You can use traffic lanes in permissive mode to isolate versions of an application and route traffic to different lanes based on a specific ratio. Your application must add headers that can be transparently transmitted throughout the corresponding traces in requests and such headers have different values. These request headers are called the end-to-end (E2E) pass-through request headers. In this example, baggage headers are used as the E2E pass-through request headers. When services in a lane call each other, if the service to be called does not exist in the lane, requests are forwarded to the same service in the baseline lane. This feature ensures the integrity of traces and simplifies traffic management.
Before you get started, make sure that you have read and understood the Use traffic lanes in permissive mode to manage end-to-end traffic topic and related content.
Scenario description
In this example, three services (mocka, mockb, and mockc) and three lanes (s1, s2, and s3) are used to simulate traces. s1 is the baseline lane that contains all three services of v1. s2 contains only mocka and mockc of v2. s3 contains only mockb of v3. First, use the auto-instrumentation capability of OpenTelemetry to enable the pods for services to pass through baggage headers. Then, create three lanes in permissive mode and configure traffic routing weights to route traffic at a specific ratio.
Step 1: Deploy sample services
Enable automatic sidecar proxy injection for the default namespace. For more information, see Manage global namespaces.
NoteFor more information about automatic sidecar proxy injection, see Enable automatic sidecar proxy injection.
Create a mock.yaml file that contains the following content:
Annotations
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-java: "true"andinstrumentation.opentelemetry.io/container-names: "default"are added to each service pod to declare that the corresponding service is implemented in Java, and the OpenTelemetry Operator is required to auto-instrument the container nameddefault.Run the following command to deploy the services:
kubectl apply -f mock.yamlBased on the auto-instrumentation mechanism of OpenTelemetry, pods for services can automatically pass through baggage headers in traces.
Step 2: Create a lane group and corresponding lanes
Create a lane group.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Traffic Lane page, click Create Swimlane Group. In the Create Swimlane Group panel, configure the required parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name of swim lane group
For this example, enter test.
Istio gateway for an ingress gateway
Select ingressgateway.
Lane Mode
Select Permissive Mode.
Pass-through Mode of Trace Context
Select Pass Through Baggage Header.
Routing Request Header
Enter x-asm-prefer-tag.
Swimlane Services
Select the cluster in which the mocka, mockb, and mockc services reside from the Kubernetes Clusters drop-down list and default from the Namespace drop-down list. Select the mocka, mockb, and mockc services in the list, and click the
 icon to add these services to the selected section.
icon to add these services to the selected section.
Create lanes named s1, s2, and s3 and bind the s1 lane to the v1 version of the sample services, the s2 lane to the v2 version of the sample services, and the s3 lane to v3 version of the sample services.
In the Traffic Rule Definition section of the Traffic Lane page, click Create swimlanes.
In the Create swimlanes dialog box, configure the required parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Swimlane Name
Name the three lanes as s1, s2, and s3 respectively.
Configure Service Tag
Label Key: Set it to ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG.
Label Value: Set it to v1 for the s1 lane, v2 for the s2 lane, and v3 for the s3 lane.
Add Service
For the s1 lane, select mocka(default), mockb(default), and mockc(default).
For the s2 lane, select mocka(default) and mockc(default).
For the s3 lane, select mockb(default).
The following figure shows the configurations of the s1 lane.
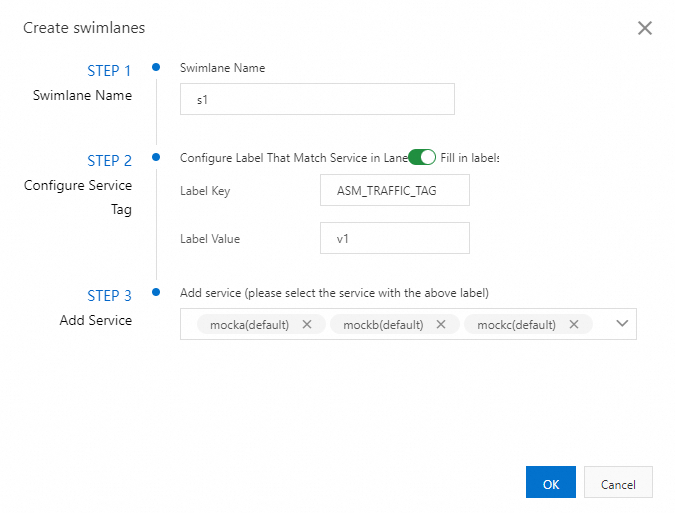
After the three lanes are created, you can view them in the Traffic Rule Definition section, as shown in the following figure.
