Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances or elastic container instances (ECI) in a scaling group can be automatically released at any time. To ensure data persistence, store your data on cloud databases. This topic describes how to associate instances in a scaling group with a cloud database by adding the private IP addresses of the instances to the database whitelist.
Association methods
Method | Applicable instance types | Supported cloud database types |
(Recommended) Method 1: Add instances and cloud databases to the same security group | ECS and ECI |
|
ECS and ECI |
| |
ECS |
|
(Recommended) Method 1: Add instances and cloud databases to the same security group
When you assign a security group to a cloud database, the private IP addresses of all instances in that security group are automatically added to the database whitelist. This allows the ECS and ECI instances in the security group to directly access the cloud database.
Configure the security group for instances in a scaling group
The security group for instances in a scaling group is determined by the scaling configuration. You can set the security group when you create or modify the scaling configuration. For more information, see Create a scaling configuration for ECS instances and Create a scaling configuration for ECI instances.
NoteIf the instance configuration source is a launch template, modify the security group in the launch template.
For existing instances in the scaling group: You can change the security group for an ECS instance on the Security Groups tab of the instance details page. You cannot change the security group for an ECI instance. You must recreate the ECI instance.
Configure a security group for the cloud database
Set the same security group for the cloud database that you use for the instances.
Cloud database type | References |
RDS | |
PolarDB | |
Redis | Add the public and private IP addresses of instances in batches using a security group |
MongoDB |
Method 2: Associate a scaling group with cloud databases
After you associate a scaling group with a cloud database, the private IP addresses of the instances in the group are automatically added to the database whitelist. This allows the ECS and ECI instances to directly access the cloud database.
Scaling group already associated with a database
Log on to the Auto Scaling console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where Auto Scaling is activated.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Scaling Groups.
On the Scaling Groups page, find the desired scaling group and click Edit in the Actions column. The Edit Scaling Group dialog box appears.
In the Edit Scaling Group dialog box, find , and click Add Database. Complete the configuration as prompted.
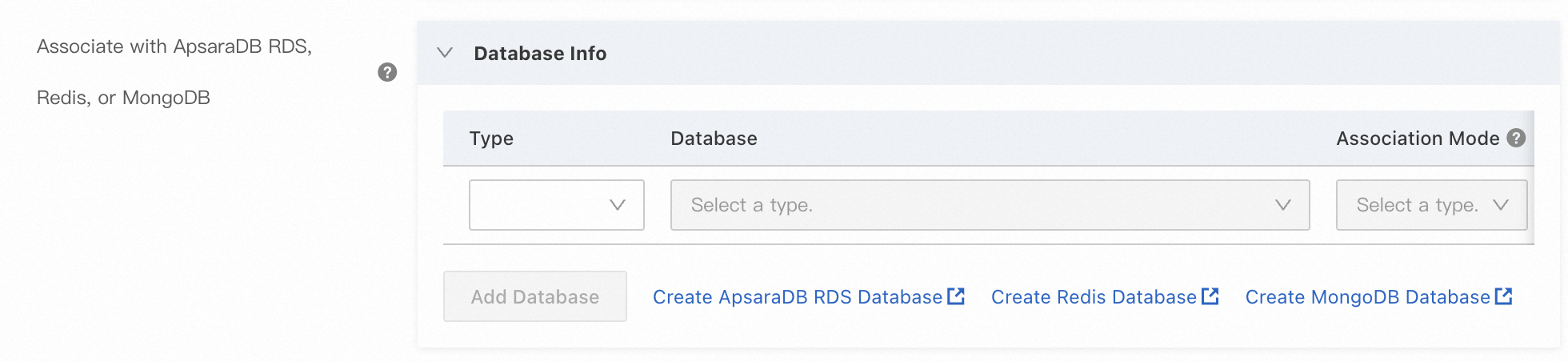
Click OK.
Associate databases when you create a scaling group
When you create a scaling group, under , configure the Associate with ApsaraDB RDS, Redis, or MongoDB parameter.
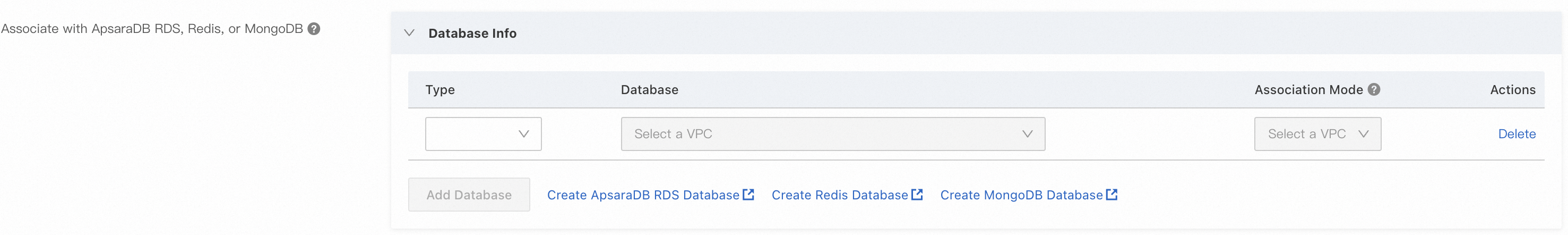
For more information, see Create an ECS scaling group and Create an ECI scaling group.
Method 3: Use a lifecycle hook and an OOS template
You can use a lifecycle hook to place newly scaled-out ECS instances into a pending state. A predefined Operation Orchestration Service (OOS) template then automatically runs to add the private IP addresses of the ECS instances to the cloud database whitelist. This allows the ECS instances to directly access the cloud database. For more information, see the following documents: