Service Mesh (ASM) allows you to configure circuit breaking rules for east-west call traffic between specific services and on specific routes. This way, ASM proxies reject requests from upstream services that experience failures, realizing non-intrusive traffic circuit breaking. This topic describes how to use ASMCircuitBreaker CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs) to configure circuit breaking rules for east-west call traffic.
Background information
Traffic circuit breaking is an overload protection mechanism, which is primarily used to prevent system crashes due to traffic bursts in a short period of time. In the case of east-west calls between cloud-native services, a failure of one service (such as slow responses or increased failure rates) may lead to cascading failures across a series of services in the trace.
You can configure circuit breaking rules for east-west call traffic between services to reject requests from upstream services when the failure rate or the number of response timeouts reaches the corresponding threshold. This protects upstream services and effectively prevents faults from affecting the entire trace and causing the entire system to crash.
After you configure a circuit breaking rule, each ASM proxy calculates the failure rate or the number of response timeouts based on the requests it receives. Therefore, for the same faulty upstream service, the time points at which circuit breaking occurs at different ASM proxies may be slightly different.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance of Enterprise Edition or Ultimate Edition is created, and the version of the ASM instance is V1.14.3 or later. For more information, see Create an ASM instance.
The sample applications, sleep and httpbin, are deployed. For more information, see Deploy the HTTPBin application in the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster on the data plane. and Deploy the sleep service in the cluster on the data plane.
Step 1: Configure request path routing for east-west traffic between the sleep and httpbin services
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Use one of the following methods to create a virtual service:
Use the ASM console
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create.
Select a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list and enter a name for the virtual service to be created in the Name field. In the Gateways section, turn on the switch next to Apply To All Sidecars.
In the Hosts section, click Add Host to add the httpbin service.
In the HTTP Route section, click Add Route and configure parameters as shown in the following figure.

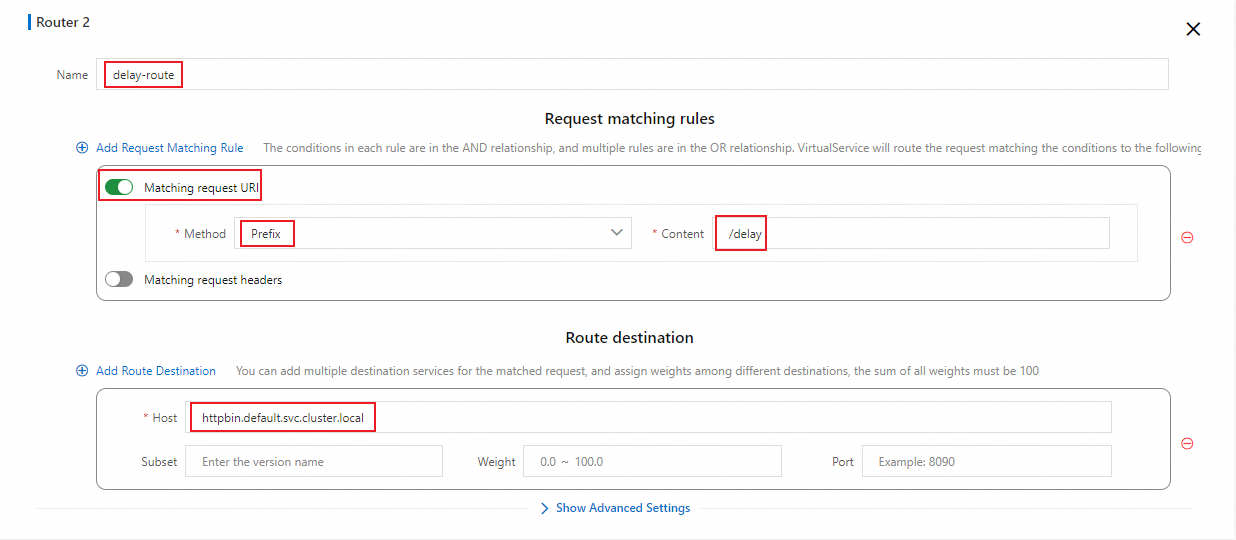
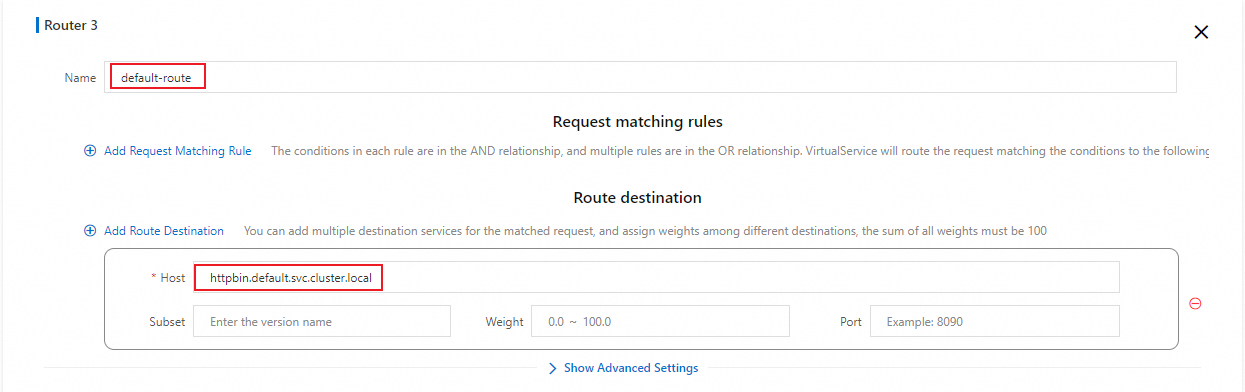
Use a YAML template
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create from YAML.
