You can set weights for different instance types based on performance metrics such as the number of vCPUs. You can specify the capacity of a single instance of a specific instance type in a scaling group. After the weights are set, Auto Scaling can measure the capacity of a scaling group by using performance metrics. This helps you determine the overall performance of a scaling group in a more precise manner.
Background information
By default, Auto Scaling measures the capacity of a scaling group based on the number of ECS instances in the scaling group. If you specify only a single instance type in the active scaling configuration of a scaling group, the number of instances in the scaling group is proportional to the overall performance of the scaling group. However, if you specify multiple instance types that have different specifications in the active scaling configuration of a scaling group and create instances of multiple instance types, the number of instances in the scaling group cannot precisely reflect the overall performance of the scaling group. For example, the performance of 10 ecs.c5.xlarge (4 vCPUs and 8 GiB memory) instances is twice that of 10 ecs.c5.large (2 vCPUs and 4 GiB memory) instances.
You can specify the weights of instance types. Even if Auto Scaling creates multiple instances of different instance types in a scaling group, you can precisely measure the performance of the scaling group. For example, if you set the weights of instance types based on the number of vCPUs in a scaling group, the capacity of the scaling group indicates the total number of vCPUs of all instances in the scaling group.
Terms
| Term | API parameter | Description |
| weight | WeightedCapacity | The weight of an instance type. You can set the weight of an instance type based on performance metrics such as the number of vCPUs. You can specify the capacity of a single instance of a specific instance type in a scaling group. |
| total capacity | TotalCapacity | The total capacity of all instances in a scaling group. |
| maximum capacity | MaxSize | The maximum value of the total capacity of a scaling group. Note After a scale-out event is executed in a scaling group, the total capacity of the scaling group may exceed the maximum capacity. This is because the maximum capacity may not be divisible by the weight of a single instance type. However, the extra capacity is less than the maximum weight. |
| minimum capacity | MinSize | The minimum value of the total capacity of a scaling group. |
| expected capacity | DesiredCapacity | The expected value of the total capacity of a scaling group. Auto Scaling ensures that the total capacity is no less than the expected capacity. Note After a scale-out event is executed in a scaling group, the total capacity of the scaling group may exceed the expected capacity. This is because the expected capacity may not be divisible by the weight of a single instance type. However, the extra capacity is less than the maximum weight. |
Rules for scaling
- When the total capacity of a scaling group is less than the expected capacity or the minimum capacity, scale-out events are triggered.
- When the total capacity of a scaling group is greater than or equal to the sum of the expected capacity and the maximum weight, scale-in events are triggered.
Usage notes
- You must set weights for all instance types in a scaling group.
- If you delete an instance type specified in the active scaling configuration of a scaling group, the weights of instances of this instance type remain unchanged in the scaling group.
- After you modify the weight of an instance type in a scaling group, Auto Scaling recalculates the capacity of the scaling group based on the modified weight if instances of this instance type have been created. Scaling activities may be triggered.
Procedure
In this example, a scaling configuration is used as the configuration source of a scaling group to set the weights of instance types.
- Create a scaling group. This step describes the parameters related to the multi-zone scaling policy. For information about other parameters of a scaling group, see Manage scaling groups.
- Set Network Type to VPC and select multiple vSwitches in the same VPC. One vSwitch belongs to only one zone. After you configure multiple vSwitches for the scaling group, Auto Scaling can create ECS instances in multiple zones. This helps you utilize available ECS resources in different zones.
- Set Multi-zone Scaling Policy to Cost Optimization Policy.
- Configure other parameters for the scaling group.
- Set Network Type to VPC and select multiple vSwitches in the same VPC.
- Create a scaling configuration. This step describes the parameters for setting the weight of an instance type based on the number of vCPUs. For information about other parameters of a scaling configuration, see Create a scaling configuration of the ECS type.
- Set Billing Method to Pay-As-You-Go.
- Select multiple instance types. You can select up to 10 instance types.
