This topic introduces the basic concepts related to Anti-DDoS services.
DDoS attack
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks include volumetric attacks and application-layer attacks.
Volumetric attacks target the network bandwidth of your service. In most cases, attackers manipulate multiple computers or attack simulators to send a large number of requests or data packets to the target server. This exhausts network bandwidths and causes your service to become unavailable.
Application-layer attacks target at servers. During application-layer attacks, the memory of the servers is exhausted by malicious requests or the CPUs of the servers are exhausted by kernels and application programs. As a result, servers cannot respond to normal requests.
Traffic scrubbing
If you want to perform traffic scrubbing, you can use an anti-DDoS device or service to analyze and filter traffic. The anti-DDoS device or service can distinguish service traffic from attack traffic and return only service traffic to your server. This reduces the pressure and risks on the server.
Blackhole filtering
If DDoS attacks exceed the mitigation capability that is provided for a service, blackhole filtering is triggered. Blackhole filtering is used to discard all inbound traffic that is destined for the service. This helps protect other services that are deployed in the same network as the attacked service. For more information, see Blackhole filtering policy of Alibaba Cloud.
Resource exhaustion attack
Resource exhaustion attacks are malicious request attacks that are launched against application-layer protocols such as HTTP and HTTPS. Resource exhaustion attacks simulate the access behavior of actual users, such as logon, registration, and search, and consume the application resources of the target websites. As a result, the target sites cannot respond to normal requests.
Connection flood attacks
Connection flood attacks are malicious session attacks at the transport layer. Attackers use multiple zombie servers to send a large number of TCP requests to the target website. The TCP requests consume resources such as the connections, CPUs, and memory of the target server. As a result, the target server cannot respond to normal requests.
Volumetric attacks
Volumetric attacks target the network bandwidth of your service. In most cases, attackers manipulate multiple computers or attack simulators to send a large number of requests or data packets to the target server. This exhausts network bandwidths and causes your service to become unavailable.
Best-effort protection of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland)
Anti-DDoS Proxy clusters use available resources to provide best-effort protection against DDoS attacks. If the maximum mitigation capabilities of the clusters cannot defend against DDoS attacks, blackhole filtering may be triggered. For more information, see Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland).
Burstable protection
Burstable protection is provided by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) of the Professional mitigation plan. You can configure the burstable protection bandwidth to defend against attack traffic that exceeds the basic protection bandwidth. If the volume of DDoS attacks exceeds the basic protection bandwidth but is smaller than the burstable protection bandwidth, burstable protection is triggered. You are charged additional fees on the day when burstable protection is triggered. For more information, see Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland).
Advanced mitigation
Advanced mitigation is provided by Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland) instances of the Advanced mitigation plan, and Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instances of the Insurance, Unlimited, Secure Chinese Mainland Acceleration (Sec-CMA), and Sec-CMA (Basic) mitigation plans. Advanced mitigation uses anti-DDoS scrubbing centers of Alibaba Cloud of the local region to protect your resources against DDoS attacks. For more information, see Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Chinese Mainland), Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) of the Insurance and Unlimited mitigation plans, and Billing of Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) of the Sec-CMA mitigation plan.
If an Anti-DDoS Proxy instance receives more than 5 Gbit/s of DDoS attack traffic, an advanced mitigation session that is provided for the instance is consumed. The advanced mitigation session protects the instance for 24 hours. All DDoS attacks that occur on the Anti-DDoS Proxy instance within 24 hours consume the same advanced mitigation session.
Anycast
Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) uses the anycast method to forward DDoS attack traffic to the nearest anti-DDoS scrubbing center of Alibaba Cloud around the world. Anycast is a network addressing and routing method. Packets that are destined for an anycast IP address can be routed to a specific group of hosts identified by the anycast IP address.
Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) uses the anycast method to route access traffic to the nearest anti-DDoS scrubbing center that has protection capabilities. The routing method allows scheduling when large concurrent traffic causes network congestion, which ensures service availability. However, cross-border data transmission may be involved.
