You can install Cloud Monitor agents on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances and third-party hosts to collect information about the active processes during a specific period of time. You can collect the following information: CPU utilization, memory usage, and the number of opened files. You can also add a process for monitoring, view the number of processes, and create an alert rule for the process. This way, you can monitor changes in the number of processes in a timely manner and make sure that the process runs properly.
Prerequisites
The Cloud Monitor agent is installed on an ECS instance and a third-party host. For more information, see Install and uninstall the CloudMonitor agent for C++.
Background information
Cloud Monitor collects the top five processes with the most CPU consumption every minute. Cloud Monitor records CPU utilization, memory usage, and the number of opened files in these processes.
CPU utilization and memory usage of a process
You can check the output of the top command in the Linux operating system to understand the two metrics.
Number of opened files in a process
You can check the output of the lsof command in the Linux operating system to understand this metric.
Cloud Monitor collects the CPU utilization of only the top five processes. The following issues may occur:
If your process occupies multiple CPU cores, the collected CPU utilization may exceed 100%. This is because Cloud Monitor collects the total CPU utilization of the process on all the occupied CPU cores.
If the top five processes vary during the time period specified in your query, the process list displays all the processes that have ranked top five over the specified time period. The time displayed in the list indicates when the processes last ranked top five.
Cloud Monitor collects only CPU utilization, memory usage, and the number of opened files for a process when the process ranks top five. If a process has not stayed in the top five within the time period specified in your query, its monitoring data is displayed as dispersed data points in the monitoring charts. The density of the data points indicates the activity level of the process on the host. Examples:
In the following figures, the data points for the wrapper process are sparse and discontinuous in the monitoring charts. This is because the wrapper process did not continuously rank top five with the highest CPU utilization during the specified time period.
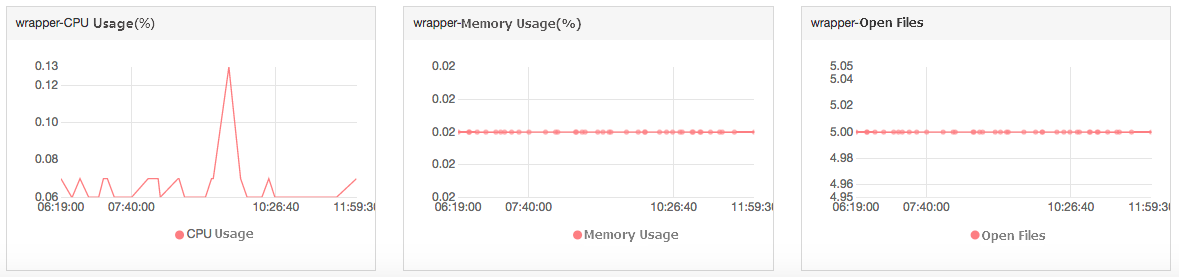
The data points for the java process are dense and continuous in the monitoring charts. This is because the java process continuously ranked top five with the highest CPU utilization during the specified time period.
Add a process
You can monitor the number and status of key processes by adding process keywords.
In this example, the following processes run on your host:
/usr/bin/java -Xmx2300m -Xms2300m org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap/usr/bin/rubynginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
You can add the following process keywords and obtain the following monitoring results:
ruby: One process matches this keyword by name. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 1.nginx: One process matches this keyword by name and parameter. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 1./usr/bin: Two processes match this keyword by path. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 2.apache.catalina: One process matches this keyword by parameter. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 1.nginx.conf: One process matches this keyword by parameter. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 1.-c: One process matches this keyword by parameter. Therefore, the number of processes that match this keyword is 1.
Log on to the Cloud Monitor console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Host Monitoring page, click the host name or click Monitoring Charts in the Actions column of the host.
Click the Process Monitoring tab.
In the Process count monitoring section, click Add Process Monitor in the upper-right corner.

In the Add Process Monitor panel, enter a process name and click Add. Then, click the
 icon in the upper-right corner. Note
icon in the upper-right corner. NoteAfter you add the process for monitoring, wait a few minutes. Then, you can view the monitoring data of the number of processes.
Configure an alert rule for a process
After you add a process, you can configure an alert rule for the process. You can then receive alert notifications if the number of processes that match the process keyword changes.
Log on to the Cloud Monitor console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Host Monitoring page, click the host name or click Monitoring Charts in the Actions column of the host.
Click the Process Monitoring tab.
In the Process count monitoring section, click the
 icon in the upper-right corner.
icon in the upper-right corner.
In the Configure Rule Description panel, enter an alert rule name. Select Process / Number of Current Processes from the Metric drop-down list and set the threshold and alert level for the metric. Then, click OK.
In the Create Alert Rule panel, configure the parameters and then click Confirm.
For more information about how to configure required parameters for an alert rule, see Create an alert rule.
View the alert rule of the process.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Alert Rules page, view the alert rules from the Process dimension in the Alert Rules column.
Delete a process
Processes added by using the Group Process submenu of the Application Groups menu can only be deleted from the Group Process page.
Log on to the Cloud Monitor console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Host Monitoring page, click the host name or click Monitoring Charts in the Actions column of the host.
Click the Process Monitoring tab.
In the Process count monitoring section, click Add Process Monitor in the upper-right corner.
In the Add Process Monitor panel, find the process that you want to delete and click Delete in the Actions column.
In the Delete confirmation message, click Confirm.
Click the
 icon in the upper-right corner.
icon in the upper-right corner.