AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL provides the zero-ETL feature that helps you synchronize and manage data in an end-to-end manner and integrate transaction processing with data analysis.
Overview
In the era of big data, enterprises must use extract, transform, load (ETL) tools to efficiently manage and use large amounts of business data distributed across different systems and platforms.
An ETL tool extracts data from an upper-level business system, transforms the data, and then loads the data to data warehouses. This process incorporates distributed data into data warehouses for further computing, analysis, and business decision-making.
Traditional ETL processes encounter the following challenges:
Increased resource costs: Different data sources may require different ETL tools, and you are charged additional fees for creating ETL tasks.
Increased system complexity: The maintenance of ETL tools increases O&M difficulty and prevents you from focusing on business application development.
Reduced data timeliness: Specific ETL processes involve periodic batch updates. In near-real-time scenarios, analysis results cannot be quickly generated.
To resolve the preceding issues, Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB provides the zero-ETL feature that allows you to create data synchronization tasks between online transaction processing (OLTP) and online analytical processing (OLAP) systems. The zero-ETL feature extracts data from OLTP systems, transforms the data, and then loads the data to OLAP systems to help you synchronize and manage data in an end-to-end manner, integrate transaction processing with data analysis, and focus on data analysis.
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL supports only the following zero-ETL tasks:
Data synchronization tasks from PolarDB for PostgreSQL to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Data synchronization tasks from PolarDB for MySQL to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Data synchronization tasks from ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Data synchronization tasks from ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Benefits
Ease of use: You do not need to create or maintain complex data pipelines to perform ETL operations. You need to only select the source and destination instances or clusters to create real-time data synchronization tasks. This reduces the challenges of building and managing data pipelines and allows you to focus on application development.
Zero costs: You are not charged additional fees for zero-ETL tasks. The zero-ETL feature allows you to analyze the data synchronized to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL free of charge.
Multi-source aggregation: The zero-ETL feature allows you to synchronize data in real time from multiple source instances or clusters to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance for global analysis.
Usage notes
Usage notes on data synchronization tasks:
For information about usage notes on data synchronization tasks from PolarDB for PostgreSQL, see the "Usage notes" section of the Synchronize data from a PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance topic.
For information about usage notes on data synchronization tasks from PolarDB for MySQL, see the "Usage notes" section of the Synchronize data from a PolarDB for MySQL cluster to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance topic.
For information about usage notes on data synchronization tasks from ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, see the "Usage notes" section of the Synchronize data from an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance topic.
For information about usage notes on data synchronization tasks from ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, see the "Usage notes" section of the Synchronize data from an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance topic.
Supported regions
The following regions support the zero-ETL feature: China (Shenzhen), China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Ulanqab), China (Qingdao), China (Guangzhou), China East 2 Finance, China (Chengdu), China (Hong Kong), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), US (Virginia), US (Silicon Valley), Germany (Frankfurt), Indonesia (Jakarta), Japan (Tokyo), and Singapore.
Billing rules
You are not charged for data synchronization tasks. You are charged only for the source PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster, PolarDB for MySQL cluster, ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, or ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and the destination AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
Prerequisites
The following instances or clusters are created:
An AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Create an instance.
An ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster, or PolarDB for MySQL cluster. For more information, see Create an instance, Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, Create a cluster, and Create a serverless cluster.
The wal_level parameter of the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster, or PolarDB for MySQL cluster is set to logical. For more information, see Synchronize data from an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
The available storage capacity of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance is larger than the used storage capacity of the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster, or PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
Preparations
Create a service-linked role for AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
Log on to the Resource Access Management (RAM) console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
Check whether a service-linked role named
AliyunServiceRoleForADBPGexists in the role list. If the service-linked role does not exist, create the role.In the upper-left corner of the Roles page, click Create Role.
Select Alibaba Cloud Service and enter a Principal Name.
Click OK. And you'll be prompted with a pop-up. Enter your role name to proceed.
Finish Security Verification.
For details, see Create a RAM role for a trusted Alibaba Cloud service.
Grant management permissions to a RAM user
To allow a RAM user to create and manage zero-ETL tasks, you must perform the following operations:
Grant the RAM user the permissions to manage AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
Before a RAM user can create and manage zero-ETL tasks of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, you must attach the AliyunGPDBFullAccess policy of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL to the RAM user. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
Grant the RAM user the permissions to manage the zero-ETL feature
Before a RAM user can create and manage zero-ETL tasks, the RAM user must have the permissions to create data synchronization tasks between the data source and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. You can configure a custom policy that allows RAM users to create data synchronization tasks for all instances or clusters of the data source and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Grant permissions on all ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for PostgreSQL, PolarDB for MySQL, and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instances and clusters. Sample script:
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "dts:*", "Resource": [ "acs:gpdb:*:*:*", "acs:rds:*:*:*", "acs:polardb:*:*:*" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dts:DescribeRegions", "dts:DescribeConfigRelations", "dts:DescribeSrcLinkConfig", "dts:DescribeDestLinkConfig", "dts:DescribeLinkConfig" ], "Resource": [ "acs:gpdb:*:*:*" ] } ] }Grant permissions on a specific ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, PolarDB for PostgreSQL cluster, PolarDB for MySQL cluster, and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance. Sample script:
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "dts:*", "Resource": [ "acs:gpdb:*:*:dbinstanc****", "acs:rds:*:*:dbinstance****", "acs:polardb:*:*:dbclus****" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dts:DescribeRegions", "dts:DescribeConfigRelations", "dts:DescribeSrcLinkConfig", "dts:DescribeDestLinkConfig", "dts:DescribeLinkConfig" ], "Resource": "acs:dts:*:*:*" } ] }
Create a custom policy in the RAM console. For more information, see Create custom policies.
