A fallback mechanism provides an alternative call path when a service call fails. When a microservice fails or cannot be used, a fallback mechanism calls an alternative service to process requests so as to ensure the stability and availability of the entire system. For example, when a service endpoint is unavailable, a fallback mechanism can be used to forward requests to an alternative service to ensure that client requests can be processed without errors or interruptions. Service Mesh (ASM) allows you to define fallback parameters in a virtual service so that a fallback can be performed when a requested service fails. This topic describes how to use an ASM fallback mechanism.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance of Enterprise Edition or Ultimate Edition is created, and its version is 1.17.2.22 or later. For more information, see Create an ASM instance.
NoteIf the version of your ASM instance is earlier than 1.17, update the ASM instance to 1.17.2.22 or later, or submit a ticket to obtain technical support. For more information about how to update an ASM instance, see Update an ASM instance.
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster is added to the ASM instance. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance.
A sample application named Bookinfo is deployed. For more information, see Deploy an application in an ASM instance.
The versions of the sidecar proxies on the data plane must be 1.17 or later.
NoteYou can view the version of the sidecar proxy in each application pod on the Instances Status page in the ASM console. For more information, see Upgrade management.
Configuration description
In this example, the reviews service in the Bookinfo application is used. When the productpage service accesses the reviews service that has three versions v1, v2, and v3, if v3 is unavailable, a fallback is performed to access the reviews service of v2 and no HTTP 503 status code is returned.
You can click Configuration file to download the YAML file that is used in this example.
Step 1: Access the Bookinfo application
Create a reviews.yaml file that contains the following content to declare the v1, v2, and v3 versions of the reviews service:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: DestinationRule metadata: name: reviews spec: host: reviews subsets: - name: v1 labels: version: v1 - name: v2 labels: version: v2 - name: v3 labels: version: v3Use kubectl to connect to the ASM instance based on the information in the KubeConfig file, and then run the following command to deploy a destination rule:
kubectl apply -f reviews.yamlUse either of the following methods to obtain the IP address of the ingress gateway:
Method 1: Run the following command to obtain the IP address of the ingress gateway:
kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'Method 2: Obtain the IP address of the ingress gateway from the Ingress Gateway page in the ASM console. For more information, see Query the IP address of the ASM instance's ingress gateway.
Visit
http://${YourGatewayIp}/productpagein a browser.${YourGatewayIp}is the IP address of the ingress gateway that is obtained in the previous step. You can determine the version of the reviews service based on the value of Reviews served by or based on the stars. The v1 version has no stars, the v2 version has black stars, and the v3 version has red stars.For example, in the following figure, the value reviews-v2 indicates the v2 version with black stars.
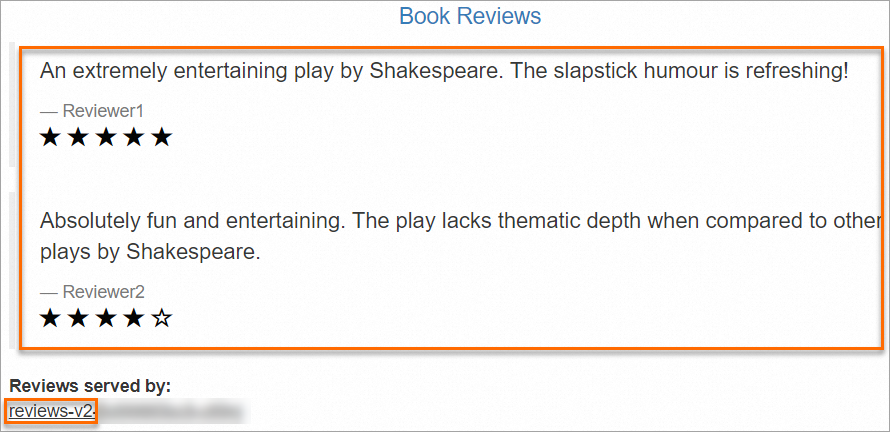
Keep refreshing the page. You can see that service requests are balanced to the v1, v2, and v3 versions of the reviews service.