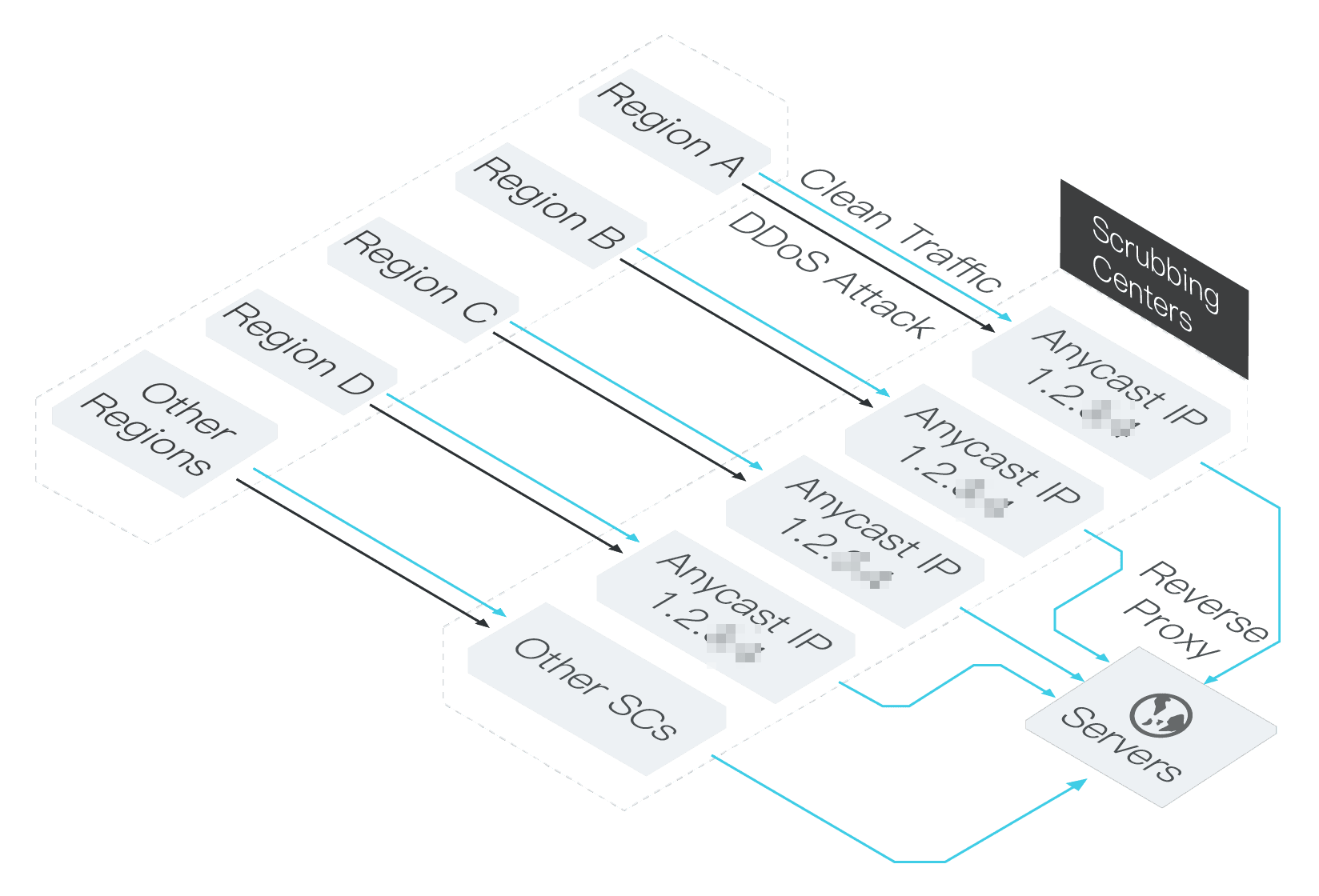
Traffic that reaches the anycast IP address can be routed to multiple data centers. When access traffic arrives at the anycast IP address, the traffic is forwarded to different data centers based on configured traffic forwarding rules. In most cases, the access traffic is forwarded to the data center nearest to the traffic source. Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) provides endpoints in the following regions for you to connect your services to Alibaba Cloud.
Area | Alibaba Cloud region |
Asia Pacific | China (Hong Kong), Singapore, Japan (Tokyo), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), and Indonesia (Jakarta) |
North America | US (Silicon Valley) and US (Virginia) |
Europe | UK (London) and Germany (Frankfurt) |
Assume that the anycast IP address of an Anti-DDoS Proxy (Outside Chinese Mainland) instance is 170.x.x.x. All anti-DDoS scrubbing centers of Alibaba Cloud outside China advertise routes to this IP address. When data packets are sent to this IP address, the data packets are forwarded to the anti-DDoS scrubbing center through a route with the least hops. When a server in an anti-DDoS scrubbing center becomes unavailable, all scrubbing centers immediately advertise that this IP address is unavailable, and data packets are routed to the nearest anti-DDoS scrubbing center excluding this one.
By default, traffic from Hong Kong (China) is routed to the anti-DDoS scrubbing center of Alibaba Cloud in Hong Kong (China).