.println("nodeId:"+dataParam.getString("nodeId"));
// The time when the auto triggered node instance started to wait for resources.
System.out.println("beginWaitResTime: "+dataParam.getString("beginWaitResTime"));
// The ID of the auto triggered node instance.
System.out.println("taskId: "+dataParam.getString("taskId"));
// The status of the node. Valid values:
// 0: The node is not running.
// 2: The node is waiting for the scheduling time to arrive. The scheduling time is specified by the dueTime or cycleTime parameter.
// 3: The node is waiting for resources.
// 4: The node is running.
// 7: The tables that are specified in the node are issued to Data Quality and data in the tables is checked based on monitoring rules in Data Quality.
// 8: Branch conditions are being checked.
// 5: The node failed to be run.
// 6: The node is successfully run.
System.out.println("status: "+dataParam.getString("status"));
}else{
System.out.println("Failed to filter out other types of events. Check the parameter configurations.");
}
}
}
Deploy and run the code on your on-premises machine
Download the demo project file:
Environment requirement: Java 8 or later and Maven. Maven is a build automation tool for Java.
Download link for the project file: event-demo-instance-status.zip.
Select a deployment mode.
On-premises deployment: After you package the project file into a JAR package, run the
java -jar yourapp.jarcommand on the on-premises server in which Java 8 and Maven are deployed to start the service program.Cloud-based deployment: After you package the project file into a JAR package, upload the package to the related runtime environment, such as Docker containers and cloud servers, for deployment.
NoteAfter you deploy the service program, make sure that EventBridge can access the service over the Internet.
After you download the project file, enter the root directory of the project and run the following command:
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true spring-boot:repackageAfter you obtain the JAR package that can be directly installed, run the following command:
java -jar target/event-demo-instance-status-1.0.jarThe following figure shows the successfully started project.
 Enter
Enter http://localhost:8080/indexin the address bar of a browser and press Enter. If"hello world!"is returned, the extension is successfully deployed. You can subscribe to event messages after network connections are established between DataWorks and your extension and between EventBridge and your extension.