Service Mesh (ASM) allows you to encapsulate Istio native security resources and provides the security policy feature. You can complete security configurations with ease in common scenarios. ASM integrates with Open Policy Agent (OPA). You can use OPA to define access control policies to implement fine-grained access control on your applications. This topic describes how to use an ASM security policy to access an OPA engine outside pods.
Prerequisites
A Kubernetes managed cluster is added to an ASM instance whose version is 1.15.3.25 or later. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance and Update an ASM instance.
The HTTPBin application is deployed and can be accessed. For more information, see Deploy the httpbin application.
Automatic sidecar proxy injection is enabled for the default namespace. For more information, see Enable automatic sidecar proxy injection.
Feature description
By default, OPA is deployed in sidecar mode in ASM. When you restart an application pod after you enable OPA, ASM injects an OPA container into the application pod. After that, all requests to the application container are authenticated by OPA. In sidecar mode, the Istio proxy accesses OPA within the same pod. Therefore, the latency is low, and this mode is suitable for latency-sensitive services.
However, the sidecar mode has the following disadvantages: A large number of resources are occupied. The pod needs to be restarted when an OPA container is injected into the pod. Requests cannot access applications in flexible manners. OPA in centralized mode can be complementary to OPA in sidecar mode in these aspects. OPA in centralized mode boasts the following advantages: The resource usage is lower. The pod does not need to be restarted for OPA container deployment and request access to applications. You can use an OPA policy for specific requests to an application. This topic describes how to deploy OPA in centralized mode for the authentication of requests to an application.
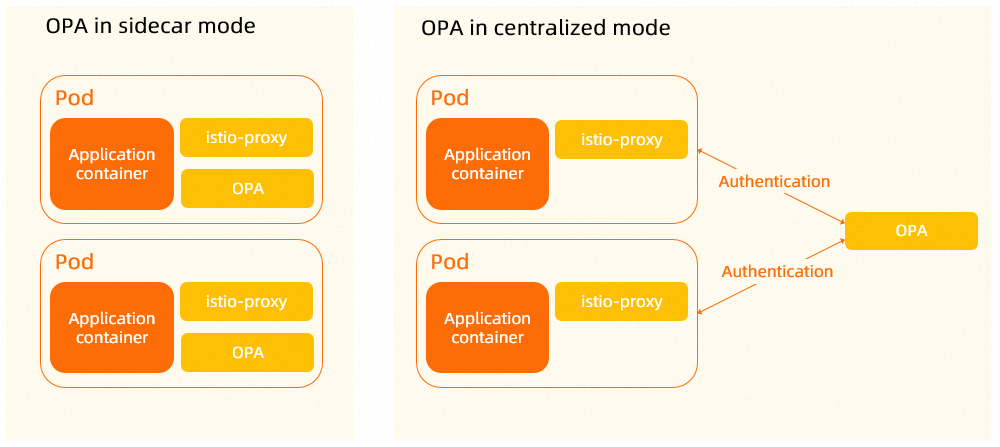
Step 1: Deploy OPA
Create a file named asm-opa.yaml and copy the following content to the file.
The YAML code deploys an OPA Service, an OPA Deployment, and a Secret.
Kind
Description
Deployment
Replace the region ID in the image
registry-vpc.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs/opa:0.46.1-istio-3-staticwith the ID of the region where your cluster is deployed.By default, logging is enabled for the OPA engine (
--set=decision_logs.console=true). This facilitates debugging.
Secret
The Secret defines the following OPA policies:
If the path of a request is
health, the request is allowed.If the method of a request is
HEAD, the request is allowed.If the user name of a request is
alice, the request is allowed.NoteThe user name is carried in the
Authorizationheader of the request, in the form ofAuthorization: Basic ${user name: Base64-encoded password string}.
Use kubectl to connect to the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster based on the information in the kubeconfig file and run the following command to deploy OPA:
kubectl apply -f asm-opa.yaml
Step 2: Associate an ASM security policy with OPA
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the ASMSecurityPolicy page, click Create. In the Create ASMSecurityPolicy dialog box, click the Custom Authorization Service card and click OK.