Copy the content shown in the following code block to the YAML code editor and click Create.
The following table describes the relationship between requests and paths.
Request path
Match type
Route name
Description
/status/500Exact match
error-routeA status code 500 is always returned.
/delayPrefix match
delay-routeA status code 200 is returned after the specified time elapses. For details about how to use /delay requests, see delay.
/*Any path
default-routeThe default route.
Step 2: Configure circuit breaking rules
This section describes how to configure circuit breaking based on the error rate and the number of slow requests. It also describes test results.
Configure circuit breaking based on the error rate
Error rate-based circuit breaking means that circuit breaking is triggered when the server response error rate detected in a given time window exceeds the specified threshold.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the page that appears, click Create. On the Create page, copy the content shown in the following code block to the YAML code editor and click Create.
The following table describes the parameters in the circuit breaking configuration.
Parameter
Description
workloadSelector.labels
The downstream service workload. In this example, the downstream service workload is the sleep service. Therefore, the
app: sleeplabel is used to select the sleep service.break_duration
The duration between the time when the circuit breaking is triggered and the time when access to the httpbin service is restored. In this example, the value is set to 60s.
window_size
The time window in which the request error rate is detected. In this example, the value is set to 10s. It indicates that if the error rate of requests on the route exceeds the specified threshold within 10 seconds, circuit breaking is triggered and requests are rejected.
error_percent
The error rate of requests in the specified time window that is used to determine whether circuit breaking is triggered. In this example, the value is set to 60. It indicates that if the error rate of requests on the route exceeds 60% within the time window of 10 seconds, circuit breaking is triggered and requests are rejected.
min_request_amount
The minimum number of requests required to trigger circuit breaking within the time window. You can configure this parameter to prevent circuit breaking from being mistakenly triggered due to a small number of requests.
In this example, the value is set to 5. It indicates that circuit breaking is triggered only when more than five requests are sent in the specified route within the time window of 10 seconds and the error rate exceeds 60%.
custom_response
The custom response content that is returned when the ASM proxies reject requests after circuit breaking is triggered.