Step 2: Define routing and fallback rules for accessing the reviews service
Create a reviews-route-fallback-sample1.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: reviews-route namespace: default spec: hosts: - reviews http: - route: - destination: host: reviews subset: v3 fallback: target: host: reviews subset: v2Use kubectl to connect to the ASM instance based on the information in the KubeConfig file, and then run the following command to deploy routing and fallback rules for accessing the reviews service:
kubectl apply -f reviews-route-fallback-sample1.yamlVisit
http://${YourGatewayIp}/productpagein a browser and keep refreshing the page.You can see that service requests have always been routed to the v3 version of the reviews service.

Run the following command to simulate a failure in reviews-v3 by changing the number of reviews-v3 instances to 0:
kubectl scale deployment reviews-v3 --replicas=0Visit
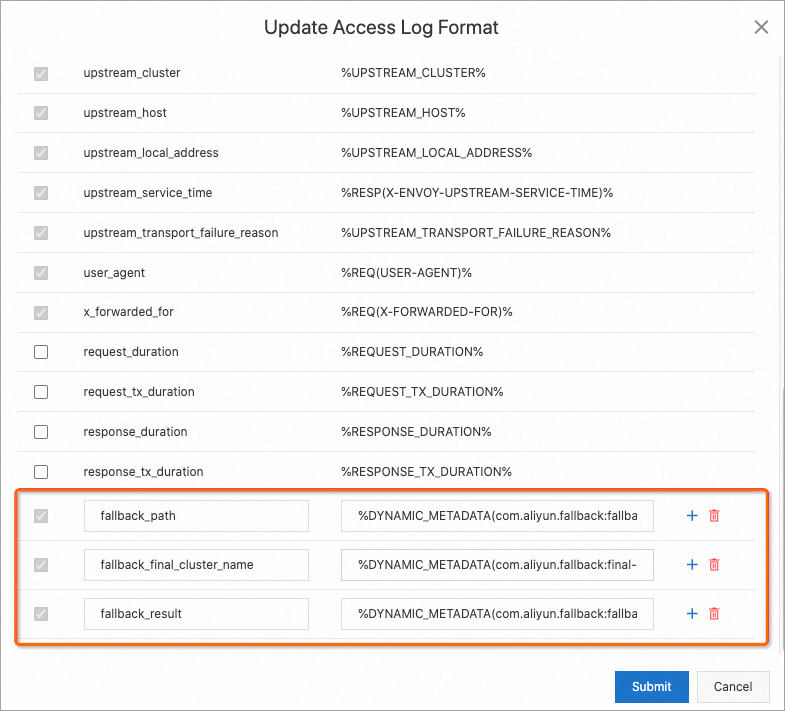
http://${YourGatewayIp}/productpagein a browser and keep refreshing the page.You can see that service requests fall back to the v2 version of the reviews service. You can add fallback-related fields to the custom access log format and then view the logs to determine whether a fallback is performed.
Step 3: Configure a fallback rule under weighted routes
Run the following command to set reviews-v3 to be available:
kubectl scale deployment reviews-v3 --replicas=1Create a reviews-route-fallback-sample2.yaml file that contains the following content to modify the definition of reviews-route:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: reviews-route namespace: default spec: hosts: - reviews http: - route: - destination: host: reviews subset: v3 fallback: target: host: reviews subset: v2 weight: 50 - destination: host: reviews subset: v2 fallback: target: host: reviews subset: v1 weight: 50 retries: attempts: 0Run the following command to deploy new routing and fallback rules for the reviews service:
kubectl apply -f reviews-route-fallback-sample1.yamlVisit
http://${YourGatewayIp}/productpagein a browser and keep refreshing the page.You can see that requests are routed to reviews-v2 and reviews-v3 at a ratio of 50:50. To allow you to easily observe the result, retry is disabled in this example.
Run the following command to change the number of reviews-v3 instances to 0 and check whether the fallback rule of reviews-v3 is as expected:
kubectl scale deployment reviews-v3 --replicas=0Keep refreshing the page. You can see that requests have always been routed to reviews-v2, which is as expected.
