In scenarios where mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS) is enabled in a Service Mesh (ASM) instance, the sidecar proxies intercept the inbound traffic of all applications in the ASM instance. Therefore, you must pass mTLS authentication to access the port through which Prometheus collects metrics. For critical services, it is essential to have encryption mechanisms in place not only for the communication among services but also for the collection of metrics. This topic describes how to configure a Prometheus instance to collect metrics of applications in an ASM instance over mTLS. In this example, a self-managed Prometheus instance is used.
Prerequisites
A Bookinfo application is deployed. For more information, see Deploy an application in an ASM instance.
Configure a Prometheus instance to collect metrics over mTLS
To enable a Prometheus instance to pass the mTLS authentication of sidecar proxies, the Prometheus instance must use a certificate issued by the root certificate of the ASM instance. To do this, you can use the certificate mounting feature of sidecar proxies. You can use the annotations defined for the pod of Prometheus to enable a sidecar proxy to mount the certificate issued by the ASM control plane to a shared volume. Then, the Prometheus container can obtain the certificate and key by mounting the shared volume. The following section describes the steps:
Add the istio-certs volume to the pod of Prometheus.
volumes: - emptyDir: medium: Memory name: istio-certsAdd the following two
annotationsto the pod of Prometheus:annotations: proxy.istio.io/config: | proxyMetadata: OUTPUT_CERTS: /etc/istio-output-certs sidecar.istio.io/userVolumeMount: '[{"name": "istio-certs", "mountPath": "/etc/istio-output-certs"}]'proxy.istio.io/config: specifies the proxy configuration.proxyMetadata.OUTPUT_CERTSspecifies to store certificates and keys in the/etc/istio-output-certspath.sidecar.istio.io/userVolumeMount: specifies to mount the volume to the/etc/istio-output-certspath of the sidecar proxy container.
Mount the
istio-certsvolume to the/etc/prom-certs/path for the Prometheus container. This way, Prometheus can obtain the certificate and key written by the sidecar proxy from the /etc/prom-certs/ path.volumeMounts: - mountPath: /etc/prom-certs/ name: istio-certsSpecify workloads that initiate requests to capture metrics over mTLS and specify the certification path used by mTLS. mTLS is required only for workloads into which sidecar proxies are injected.
In this example, Prometheus Operator is used.
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: ServiceMonitor metadata: name: productpage labels: app: productpage team: bookinfo spec: selector: matchLabels: app: productpage endpoints: - port: http-9080 interval: 30s path: /metrics scheme: https tlsConfig: caFile: /etc/prom-certs/root-cert.pem certFile: /etc/prom-certs/cert-chain.pem keyFile: /etc/prom-certs/key.pem insecureSkipVerify: trueIn the preceding YAML file, you can use the
labelsfield to specify that the metrics collection is performed on the productpage application. The YAML file also defines the endpoint on which the metrics collection is performed. In the endpoints section, the following mTLS-related configurations are specified:scheme: https: specifies that requests are initiated over HTTPS.tlsConfig: specifies the file paths of the certificate, certificate authority (CA) certificate, and key.insecureSkipVerify: true: Prometheus does not support identity naming in Istio. Therefore, the insecureSkipVerify field is set to true to skip certificate verification, allowing insecure connections.
The preceding configurations enable Prometheus to attach the certificate and key provided by the sidecar proxy and use the certificate and key to initiate requests over mTLS.
Procedure
Step 1: Install Prometheus Operator
Run the following command to clone the source code repository of Prometheus Operator from GitHub to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator.gitUse the kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster and run the following command to install Prometheus Operator:
cd prometheus-operator/ kubectl create -f bundle.yamlRun the following command to query the status of the prometheus-operator pod:
kubectl get podsExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS prometheus-operator-58dd988c9c-qhrrp 2/2 Running 0The output indicates that Prometheus Operator is installed.