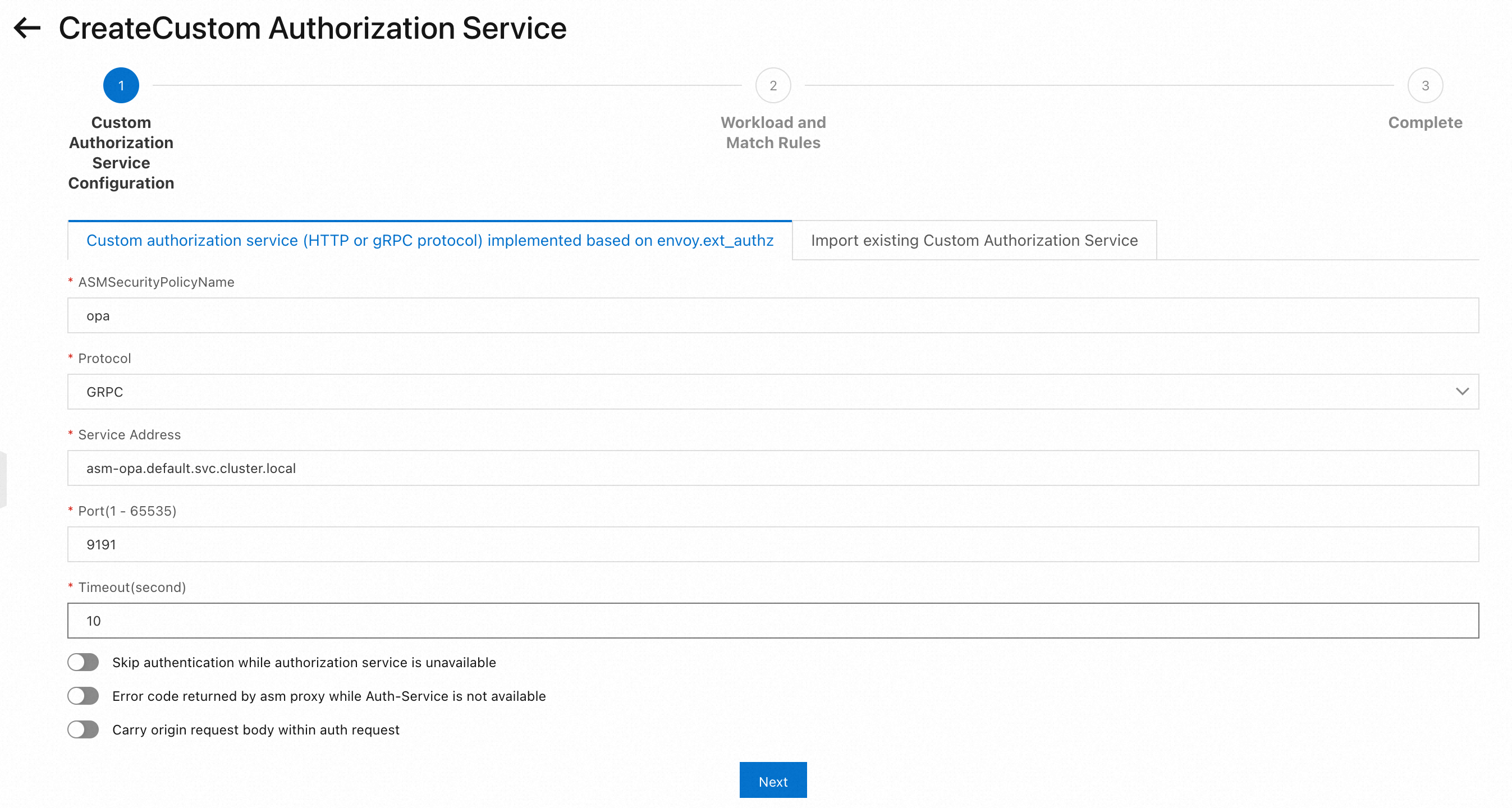
Configure the custom authorization service.
On the CreateCustom Authorization Service page, configure the information about the OPA authorization service that is deployed in Step 1 and click Next.
In the Workload and Match Rules step, click Add Workload Group. In the New Workload Group dialog box, set Workload Group Name and click Add Workload.
