Auto Scaling can rapidly deploy a computing cluster containing Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances evenly distributed across multiple zones. It monitors instance status in real time to ensure high cluster availability. This topic describes how to use Auto Scaling to deploy a high-availability ECS cluster, ensuring even distribution across zones, and how to cut costs with preemptible instances
Scenarios
Description
During peak hours in distributed big data computing or AI training, you need to rapidly provision high-availability computing clusters to meet demand.
For example, an online advertising company using machine learning for targeted ads requires significant computing resources during high-traffic periods. When deploying a computing cluster with multiple ECS instances, you may encounter risks such as creation failures caused by lengthy manual processes or insufficient resources, as well as temporary downtime due to zone-level instance failures, which could disrupt your business operations.
Solutions
Auto Scaling enables the automatic deployment of ECS instances across multiple zones, ensuring balanced distribution for high availability. Additionally, you can reduce costs by incorporating preemptible instances, which provide the same functionality at a lower price. This approach optimizes both resource allocation and cost efficiency.

Solution benefits
Using Auto Scaling for a high-availability computing cluster provides these benefits:
Zero O&M costs
Auto Scaling adjusts ECS instances automatically, eliminating manual intervention.
High availability
Auto Scaling's balanced distribution policy evenly allocates ECS instances across multiple zones, preventing scaling failures from resource shortages in any single zone. By default, the instance health check feature ensures all scaling group instances remain available.
Cost-effectiveness
Using preemptible instances as compute nodes significantly lowers resource costs.
Procedure
Before proceeding, assess your business modules per your architecture and set up a scaling group for high-availability needs.
To ensure ECS instances meet your business needs, create a custom image from your application and specify it in the scaling configuration. For more information, see Create a custom image from an instance.
Log on to the Auto Scaling console.
Create a scaling group.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Scaling Groups.
Select your Auto Scaling region in the top navigation bar.
In the upper-left corner of the Scaling Groups page, click Create.
On the Create by Form tab, configure the scaling group and click Create.
The following table describes the parameter settings used in this topic. Any parameters not included retain their default values. For information about how to create a scaling group, see Create scaling groups.
Parameter
Example
Description
Scaling Group Name
test
Enter a name for the scaling group. The name must adhere to the format requirements displayed on the UI.
Type
ECS
Select ECS, which specifies that the scaling group contains ECS instances.
Instance Configuration Source
Create from Scratch
Do not specify the template for automatically creating ECS instances at this stage. After the scaling group is created, you can proceed to create a scaling configuration.
Minimum Number of Instances
100
Specify the minimum number of instances in the scaling group. If the number of instances in the scaling group is smaller than the value of this parameter, Auto Scaling adds ECS instances to the scaling group until the number of ECS instances in the scaling group reaches the lower limit.
Maximum Number of Instances
120
Specify the maximum number of instances in the scaling group. If the number of instances in the scaling group is greater than the value of this parameter, Auto Scaling removes ECS instances from the scaling group until the number of ECS instances in the scaling group does not exceed the upper limit.
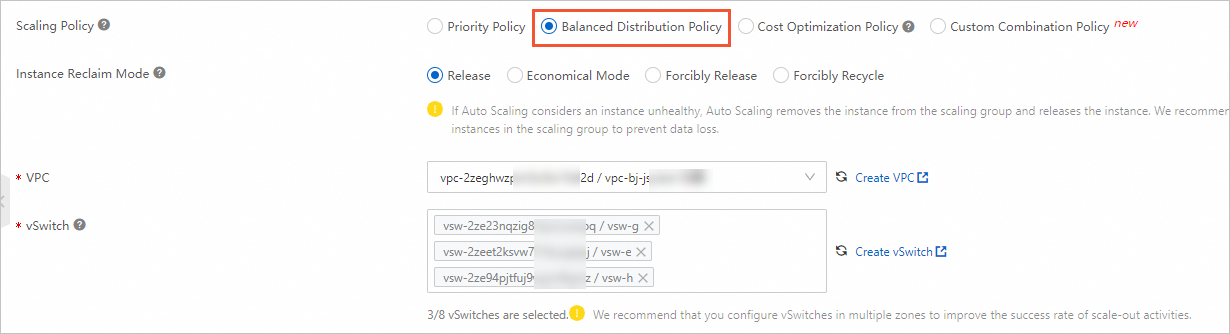
Balanced Distribution Policy
In this example, set this parameter to Balanced Distribution Policy. You must select multiple vSwitches to allow the policy to take effect.
VPC
vpc-2zeghwzptn5zii0w7****
Select a VPC for the ECS instances in the scaling group.
vSwitch
vsw-2ze23nqzig8inprou****
vsw-2zeet2ksvw7f14ryz****
vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaymf****
Select one or more vSwitches for the ECS instances in the scaling group.
For better balance and higher scale-out success, we recommend that you select multiple vSwitches to evenly distribute ECS instances across zones.
Create a scaling configuration.
On the Scaling Groups page, find the desired scaling group and click its ID.
In the upper part of the scaling group details page, click the Instance Configuration Sources tab.
On the Scaling Configurations tab, click Create Scaling Configuration.
On the Create Scaling Configuration page, configure parameters to complete the process for creating a scaling configuration and click Create.
The following table describes the parameter settings used in this topic. Any parameters not included retain their default values. For more information about how to create a scaling configuration, see Create a scaling configuration of the ECS type.
Section
Parameter
Example
Description
Basic Information
Scaling Configuration Name
test
Enter a name for the scaling configuration. The name must adhere to the format requirements displayed on the UI.
Billing method
Preemptible Instance
Auto Scaling is free, but you are charged for the ECS instances launched during scale-out events. In this example, set the Billing Method parameter to Preemptible Instance. For more information, see Billing overview.
Image and Instance
Instance Configuration Mode
Specify Instance Pattern
Select Specify Instance Pattern to configure the specifications of ECS instances.
Instance Attribute Combination
2 vCPUs, 4 GiB of Memory, Enterprise Level
Specify the appropriate number of vCPUs and memory size for ECS instances based on your business requirements.
Select Image
test
Select an image to deploy ECS instances.
For real-world business use, we recommend that you choose the custom image created from your application.
Storage
System Disk
Enterprise SSD (ESSD), 40 GiB, PL0
Select a system disk for ECS instances. We recommend that you configure parameters in this section based on your business requirements.
Network and Security Group
Security Group
sg-bp18kz60mefsicfg****
Select an existing security group. For information about how to create a security group, see Create a security group.
Management Settings
Logon Credentials
Set Later
Select Set Later to manually configure passwords for ECS instances after creation.
Follow the on-screen instructions to enable the scaling group and scaling configuration.
Results
Setting the Minimum Number of Instances to 100 ensures Auto Scaling distributes 100 ECS instances evenly across the specified zones. This optimizes resource costs while maintaining high availability for the computing cluster.
When insufficient resources in one zone cause issues, Auto Scaling deploys ECS instances in other zones to minimize business impact.
When preemptible instances are reclaimed, Auto Scaling replaces them and any unhealthy ECS instances with new ones.
What to do next
If ECS instances are unevenly distributed across zones due to insufficient resources, you can rebalance them. For more information, see Rebalance the distribution of ECS instances.