Procedure
Log on to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL console.
In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region.
Find the instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Zero-ETL. In the upper-left corner of the page, click Create Zero-ETL Task.
In the Configure Source and Destination Databases step of the Create Zero-ETL Task page, configure the parameters of the source and destination instances and clusters.
The following table describes the parameters of the source instance or cluster.
Parameter
Description
Example
Task Name
The name of the zero-ETL task.
Zeroetltest
Database Type
The database engine of the source instance or cluster. Select RDS for PostgreSQL, RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, or PolarDB for PostgreSQL.
RDS for PostgreSQL
Access Method
The access method of the source instance or cluster. The value is automatically set to Alibaba Cloud Instance.
Alibaba Cloud Instance
Instance Region
The region in which the source instance or cluster resides.
China (Shanghai)
Instance ID
The ID of the source instance or cluster.
pgm-2ze****
Database Name
The name of the database in the source instance or cluster.
testdb
Database Account
The name of the database account of source instance or cluster.
test
Database Password
The password of the database account of source instance or cluster.
password****
Encryption
The encryption method that is used to connect to the source instance or cluster. Select Non-encrypted or SSL-encrypted.
NoteSSL encryption uses certificates to encrypt the transmitted data. This prevents the data from being decrypted even if data leaks occur.
SSL-encrypted
The following table describes the parameters of the destination instance.
Parameter
Description
Example
Database Type
The database engine of the destination instance. The value is automatically set to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
Access Method
The access method of the destination instance. The value is automatically set to Alibaba Cloud Instance.
Alibaba Cloud Instance
Instance Region
The region in which the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance resides.
China (Shanghai)
Instance ID
The ID of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
gp-2zeod****
Database Name
The name of the database in the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
testdb
Database Account
The name of the database account of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
test
Database Password
The password of the database account of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
password****
Click Test Connectivity and Proceed. In the Configure Zero-ETL step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Example
DDL and DML Operations to Be Synchronized
The DML operations (INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE)
and DDL operations (CREATE, ALTER, DROP, RENAME, and TRUNCATE) that you want to synchronize.
DML operations (INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE).
DDL operations (CREATE, ALTER, DROP, RENAME, and TRUNCATE).
Source Objects and Selected Objects
The source objects and the objects that you want to synchronize.
public
Advanced Settings (Optional)
The retry time for failed connections between the source and destination instances and clusters and the retry time for other issues that occur on the source and destination instances and clusters.
Retry Time for Failed Connections: 10 Minutes.
Retry Time for Other Issues: 10 Minutes.
Click Next: Configure Database and Table Fields. In the Configure Database and Table Fields step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Example
Database Name
The name of the selected database.
public
Table Name
The name of the selected table.
table1
Primary Key Column
The primary key column of the selected table.
id
Distribution Key
One or more distribution key columns of the selected table.
id
Type
The data partition type of the selected table.
Hash-Distributed Table
Definition Status
The status of the selected table. After you configure the table fields, the status of the table changes from Undefined to Defined.
Defined
After you configure the preceding parameters, click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck.
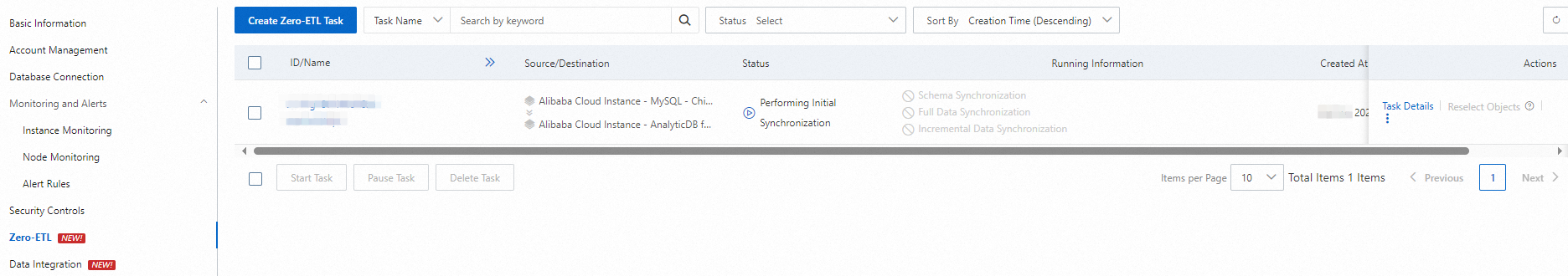
If the precheck is successful, the system automatically starts the zero-ETL task. View the progress of the task in the task list.
Monitoring and alerting of zero-ETL tasks
After you create a zero-ETL task and the task starts, you can configure alert rules for the task and monitor the running status of the task in the CloudMonitor console. Perform the following steps:
Log on to the CloudMonitor console.
View the monitoring information.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Move the pointer over the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL card and click AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL - Zero-ETL Latency.
Find the instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID to view the monitoring information about zero-ETL tasks.
Create an alert rule.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click Create Alert Rule. In the Create Alert Rule panel, configure alert rule parameters for zero-ETL tasks. For more information, see Create an alert rule.
Create a subscription policy.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click Create Subscription Policy. On the Create Subscription Policy page, configure subscription policy parameters for zero-ETL tasks. For more information, see the "Create a subscription policy" section of the Manage event subscription policies (recommended) topic.