In the Add Workload dialog box, select Workload Scope, set Namespace to default, and then set Workload Type to Service. Then, select httpbin in the Select workloads section, click the
 icon, and then click OK.
icon, and then click OK.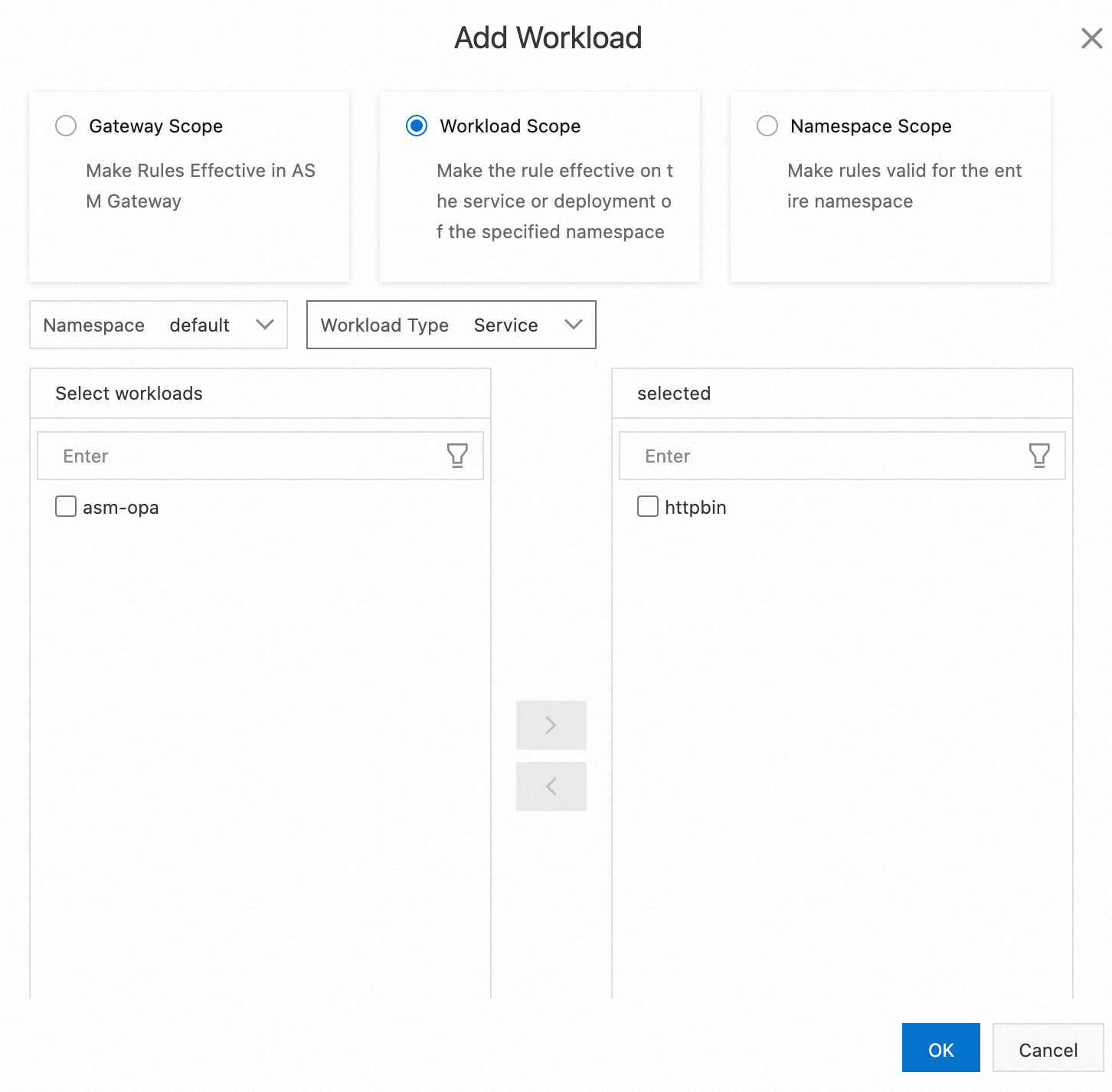