Step 2: Configure Prometheus CRs and deploy a Prometheus instance
Save the following YAML file to your computer and name it prometheus.yaml.
The YAML file declares the Prometheus instance and ServiceAccount, ClusterRole, and ClusterRoleBinding that the Prometheus instance depends on. In the Deployment YAML file, you can view the certificate volume mount configurations that are described in the Configure a Prometheus instance to collect metrics over mTLS section.
NoteThe custom resources (CRs) related to Prometheus provided in this topic are for demonstration only. We recommend that you modify the CRs according to the actual production environment.
Use the kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster and run the following command to apply the prometheus.yaml file to the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f prometheus.yamlRun the following command to check whether the Prometheus instance is properly started:
kubectl get podsExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS prometheus-default-0 3/3 Running 0 prometheus-default-1 3/3 Running 0 prometheus-operator-58dd988c9c-qhrrp 2/2 Running 0The output indicates that the prometheus-default-0 and prometheus-default-1 pods are started.
Step 3: Define a ServiceMonitor CR to declare metrics collection rules
Save the following YAML file to your computer and name it service-monitor.yaml.
The YAML file declares the ServiceMonitor API that describes how to collect metrics from a workload. In the YAML file, you can find the settings of the certification path mentioned in the Configure a Prometheus instance to collect metrics over mTLS section and the settings of the
schemefield.NoteThe Prometheus-related CRs provided in this topic are for demonstration only. We recommend that you modify the CRs according to the actual production environment.
iVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: ServiceMonitor metadata: name: productpage labels: app: productpage team: bookinfo spec: selector: matchLabels: app: productpage endpoints: - port: http-9080 interval: 30s path: /metrics scheme: https tlsConfig: caFile: /etc/prom-certs/root-cert.pem certFile: /etc/prom-certs/cert-chain.pem keyFile: /etc/prom-certs/key.pem insecureSkipVerify: trueUse the kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster and run the following command to apply the service-monitor.yaml file to the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl apply -f service-monitor.yaml
Step 4: Map a local port to the corresponding port of Prometheus Operator to view metrics collected by Prometheus
Run the following command to create port forwarding to map the local port 9090 to the port 9090 of the Prometheus Operator service:
kubectl port-forward svc/prometheus-operated 9090Enter
localhost:9090in a browser to open the web UI of Prometheus.
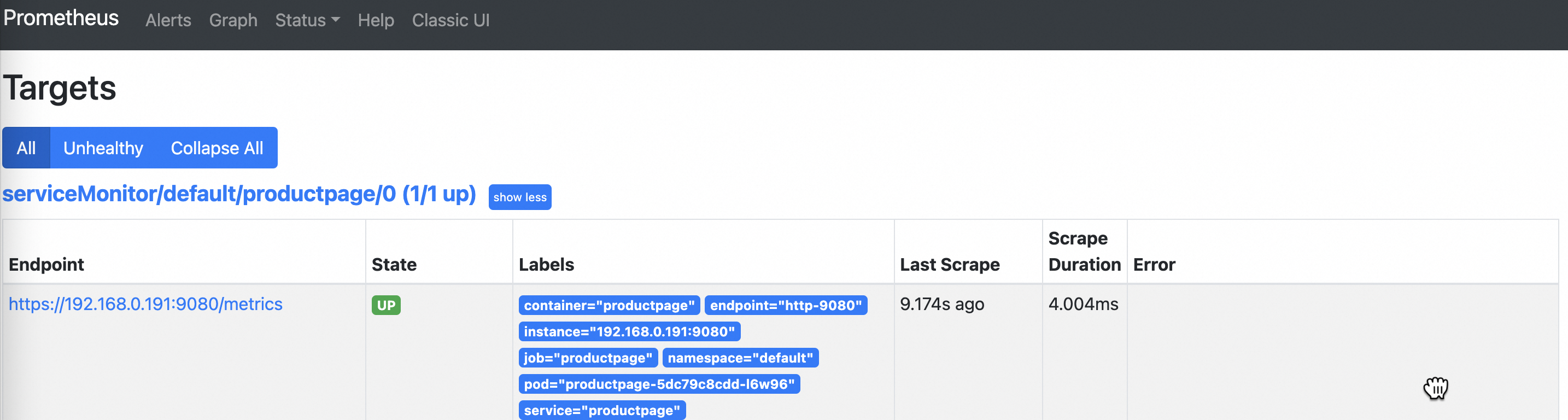
In the top navigation bar, click to view the status of the monitored object.
