ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ provides a distributed transaction processing feature similar to eXtended Architecture (X/Open XA) to ensure transaction consistency in ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ. This topic provides sample code on how to send and receive transactional messages by using the HTTP client SDK for Java.
Background information
The following figure shows the interaction process of transactional messages.
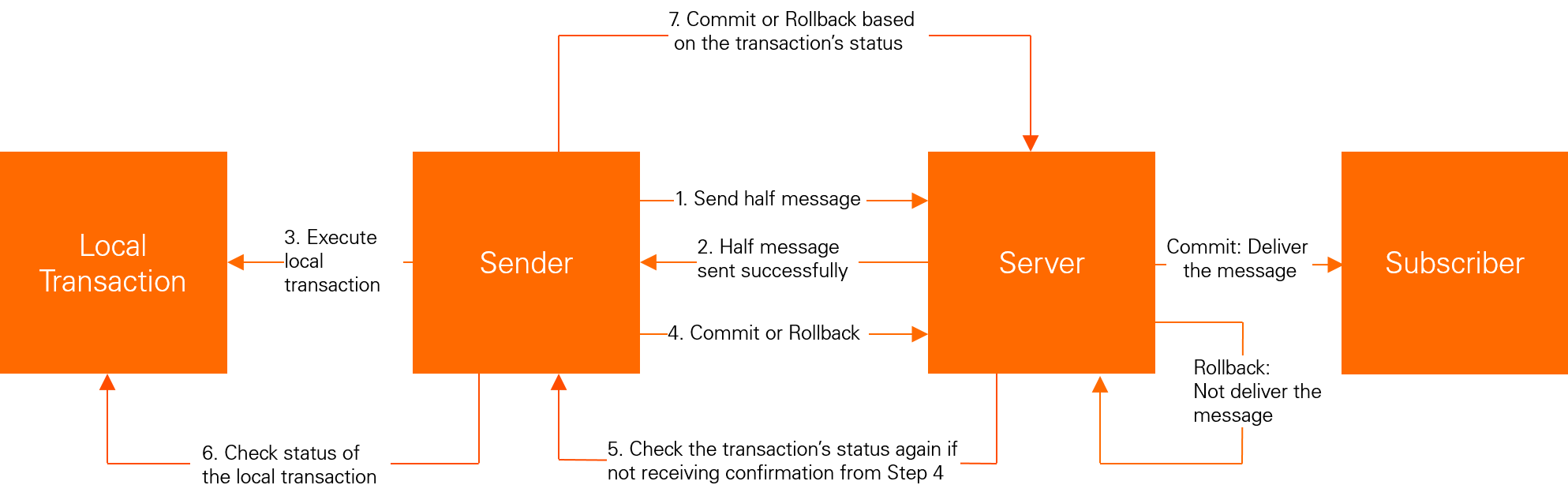
For more information, see Transactional messages.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that the following operations are performed:
Install the SDK for Java. For more information, see Prepare the environment.
Create the resources that you want to specify in the code in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console. The resources include instances, topics, and consumer groups. For more information, see Create resources.
Obtain the AccessKey pair of your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.
Send transactional messages
The following sample code provides an example on how to send transactional messages by using the HTTP client SDK for Java:
import com.aliyun.mq.http.MQClient;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.MQTransProducer;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.common.AckMessageException;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.model.Message;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.model.TopicMessage;
import java.util.List;
public class TransProducer {
static void processCommitRollError(Throwable e) {
if (e instanceof AckMessageException) {
AckMessageException errors = (AckMessageException) e;
System.out.println("Commit/Roll transaction error, requestId is:" + errors.getRequestId() + ", fail handles:");
if (errors.getErrorMessages() != null) {
for (String errorHandle :errors.getErrorMessages().keySet()) {
System.out.println("Handle:" + errorHandle + ", ErrorCode:" + errors.getErrorMessages().get(errorHandle).getErrorCode()
+ ", ErrorMsg:" + errors.getErrorMessages().get(errorHandle).getErrorMessage());
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
MQClient mqClient = new MQClient(
// The HTTP endpoint. You can obtain the endpoint in the HTTP Endpoint section of the Instance Details page in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console.