The body parameter is set to
error break!. It indicates that the custom response body iserror break!.The header_to_add parameter is set to
x-envoy-overload: 'true'. It indicates thatx-envoy-overload: 'true'is added to the response headers of the rejected requests after circuit breaking is triggered.The status_code parameter is set to
499. It indicates that the response code499is returned for requests after circuit breaking is triggered.
match.vhost
The route. The route must match the route declared in the virtual service.
name: It must be set to the domain name of the upstream service in the trace. In this example, the value is set to the domain name of the httpbin service,
httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local. The httpbin service is the upstream service of the sleep service.port: It must be set to the service port of the upstream service. In this example, the value is set to the service port of the httpbin service,
8000.route.name_match: It must be set to the route name configured in the virtual service. The circuit breaking configuration takes effect on the corresponding route. In this example, the value is set to
error-routeconfigured in Step 2. The status code 500 is always returned for requests that match this route. This ensures that circuit breaking is triggered.
Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster and run the following command:
for i in {1..100}; do kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl httpbin:8000/status/500 -I | grep 'HTTP'; echo ''; sleep 0.1; done;Expected output:
The output indicates that when the sixth request is sent, circuit breaking is triggered. After circuit breaking is triggered, the status code 499 is returned for subsequent requests. Circuit breaking takes effect for 60 seconds.
During circuit breaking, you can run the following command to access another path of the httpbin service:
for i in {1..100}; do kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl httpbin:8000/status/503 -I | grep 'HTTP'; echo ''; sleep 0.1; done;Expected output:
The output indicates that requests sent to another path of the httpbin service are not affected by the circuit breaking configuration for the
error-routeroute and can be normally responded to by the httpbin service.
Configure circuit breaking based on the number of slow requests
Slow request-based circuit breaking means that circuit breaking is triggered when the number of slow requests detected in a given time window exceeds the specified threshold. Requests whose response time exceeds a threshold within the specified time window are called slow requests.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the page that appears, click Create. On the Create page, copy the content shown in the following code block to the YAML code editor and click Create.
The following table describes the parameters in the circuit breaking configuration.
Parameter
Description
workloadSelector.labels
The downstream service workload. In this example, the downstream service workload is the sleep service. Therefore, the
app: sleeplabel is used to select the sleep service.break_duration
The duration between the time when the circuit breaking is triggered and the time when access to the httpbin service is restored. In this example, the value is set to 60s.
window_size
The time window in which the request error rate is detected. In this example, the value is set to 10s. It indicates that if the number of slow requests on the route exceeds the specified threshold within 10 seconds, circuit breaking is triggered and requests are rejected.
slow_request_rt
The baseline response time that is used to determine slow requests. In this example, the value is set to 0.5s. It indicates that requests whose response time exceeds 0.5s are considered as slow requests.
max_slow_requests
The maximum number of slow requests that are allowed in the time window before circuit breaking is triggered. In this example, the value is set to 5. It indicates that if more than five slow requests occur within the time window of 10 seconds, circuit breaking is triggered and requests are rejected.
min_request_amount
The minimum number of requests required to trigger circuit breaking within the time window. You can configure this parameter to prevent circuit breaking from being mistakenly triggered due to a small number of requests.
In this example, the value is set to 5. It indicates that circuit breaking is triggered only when more than 5 requests are sent on the specified route within the time window of 10 seconds and the number of slow requests exceeds 5.
custom_response
The custom response content that is returned when the ASM proxies reject requests after circuit breaking is triggered.
The body parameter is set to
error break!. It indicates that the custom response body iserror break!.The header_to_add parameter is set to
x-envoy-overload: 'true'. It indicates thatx-envoy-overload: 'true'is added to the response headers of the rejected requests after circuit breaking is triggered.The status_code parameter is set to
498. It indicates that the response code498is returned for requests after circuit breaking is triggered.
match.vhost
The route. The route must match the route declared in the virtual service.
name: It must be set to the domain name of the upstream service in the trace. In this example, the value is set to the domain name of the httpbin service,
httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local. The httpbin service is the upstream service of the sleep service.port: It must be set to the service port of the upstream service. In this example, the value is set to the service port of the httpbin service,
8000.route.name_match: It must be set to the route name configured in the virtual service. The circuit breaking configuration takes effect on the corresponding route. In this example, the value is set to
delay-routeconfigured in Step 2. Requests that match this route can be manually configured to respond at a time more than 0.5 seconds. This ensures that circuit breaking is triggered.
Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster and run the following command:
for i in {1..100}; do kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl httpbin:8000/delay/1 -I | grep 'HTTP'; echo ''; sleep 0.1; done;Expected output:
The output indicates that when the sixth request is sent, circuit breaking is triggered. After circuit breaking is triggered, the status code 498 is returned for subsequent requests. Circuit breaking takes effect for 60 seconds.
During circuit breaking, you can run the following command to test error rate-based circuit breaking that is configured in Step 3:
for i in {1..100}; do kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl httpbin:8000/status/500 -I | grep 'HTTP'; echo ''; sleep 0.1; done;Expected output:
The preceding output indicates that circuit breaking rules configured on different routes do not affect each other. You can flexibly configure circuit breaking rules for east-west service call traffic with different characteristics to implement circuit breaking based on your business requirements.
Related operations
View metrics related to service-level circuit breaking
For ASM instances of V1.22.6.28 and later, you can view the metrics related to service-level circuit breaking configured by using ASMCircuitBreaker CRDs.
Metric | Type | Description |
envoy_asm_circuit_breaker_total_broken_requests | Counter | The total number of requests that are rejected due to circuit breaking |
You can configure proxyStatsMatcher of a sidecar proxy to report related metrics.
After you select proxyStatsMatcher, select Regular Expression Match and set the value to
.*circuit_breaker.*. For more information, see proxyStatsMatcher.Redeploy the httpbin service to make the new proxy configuration take effect. For more information, see Redeploy workloads.
Perform Step 1 and Step 2 again to reconfigure circuit breaking.
Run the following command to view the service-level circuit breaking metrics of the httpbin service:
kubectl exec -it deploy/httpbin -c istio-proxy -- curl localhost:15090/stats/prometheus|grep asm_circuit_breakerExpected output:
# TYPE envoy_asm_circuit_breaker_total_broken_requests counter envoy_asm_circuit_breaker_total_broken_requests{cluster="outbound|8000||httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local",uuid="af7cf7ad-67e8-49c5-b5fe-xxxxxxxxx"} 1430 # TYPE envoy_total_asm_circuit_breakers gauge envoy_total_asm_circuit_breakers{} 1
Configure metric collection and alerts for service-level circuit breaking
After you configure metrics related to service-level circuit breaking, you can configure settings to collect the metrics to Prometheus and configure alert rules based on key metrics. This way, alerts can be generated when circuit breaking occurs. The following section demonstrates how to configure metric collection and alerts for service-level circuit breaking. In this example, Managed Service for Prometheus is used.
In Managed Service for Prometheus, you can connect the cluster on the data plane to the Alibaba Cloud ASM component or upgrade the Alibaba Cloud ASM component to the latest version. This ensures that the exposed metrics related to circuit breaking can be collected by Managed Service for Prometheus. For more information about how to integrate components into ARMS, see Component management. (If you have configured settings to use a self-managed Prometheus instance to collect metrics of an ASM instance by referring to Monitor ASM instances by using a self-managed Prometheus instance, you do not need to perform this step.)
Create an alert rule for service-level circuit breaking. For more information, see Use a custom PromQL statement to create an alert rule. The following example demonstrates how to specify key parameters for configuring an alert rule. For more information about how to configure other parameters, see the preceding documentation.
Parameter
Example
Description
Custom PromQL Statements
(sum by(cluster, namespace) (increase(envoy_asm_circuit_breaker_total_broken_requests[1m]))) > 0
The increase statement queries the number of requests that are rejected due to circuit breaking in the last one minute. The number of requests is grouped by the namespace and name of the service that triggers circuit breaking. An alert is reported when the number of requests that are rejected due to circuit breaking within one minute is greater than 0.
Alert Message
Service-level circuit breaking occurred. Namespace: {{$labels.namespace}}, Service that triggers circuit breaking: {{$labels.cluster}}. The number of requests that are rejected due to circuit breaking within the current one minute: {{ $value }}
The alert information shows the namespace of the service that triggers the circuit breaking, the service name, and the number of requests that are sent to the service but are rejected due to circuit breaking in the last one minute.