NoteIf the communication with an object is encrypted by using mTLS, "Unavailable" may appear on the interface. This may be because mTLS is configured but mTLS authentication is not properly configured.
The following figure shows that the State of the monitored object is Up. This indicates that the metrics of the object are captured.
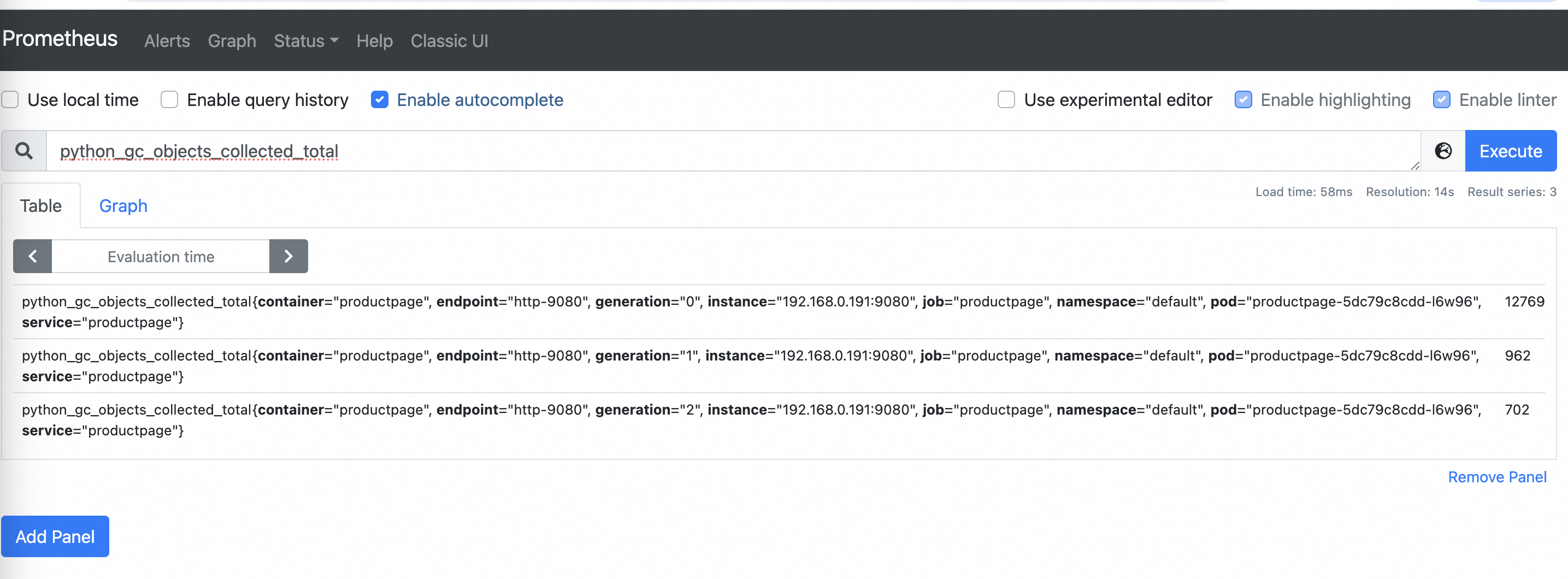
In the top navigation bar, click Graph to return to the query page. Enter
python_gc_objects_collected_totalin the search box and click Execute on the right.The following figure shows the reported metrics.