"${HTTP_ENDPOINT}",
// Make sure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET are configured.
// The AccessKey ID that is used for authentication.
System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),
// The AccessKey secret that is used for authentication.
System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
);
// The topic in which the message is produced. You must create the topic in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console.
// Each topic can be used to send and receive messages of a specific type. For example, a topic that is used to send and consume normal messages cannot be used to send or receive messages of other types.
final String topic = "${TOPIC}";
// The ID of the instance to which the topic belongs. You must create the instance in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console.
// If the instance has a namespace, specify the ID of the instance. If the instance does not have a namespace, set the instanceID parameter to null or an empty string. You can obtain the namespace of the instance on the Instance Details page in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console.
final String instanceId = "${INSTANCE_ID}";
// The ID of the consumer group that you created in the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console.
final String groupId = "${GROUP_ID}";
final MQTransProducer mqTransProducer = mqClient.getTransProducer(instanceId, topic, groupId);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
TopicMessage topicMessage = new TopicMessage();
topicMessage.setMessageBody("trans_msg");
topicMessage.setMessageTag("a");
topicMessage.setMessageKey(String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// The time interval between the sending time of the transactional message and the start time of the first check for the status of the local transaction. This time interval specifies the relative time when the status is first checked. Unit: seconds. Valid values: 10 to 300.
// If the message is not committed or rolled back after the first transaction status check is performed, the broker initiates a request to check the status of the local transaction at an interval of 10 seconds within the next 24 hours.
topicMessage.setTransCheckImmunityTime(10);
topicMessage.getProperties().put("a", String.valueOf(i));
TopicMessage pubResultMsg = null;
pubResultMsg = mqTransProducer.publishMessage(topicMessage);
System.out.println("Send---->msgId is: " + pubResultMsg.getMessageId()
+ ", bodyMD5 is: " + pubResultMsg.getMessageBodyMD5()
+ ", Handle: " + pubResultMsg.getReceiptHandle()
);
if (pubResultMsg != null && pubResultMsg.getReceiptHandle() != null) {
if (i == 0) {
// After the producer sends the transactional message, the broker obtains the handle of the half message that corresponds to the transactional message and commits or rolls back the transactional message based on the status of the handle.
try {
mqTransProducer.commit(pubResultMsg.getReceiptHandle());
System.out.println(String.format("MessageId:%s, commit", pubResultMsg.getMessageId()));
} catch (Throwable e) {
// If the transactional message is not committed or rolled back before the period of time specified by the TransCheckImmunityTime parameter for the handle of the transactional message elapses, the commit or rollback operation fails.
if (e instanceof AckMessageException) {
processCommitRollError(e);
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
// The client needs a thread or a process to process unacknowledged transactional messages.
// Start a thread to process unacknowledged transactional messages.
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int count = 0;
while(true) {
try {
if (count == 3) {
break;
}
List<Message> messages = mqTransProducer.consumeHalfMessage(3, 3);
if (messages == null) {
System.out.println("No Half message!");
continue;
}
System.out.println(String.format("Half---->MessageId:%s,Properties:%s,Body:%s,Latency:%d",
messages.get(0).getMessageId(),
messages.get(0).getProperties(),
messages.get(0).getMessageBodyString(),
System.currentTimeMillis() - messages.get(0).getPublishTime()));
for (Message message : messages) {
try {
if (Integer.valueOf(message.getProperties().get("a")) == 1) {
// Confirm to commit the transactional message.
mqTransProducer.commit(message.getReceiptHandle());
count++;
System.out.println(String.format("MessageId:%s, commit", message.getMessageId()));
} else if (Integer.valueOf(message.getProperties().get("a")) == 2
&& message.getConsumedTimes() > 1) {
// Confirm to commit the transactional message.
mqTransProducer.commit(message.getReceiptHandle());
count++;
System.out.println(String.format("MessageId:%s, commit", message.getMessageId()));
} else if (Integer.valueOf(message.getProperties().get("a")) == 3) {
// Confirm to roll back the transactional message.
mqTransProducer.rollback(message.getReceiptHandle());
count++;
System.out.println(String.format("MessageId:%s, rollback", message.getMessageId()));
} else {
// Check the status next time.
