If you want to add multiple domain names that are hosted on the same server to an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance, you can enable the CNAME reuse feature. This feature allows you to add a domain name to the instance only once and map the other domain names hosted on the same server to the CNAME assigned by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland). This way, the traffic of all the domain names are processed by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland). This topic describes how to use the CNAME reuse feature.
Feature description
After CNAME reuse is enabled, you can modify the CNAME to map the domain names hosted on the same server to the CNAME assigned by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland). This way, all the domain names are protected by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland).
Usage notes
Only Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) supports CNAME reuse. Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) does not support CNAME reuse.
Scenarios
CNAME reuse is suitable for the following scenarios:
Customers, such as agents, independent software vendors (ISVs), or distributors, want to add a large number of domain names to an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance. Most of the domain names are hosted by the same server, and the number of domain names frequently changes.
Multiple second-level domain names are required for the promotion and search engine optimization (SEO) of the same service.
Multiple alternative domain names are required for a service.
Limits
The following table describes the limits of CNAME reuse.
Limit | Description |
Protocol | HTTP and HTTPS are supported. Note If you add domain names by using HTTPS, all the domain names that are mapped to the same CNAME share an SSL certificate after CNAME reuse is enabled. |
Origin server | Domain names that are mapped to the same CNAME must be hosted by the same origin server. |
Enable CNAME reuse
You can use CNAME reuse along with Sec-Traffic Manager. When you enable CNAME reuse, you can determine whether to use Sec-Traffic Manager. For more information, see Overview.
If you use Sec-Traffic Manager, you must select a general interaction rule. Then, the CNAME configured in the rule is reused to resolve a domain name.
If you do not use Sec-Traffic Manager, the CNAME assigned by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) is reused to resolve a domain name.
The configuration descriptions in this topic are based on the following assumptions:
The origin server has two IP addresses: 192.10.XX.XX and 192.11.XX.XX.
IP address 192.10.XX.XX hosts three domain names: a.example, b.example, and c.example.
The following procedure describes how to use CNAME reuse to add the following domain names that are hosted on the IP address 192.10.XX.XX to an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance: a.example, b.example, and c.example.
Enable CNAME reuse when you add a domain name.
Log on to the Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) console.
In the top navigation bar, select Outside Chinese Mainland.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Add a website and enable CNAME reuse, or enable this feature for an existing domain name. For more information, see Add one or more websites.
In the example, the Origin IP Address is 192.10.XX.XX, and the Websites is a.example, b.example, or c.example.

Specify whether to use Sec-Traffic Manager. Update the CNAME of the protected domain name.
When you enable CNAME reuse, you must determine whether to use Sec-Traffic Manager.
Enable CNAME reuse without Sec-Traffic Manager
In the Select Traffic Scheduling Rule dialog box, enable CNAME reuse without Sec-Traffic Manager and then OK.
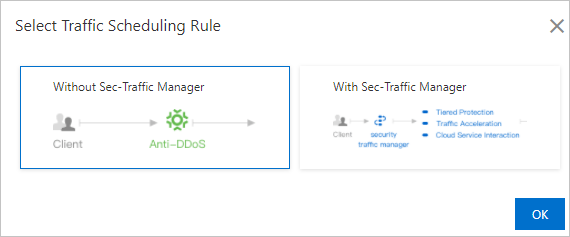
After a domain name is added, record the CNAME assigned for the domain name.
In the console of your DNS provider, update the DNS records for all the domain names that are hosted on the IP address 192.10.XX.XX. The domain names are a.example, b.example, and c.example. Then, create a CNAME and set the record value of the CNAME to that recorded in the previous step.
Enable CNAME reuse with Sec-Traffic Manager
In the Select Traffic Scheduling Rule dialog box, enable CNAME Reuse with Sec-Traffic Manager and then OK.
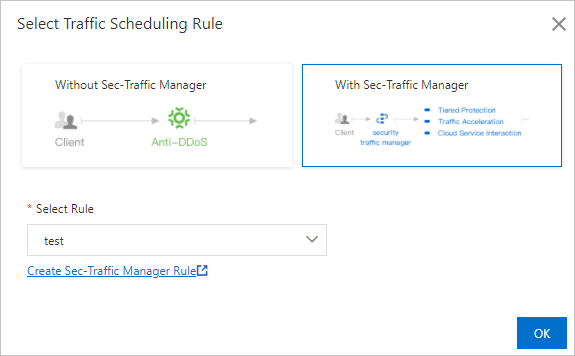
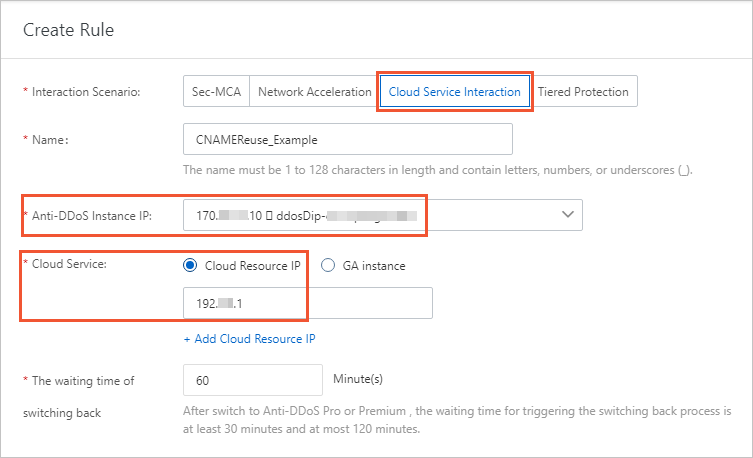
If you enable CNAME reuse with Sec-Traffic Manager, the Sec-Traffic Manager rule must be associated with both the IP address of the origin server and the IP address of the Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance used in the website configuration. The IP address of the origin server is 192.10.XX.XX in this example. If no rules are available, click Create Sec-Traffic Manager Rule to create a rule. Then, apply the rule.
ImportantThe IP address of the Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance in the Sec-Traffic Manager rule must be the same as that used in the website configuration.
After you select a Sec-Traffic Manager rule, record the CNAME of the rule.

In the console of the DNS provider, update the DNS records for all the domain names that are hosted on the IP address 192.10.XX.XX. The domain names are a.example, b.example, and c.example. Then, create a CNAME and set the record value of the CNAME to that recorded in the previous step.
Optional: To add domain names that are hosted on another IP address of the origin server (192.11.XX.XX), repeat Step 1 and Step 2.
Disable CNAME reuse
You can disable CNAME reuse on the Website Config page.
Before you disable this feature, make sure that the service traffic of all the domain names mapped to the CNAME is no longer rerouted to your Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance. Otherwise, the inbound traffic cannot be forwarded to the origin server.
Log on to the Anti-DDoS Proxy console.
In the top navigation bar, select Outside Chinese Mainland.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Find the required domain name, click Edit in the Actions column, and then disable CNAME Reuse.
Specify whether to retain the website configuration or the Sec-Traffic Manager rule.
If you retain the website configuration, the traffic forwarding rules still take effect.
If you retain the Sec-Traffic Manager rule, Sec-Traffic Manager still takes effect.