In the Match Rule List section of the New Workload Group dialog box, set Match Mode to The selected request must be authenticated and Matching Rules to Custom Matching Rules. Turn on the Path switch, enter
/status/*in the field, and then click OK.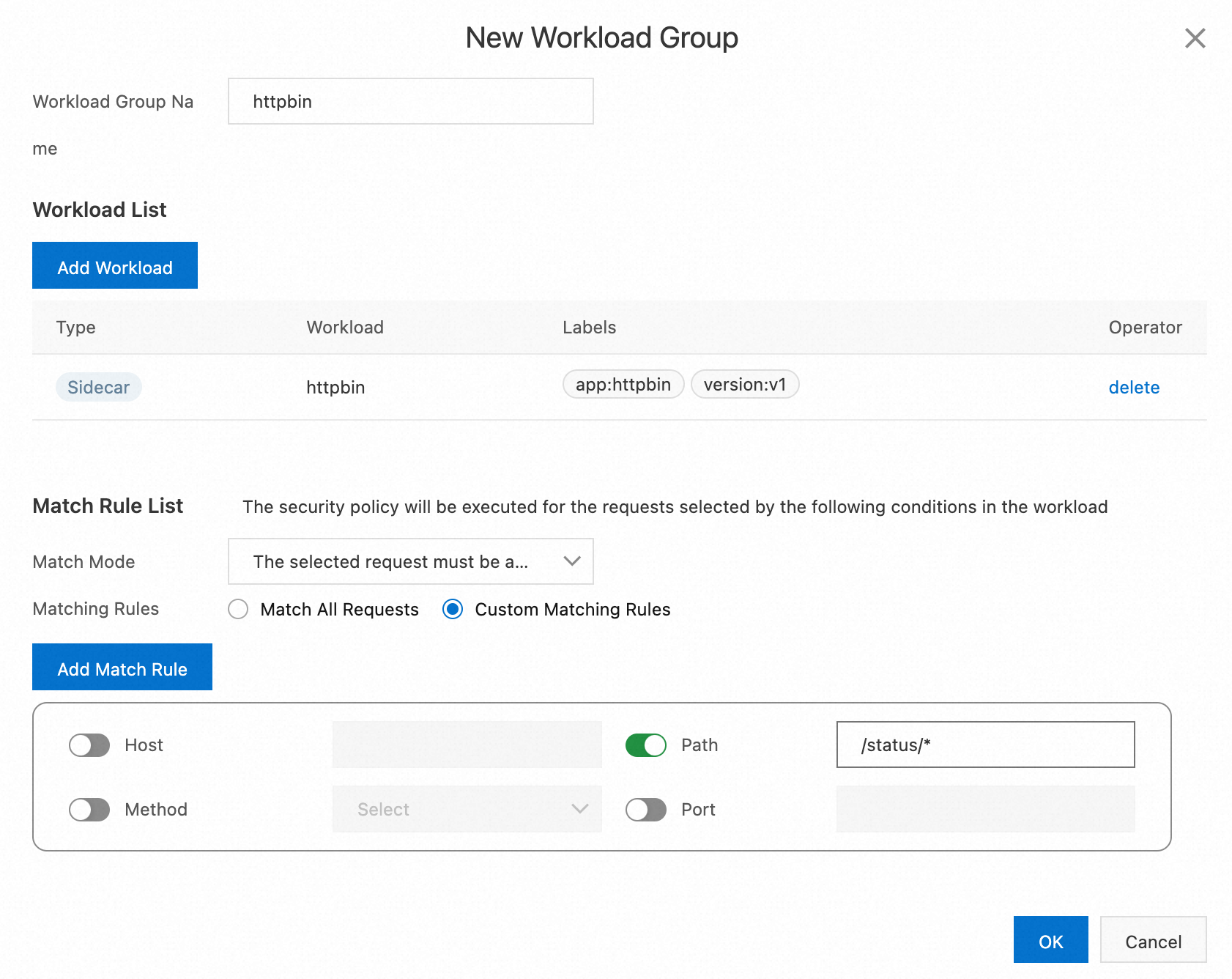
In the Workload and Match Rules step, click submit.