System.out.println(String.format("MessageId:%s, unknown", message.getMessageId()));
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
// If the transactional message is committed or rolled back after the time specified by the TransCheckImmunityTime parameter for the handle of the transactional message elapses or after the timeout period specified for the handle of consumeHalfMessage elapses, the commit or rollback fails. In this example, the timeout period is specified as 10 seconds for the handle of consumeHalfMessage.
processCommitRollError(e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
});
t.start();
t.join();
mqClient.close();
}
}Subscribe to transactional messages
The following sample code provides an example on how to subscribe to transactional messages by using the HTTP client SDK for Java:
import com.aliyun.mq.http.MQClient;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.MQConsumer;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.common.AckMessageException;
import com.aliyun.mq.http.model.Message;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MQClient mqClient = new MQClient(
// The HTTP endpoint. To obtain the HTTP endpoint, log on to the Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances. On the Instances page, click the name of your instance. On the Instance Details page, scroll to the Basic Information section and view the HTTP endpoint on the Endpoints tab.
"${HTTP_ENDPOINT}",
// The AccessKey ID is used as an identifier of Alibaba Cloud service users. For more information, see .
"${ACCESS_KEY}",
// The AccessKey Secret is used to verify the identity of Alibaba Cloud service users. For more information, see .
"${SECRET_KEY}"
);
// The topic of the message. The topic must have been created in the Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ console.
// Each topic can be used to send and subscribe to messages of a specific type. For example, a topic that is used to send and subscribe to normal messages cannot be used to send and subscribe to messages of other types.
final String topic = "${TOPIC}";
// The ID of the group that you created in the Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ console.
final String groupId = "${GROUP_ID}";
// The ID of the instance to which the topic belongs. The instance must have been created in the Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ console.
// If the instance has a namespace, the instance ID must be passed in. If the instance does not have a namespace, pass in null or an empty string. Check whether your instance has a namespace on the Instance Details page in the Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ console.
final String instanceId = "${INSTANCE_ID}";
final MQConsumer consumer;
if (instanceId != null && instanceId != "") {
consumer = mqClient.getConsumer(instanceId, topic, groupId, null);
} else {
consumer = mqClient.getConsumer(topic, groupId);
}
// Cyclically consume messages in the current thread. We recommend that you use multiple threads to concurrently consume messages.
do {
List<Message> messages = null;
try {
// Consume messages in long polling mode.
// In long polling mode, if no message in the topic is available for consumption, the request is suspended on the broker for a specified period of time. If a message is available for consumption within the duration, a response is immediately sent to the consumer. In this example, the duration is 3 seconds.
messages = consumer.consumeMessage(
3,// The maximum number of messages that can be consumed at a time. In this example, the value is set to 3. The largest value you can set is 16.
3// The duration of a long polling cycle. Unit: seconds. In this example, the value is set to 3. The largest value you can set is 30.
);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
// No messages in the topic are available for consumption.
if (messages == null || messages.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": no new message, continue!");
continue;
}
// Specify the business processing logic.
for (Message message : messages) {
System.out.println("Receive message: " + message);
}
// If the broker does not receive an acknowledgment (ACK) for a message from the consumer before the delivery retry interval elapses, the message will be consumed again.
// A unique timestamp is specified for the handle of a message each time the message is consumed.
{
List<String> handles = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Message message : messages) {
handles.add(message.getReceiptHandle());
}
try {
consumer.ackMessage(handles);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// The broker may fail to receive an ACK for a message from the consumer if the handle of the message times out.
if (e instanceof AckMessageException) {
AckMessageException errors = (AckMessageException) e;
System.out.println("Ack message fail, requestId is:" + errors.getRequestId() + ", fail handles:");
if (errors.getErrorMessages() != null) {
for (String errorHandle :errors.getErrorMessages().keySet()) {
System.out.println("Handle:" + errorHandle + ", ErrorCode:" + errors.getErrorMessages().get(errorHandle).getErrorCode()
+ ", ErrorMsg:" + errors.getErrorMessages().get(errorHandle).getErrorMessage());
}
}
continue;
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} while (true);
}
}