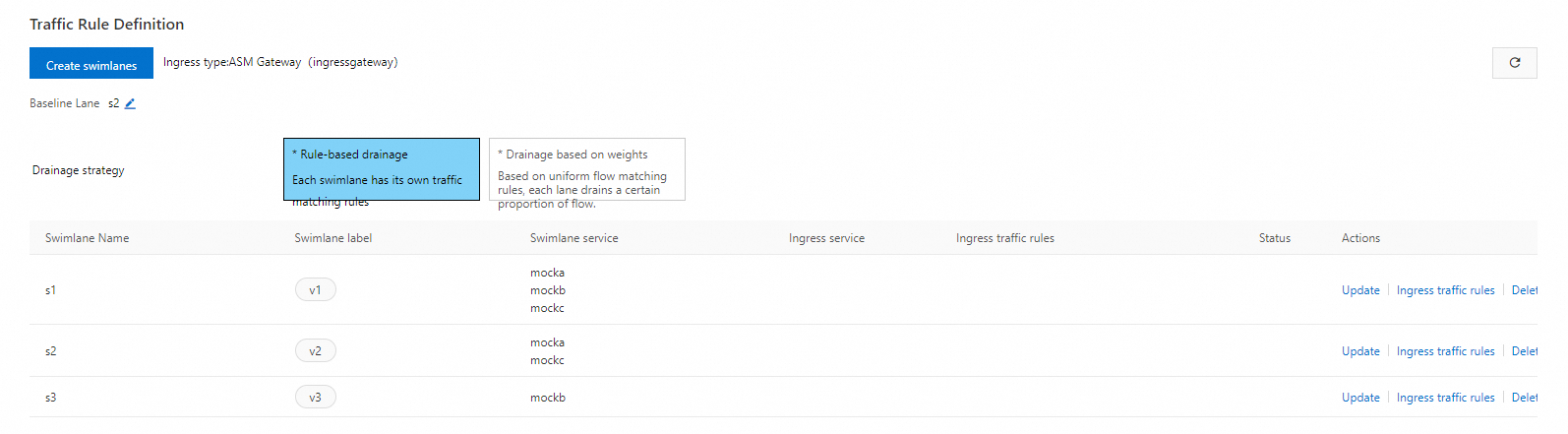
By default, the first lane you create in a lane group is set as the baseline lane. However, you can change the baseline lane. When traffic is destined for services that do not exist in the other lanes, requests are forwarded to the baseline lane according to the fallback mechanism. For more information about how to change the baseline lane, see Change the baseline lane in permissive mode.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ASM console, choose Traffic Management Center > DestinationRule or VirtualService to view the destination rule or virtual service that is automatically generated for each service in the lane group. For example, the following destination rule and virtual service are automatically created for the mocka service.
Create a unified weight-based traffic routing rule.
In the Traffic Rule Definition section of the Traffic Lane page, click Weight-based Routing in the Traffic Routing Rule section.
In the Set Unified Routing Rules dialog box, configure the required parameters and click OK. The following example assumes that the inbound request path of all services in the lanes is /mock, and the same traffic routing rule is configured for each lane.
Parameter
Description
realm name
Set it to *.
Matching request URI
Set the Method parameter to Prefix and the Content parameter to /.
The following figure shows an example of configuring a unified traffic routing rule:
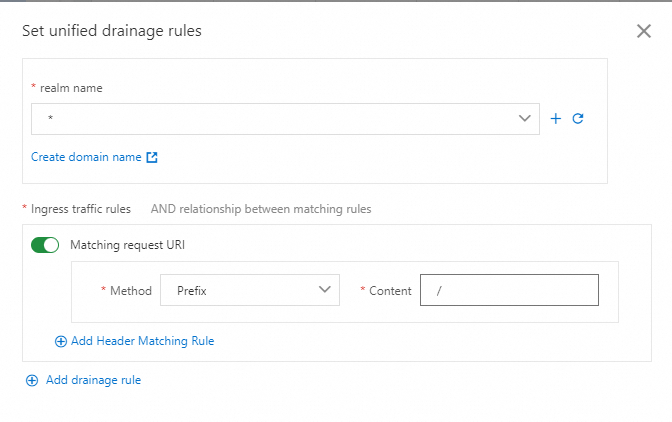
Set the traffic routing weights for the three lanes. The weights determine the proportions of traffic sent to each lane.
In the Traffic Rule Definition section of the Traffic Lane page, click the
 button next to the number in the Traffic Routing Weight column. In the Edit Traffic Routing Weight dialog box, configure the required parameters and click OK.
button next to the number in the Traffic Routing Weight column. In the Edit Traffic Routing Weight dialog box, configure the required parameters and click OK. Parameter
Description
Ingress service
Set it to mocka.default.svc.cluster.local for the three lanes.
Weight Value
For the s1 lane, set the value to 60.
For the s2 lane, set the value to 20.
For the s3 lane, set the value to 20.
The following figure shows an example of configuring traffic routing weights.

Step 3: Verify that the end-to-end canary release feature takes effect
Obtain the public IP address of the ingress gateway. For more information, see Step 2: Obtain the IP address of the ASM ingress gateway.
Run the following command to configure environment variables. xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address obtained in the previous step.
export ASM_GATEWAY_IP=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxxVerify that the end-to-end canary release feature takes effect.
Run the following command to view the calls of services in the three lanes:
for i in {1..100}; do curl http://${ASM_GATEWAY_IP}/ ; echo ''; sleep 1; done;Expected output:
-> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v3, ip: 192.168.0.2)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.184)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 192.168.0.189) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190) -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.193)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.1)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 192.168.0.190)The output indicates that traffic is sent to the s1, s2, and s3 lanes at a ratio of about 6:2:2, and s1 is used as the baseline lane. If a specific version of a service does not exist in the trace, the corresponding service in the s1 lane is called.