Run the following command to change the number of reviews-v2 instances to 0:
kubectl scale deployment reviews-v2 --replicas=0Keep refreshing the page. Pages similar to the following page appear, which indicate that the productpage service fails to access the reviews service. The probability that this page appears is 50%, and the other 50% probability is that requests are routed to reviews-v2. Because reviews-v2 is unhealthy, the requests actually fall back to reviews-v1.
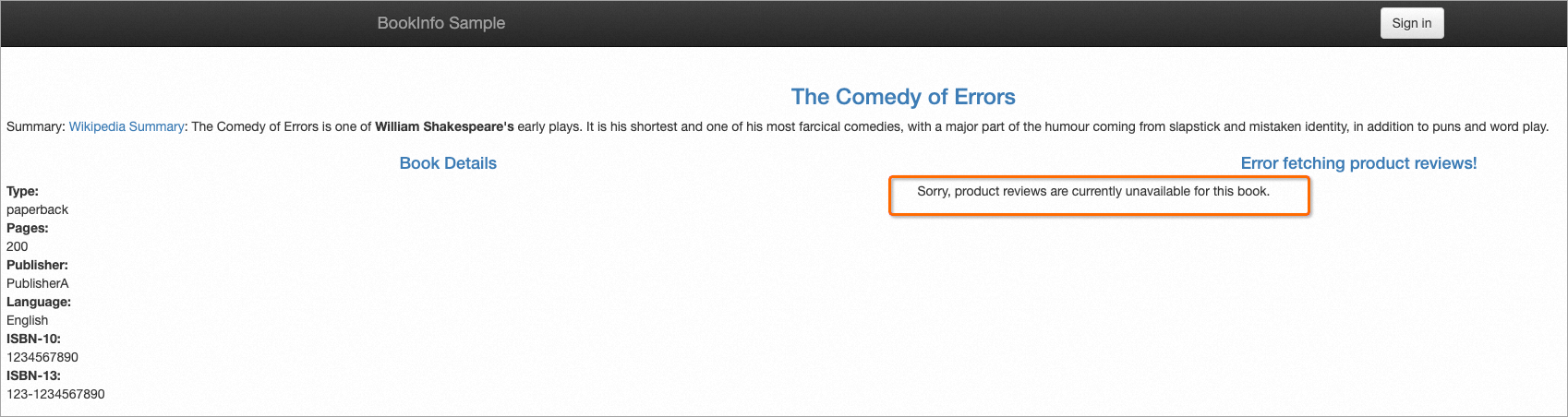
Run the following command to query the logs:
kubectl logs -f deployment/productpage-v1 -c istio-proxy --tail=10Expected output:
{ "authority":"reviews:9080", "authority_for":"reviews:9080", "bytes_received":"0", "bytes_sent":"19", "downstream_local_address":"192.168.255.46:9080", "downstream_remote_address":"172.16.0.252:47738", "duration":"0", "fallback_path":"outbound|9080|v3|reviews.default.svc.cluster.local:outbound|9080|v2|reviews.default.svc.cluster.local", "fallback_final_cluster_name":"-", "fallback_result":"fallback cluster is unhealthy", "istio_policy_status":"-", "method":"GET", "path":"/reviews/0", "protocol":"HTTP/1.1", "request_id":"b207a764-b6d7-4ef8-bc71-59f264c3****", "requested_server_name":"-", "response_code":"503", "response_flags":"UH", "route_name":"-", "start_time":"2023-05-30T07:32:08.999Z", "trace_id":"a40c32a7b2cf****", "upstream_cluster":"outbound|9080|v3|reviews.default.svc.cluster.local", "upstream_host":"-", "upstream_local_address":"-", "upstream_service_time":"-", "upstream_transport_failure_reason":"-", "user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/113.0.X.X Safari/537.36", "x_forwarded_for":"-" }You can see that logs similar to the above HTTP 503 status code exist in productpage-v1. Based on the weighted routing configuration of reviews-route, the productpage service has a 50% probability of requesting reviews-v3. Because reviews-v3 is unavailable, the sidecar proxy (istio-proxy) attempts a fallback from reviews-v3 to reviews-v2 based on the fallback rule. The requests are sent to reviews-v3 because reviews-v2 is unhealthy. You can confirm the fallback based on the field
"upstream_cluster":"outbound|9080|v3|reviews.default.svc.cluster.local".