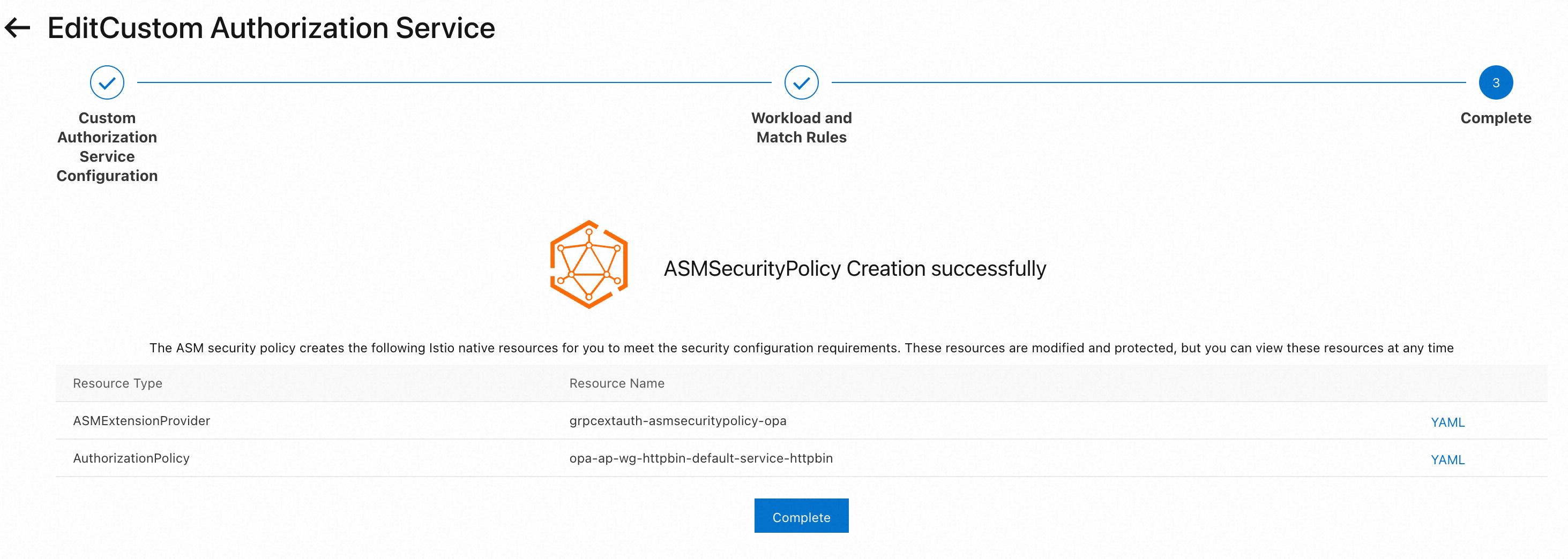
The following figure shows the page after the security policy is created and associated with OPA.
Step 3: Test the access to the HTTPBin application
Run the following command to access the
/path:curl ${IP address of the ASM gateway}/ -I -X GETExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK server: istio-envoy date: Tue, 25 Jul 2023 08:30:58 GMT content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 content-length: 9593 access-control-allow-origin: * access-control-allow-credentials: true x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 2The output indicates that authentication is not required for the access requests to the path.
Run the following command to access the
/status/201path without valid parameters:curl ${IP address of the ASM gateway}/status/201 -I -X GETExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden date: Tue, 25 Jul 2023 08:31:18 GMT server: istio-envoy content-length: 0 x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 1The output indicates that the access request without valid parameters is rejected.
Run the following command to access the
/status/201path with valid parameters:curl ${IP address of the ASM gateway}/status/201 -I -X GET --user alice:testpasswordExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created server: istio-envoy date: Tue, 25 Jul 2023 08:31:38 GMT content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 access-control-allow-origin: * access-control-allow-credentials: true content-length: 0 x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3The output indicates that the access request with valid parameters is allowed.
Step 4: Update the OPA policy
Call the HTTP API of the OPA engine to update the OPA policy.
Run the following commands to allow only the user named bob to access the HTTPBin application over HTTP and reject the user named alice from accessing the HTTPBin application over HTTP.
kubectl exec deployment/httpbin -c istio-proxy -- curl asm-opa:8181/v1/policies/policy/policy.rego -XPUT --data-binary 'package asm.authz import future.keywords import input.attributes.request.http as http_request import input.parsed_path default allow := false allow if { parsed_path[0] == "health" } allow if { http_request.method == "HEAD" } allow if { user_name == "bob" } user_name := parsed if { [_, encoded] := split(http_request.headers.authorization, " ") [parsed, _] := split(base64url.decode(encoded), ":") }'Run the following command to access the HTTPBin application by using the user named bob:
curl ${IP address of the ASM gateway}/status/201 -I -X GET --user bob:testpasswordExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created server: istio-envoy date: Tue, 25 Jul 2023 08:32:16 GMT content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 access-control-allow-origin: * access-control-allow-credentials: true content-length: 0 x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3The output indicates that the access of the user named bob is successful.
Run the following command to access the HTTPBin application by using the user named alice:
curl ${IP address of the ASM gateway}/status/201 -I -X GET --user alice:testpasswordExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden date: Tue, 25 Jul 2023 08:32:49 GMT server: istio-envoy content-length: 0 x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 1The output indicates that the access of the user named alice is forbidden.