- Select Set vCPU Capacity. By default, the system sets weights for all selected instance types based on the number of vCPUs.
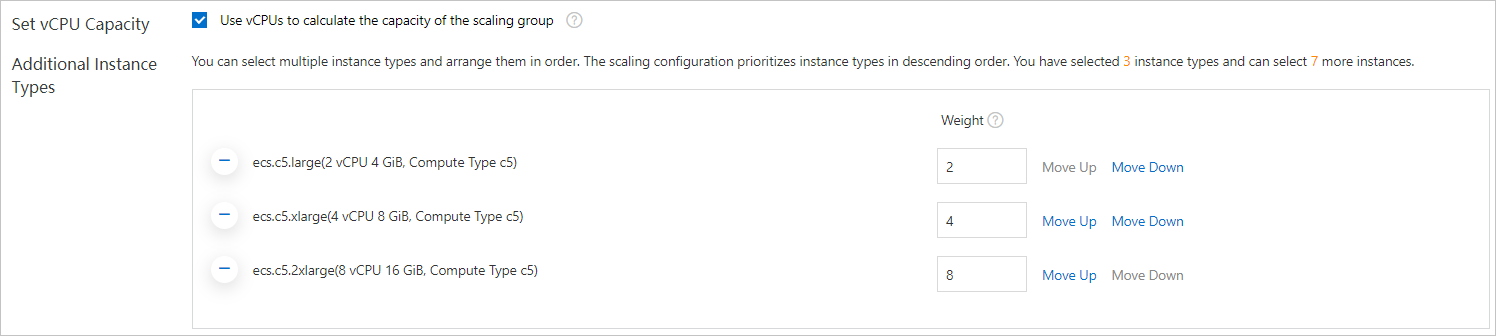
You can customize the weights of instance types. When you customize weights, we recommend that you take note of the following items:
- Use performance metrics related to instance types to set weights. For example, you can set weights based on the number of CPU cores or the amount of memory. You can use an instance type that has 1 vCPU and 1 GiB memory or provides the minimum performance as the capacity unit of a scaling group. The capacity of the scaling group is calculated based on the capacity unit.
- Set appropriate weight values to ensure that the current capacity of a scaling group is two to three times the maximum weight of instance types.
- Set the weights of different instance types to values that have small differences. For example, do not set the weight of an instance type that has lower specifications to 1 and the weight of an instance type that has higher specifications to 200. If the difference between the weights of instance types in a scaling group is large, the overall costs of the scaling group may increase.
For information about the priority of multiple instance types when they are used to create instances, see Calculation of weighted unit prices.
- Configure other parameters for the scaling configuration.
- Enable the scaling group.
- Create a scaling rule. This step describes the parameters for creating a simple scaling rule to verify the cost optimization policy. For information about other parameters of a scaling rule, see Manage scaling rules.
- Set Rule Type to Simple Scaling Rule.
- Set Operation to Add 10 Capacity Unit.
- Configure other parameters for the scaling rule.
- Execute the scaling rule. In this example, the weighted unit price of the ecs.c5.2xlarge instance type is the lowest. Therefore, Auto Scaling creates two instances of the ecs.c5.2xlarge instance type for the scaling group. This adds 16 capacity units to the scaling group.
Calculation of weighted unit prices
If you set the multi-zone scaling policy to Cost Optimization Policy for a scaling group and set the weights of instance types, Auto Scaling attempts to create instances based on the weighted unit prices in ascending order. For more information, see Combine a cost optimization policy with the selection of multiple instance types.
| Instance type | vCPU | Market price | Weight | Weighted unit price |
| ecs.c5.large | 2 | USD 0.073/Hour | 2 | USD 0.037/Hour |
| ecs.c5.xlarge | 4 | USD 0.144/Hour | 4 | USD 0.036/Hour |
| ecs.c5.2xlarge | 8 | USD 0.288/Hour | 8 | USD 0.036/Hour |